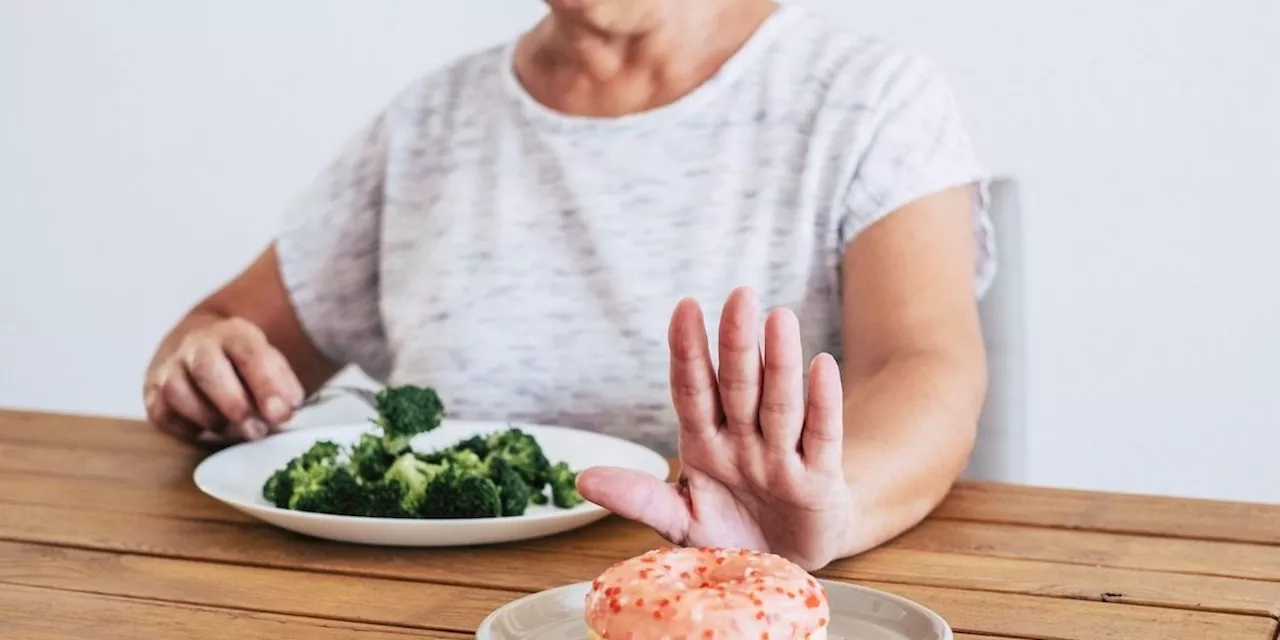
This article examines the link between diet and dementia risk, highlighting studies that show the potential impact of processed meats, ultra-processed foods, and chili peppers on cognitive health. It also explores the benefits of moderate alcohol consumption and provides strategies for mitigating dementia risk.
Living a healthy and fulfilling life involves making informed decisions about various aspects, including diet, exercise, and social interactions. This text explores the connection between lifestyle choices and cognitive health, specifically focusing on the potential impact of certain foods on dementia risk.
It highlights research findings that suggest a correlation between consuming processed meats, ultra-processed foods, and high amounts of chili peppers with an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Conversely, the text emphasizes the benefits of moderate alcohol consumption and provides insights into strategies for mitigating dementia risk.It delves into the reasons behind these associations, explaining how processed meats contribute to cardiovascular problems and oxidative stress, while ultra-processed foods lack essential nutrients and may negatively affect brain function. The text also discusses the study on chili peppers, noting that its impact on memory loss appears to be more pronounced in individuals with lower BMIs and higher physical activity levels.This information aims to empower individuals to make healthier choices and reduce their risk of developing dementia. It encourages readers to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and to stay informed about the latest research in cognitive health
DEMTENCIA DIET HEALTH FOOD PROCESSED MEATS ULTRA-PROCESSED FOODS CHILI PEPPERS ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 This Little-Known Risk Factor Can Increase Your Dementia Risk By 31%Elevated homocysteine levels, linked to genetic mutations and lifestyle factors, are a significant risk factor for dementia. The article highlights the connection between homocysteine and cognitive decline, explaining how methylation, involving folate, plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy homocysteine levels. It emphasizes that this risk is modifiable through lifestyle changes that can optimize homocysteine levels and reduce dementia risk.
This Little-Known Risk Factor Can Increase Your Dementia Risk By 31%Elevated homocysteine levels, linked to genetic mutations and lifestyle factors, are a significant risk factor for dementia. The article highlights the connection between homocysteine and cognitive decline, explaining how methylation, involving folate, plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy homocysteine levels. It emphasizes that this risk is modifiable through lifestyle changes that can optimize homocysteine levels and reduce dementia risk.
Read more »
 Sticking to The MIND Diet Could Reduce Your Risk of Developing DementiaThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Sticking to The MIND Diet Could Reduce Your Risk of Developing DementiaThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »
 These Risk Factors At Age 60 May Be The Strongest Predictors Of DementiaKimberley Richards is a Trends Reporter at HuffPost.
These Risk Factors At Age 60 May Be The Strongest Predictors Of DementiaKimberley Richards is a Trends Reporter at HuffPost.
Read more »
 Gut Bacteria Linked to Dementia RiskA new study suggests a link between certain gut bacteria and the risk of developing dementia, specifically dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). Researchers found that individuals with DLB had an increase in the genera Collinsella and Ruminococcus and a decrease in the genus Bifidobacterium compared to those without DLB.
Gut Bacteria Linked to Dementia RiskA new study suggests a link between certain gut bacteria and the risk of developing dementia, specifically dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). Researchers found that individuals with DLB had an increase in the genera Collinsella and Ruminococcus and a decrease in the genus Bifidobacterium compared to those without DLB.
Read more »
 Smaller Jaw Muscle May Indicate Increased Dementia RiskA new study suggests a link between reduced size of the temporalis muscle (jaw muscle) and an increased risk of developing dementia. Researchers found that individuals with smaller temporalis muscles had a 60% higher chance of developing Alzheimer's disease or dementia. The study also linked smaller muscle size to memory decline, reduced functional abilities, and brain volume reduction.
Smaller Jaw Muscle May Indicate Increased Dementia RiskA new study suggests a link between reduced size of the temporalis muscle (jaw muscle) and an increased risk of developing dementia. Researchers found that individuals with smaller temporalis muscles had a 60% higher chance of developing Alzheimer's disease or dementia. The study also linked smaller muscle size to memory decline, reduced functional abilities, and brain volume reduction.
Read more »
 Reduced Baroreflex Sensitivity Linked to Dementia and Mortality Risk in Older AdultsA new study suggests that impaired cardiac baroreflex sensitivity, a mechanism that helps regulate blood pressure, increases the risk of dementia and death in older adults not taking blood pressure medications.
Reduced Baroreflex Sensitivity Linked to Dementia and Mortality Risk in Older AdultsA new study suggests that impaired cardiac baroreflex sensitivity, a mechanism that helps regulate blood pressure, increases the risk of dementia and death in older adults not taking blood pressure medications.
Read more »
