In Brief: VerveTx forges $60 million deal with EliLillyandCo to advance its in vivo gene editing program targeting Lp(a) for the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
with big pharma Eli Lilly to tackle the most common inherited risk factor for cardiovascular disease, apolipoprotein a. Few people know about the atherosclerosis-inducing particle known as ‘LP little a’ or Lp. It is a close relative of the low-density lipoprotein particles, but with some profound differences.
Like LDL, it is composed of apolipoprotein B100, but linked to the small protein apolipoprotein. The protein’s addition prevents its interaction with LDL receptors that remove cholesterol from circulation, leading to its long half-life and resulting in pathological plaque build-up. Elevated Lp is an established risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, ischemic stroke, thrombosis and aortic stenosis.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
Targeted glioma therapy makes strides - Nature BiotechnologyIn Brief: Servier's successful phase 3 trial of vorasidenib in patients with a slow but usually fatal form of brain cancer, the first clinical breakthrough in the field for two decades, is likely to become a new standard of care
Read more »
 The need for need-finding in medical education - Nature BiotechnologyThe paradigm of developing a novel technology and applying it to a clinically relevant problem may be dominant in academic medicine, but more emphasis is needed in identifying important clinical problems before looking for solutions.
The need for need-finding in medical education - Nature BiotechnologyThe paradigm of developing a novel technology and applying it to a clinically relevant problem may be dominant in academic medicine, but more emphasis is needed in identifying important clinical problems before looking for solutions.
Read more »
 Flush With Private Equity Cash, Gersh Makes Overture to VerveArmed with outside financing, the Beverly Hills-based agency was rebuffed by Verve but is now focused on expansion opportunities in the live entertainment, sports or music representation sector, insiders say.
Flush With Private Equity Cash, Gersh Makes Overture to VerveArmed with outside financing, the Beverly Hills-based agency was rebuffed by Verve but is now focused on expansion opportunities in the live entertainment, sports or music representation sector, insiders say.
Read more »
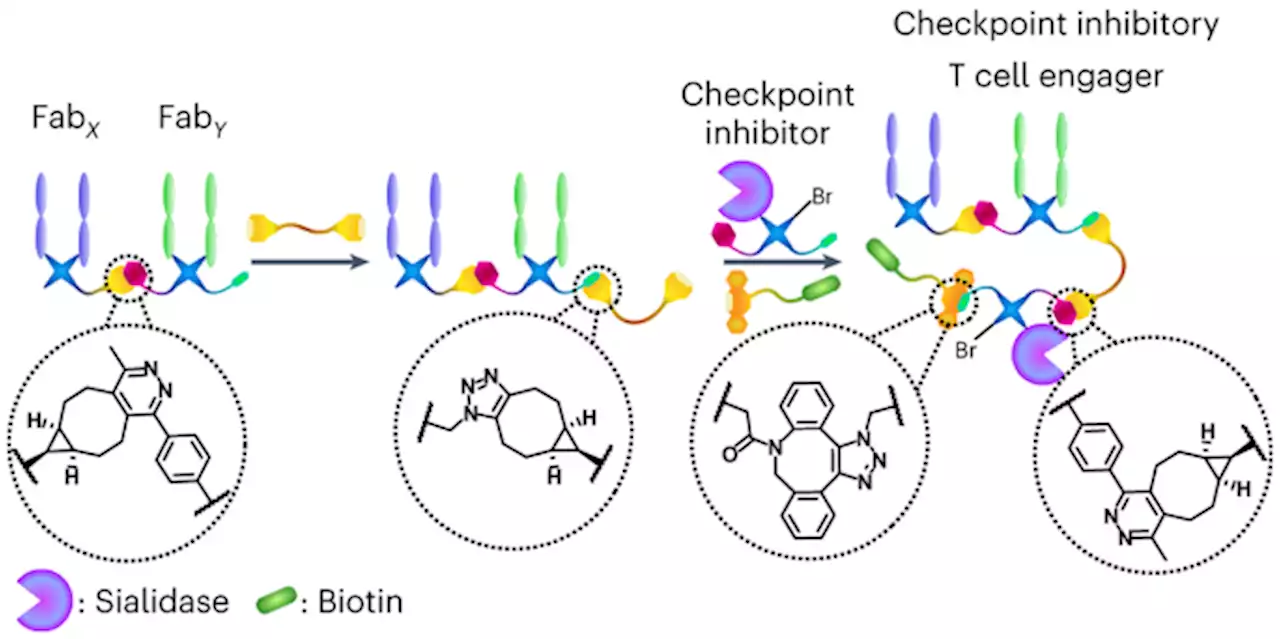 Chemical generation of checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers for the treatment of cancer - Nature ChemistryThree-protein conjugates, which have so far been produced using protein-engineering strategies, can now be generated using a chemical approach that enables the addition of small-molecule functionality. Checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers (CiTEs) were assembled and shown to have enhanced in vitro potency compared to a traditional T cell engager.
Chemical generation of checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers for the treatment of cancer - Nature ChemistryThree-protein conjugates, which have so far been produced using protein-engineering strategies, can now be generated using a chemical approach that enables the addition of small-molecule functionality. Checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers (CiTEs) were assembled and shown to have enhanced in vitro potency compared to a traditional T cell engager.
Read more »
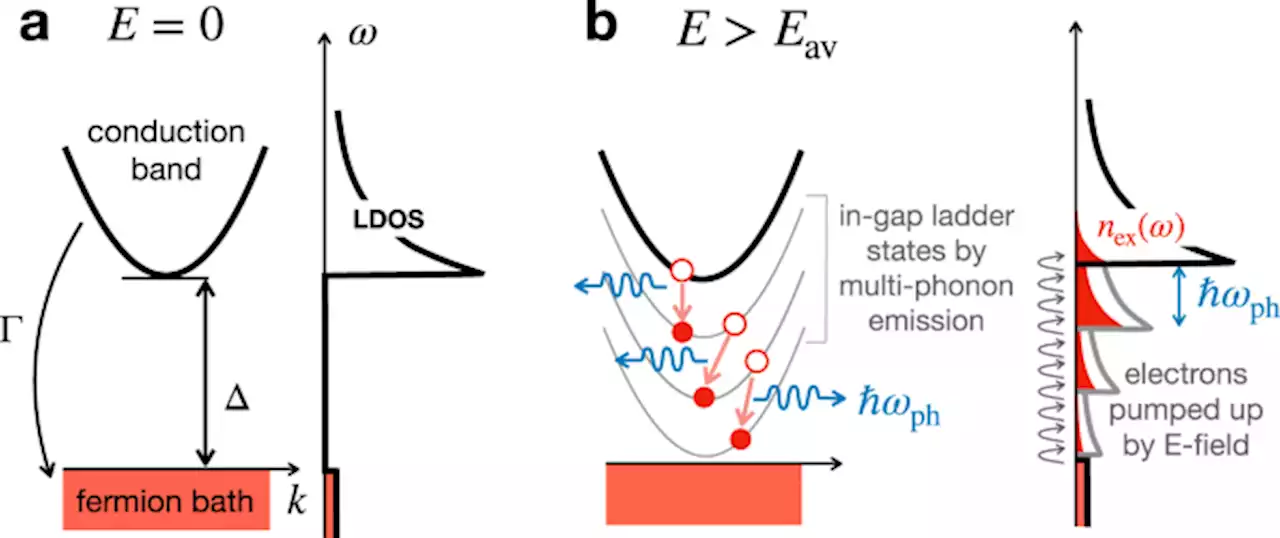 Correlated insulator collapse due to quantum avalanche via in-gap ladder states - Nature CommunicationsThe microscopic mechanism of the electric-field-driven insulator-metal transition in strongly correlated systems has been debated. Here the authors present a general theory based on a quantum avalanche mediated by the formation of in-gap ladder states from multiple-phonon emission.
Correlated insulator collapse due to quantum avalanche via in-gap ladder states - Nature CommunicationsThe microscopic mechanism of the electric-field-driven insulator-metal transition in strongly correlated systems has been debated. Here the authors present a general theory based on a quantum avalanche mediated by the formation of in-gap ladder states from multiple-phonon emission.
Read more »
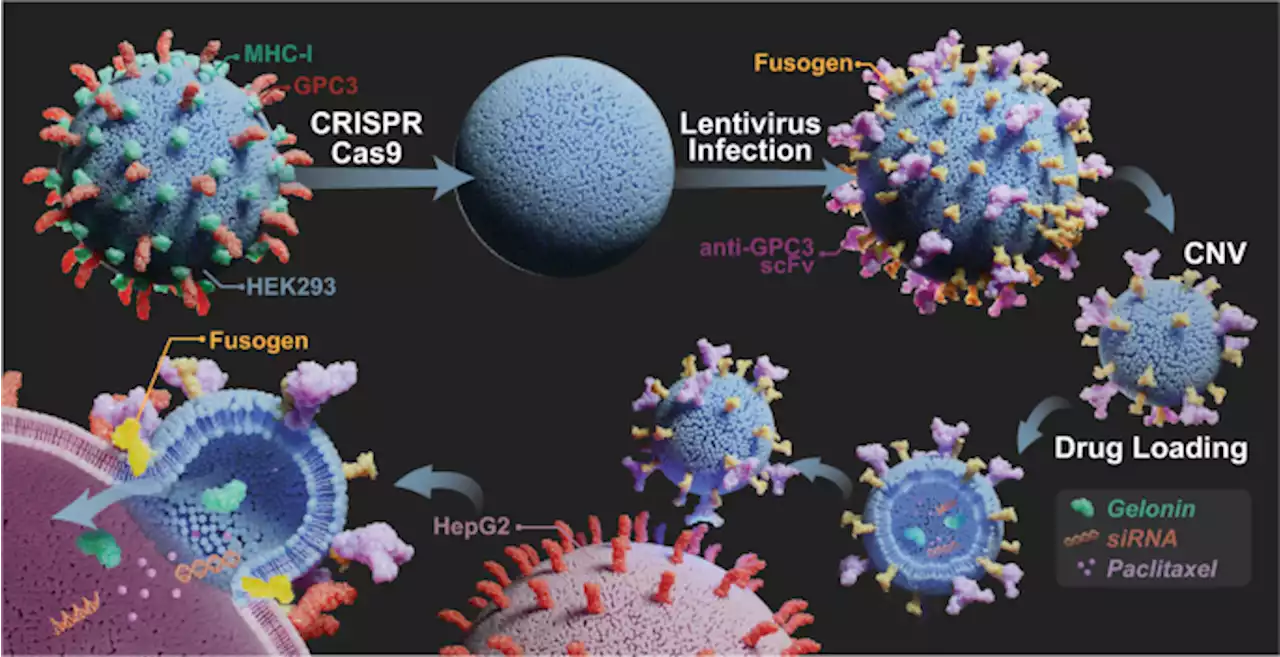 Bioinspired engineering of fusogen and targeting moiety equipped nanovesicles - Nature CommunicationsActive targeting and cytosolic delivery of therapeutic payloads are challenging in small extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems. Here, the authors engineer fusogen and targeting moiety co-functionalized cell-derived nanovesicles, which can selectively bind to target cells and efficiently fulfill cytosolic delivery through membrane fusion.
Bioinspired engineering of fusogen and targeting moiety equipped nanovesicles - Nature CommunicationsActive targeting and cytosolic delivery of therapeutic payloads are challenging in small extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems. Here, the authors engineer fusogen and targeting moiety co-functionalized cell-derived nanovesicles, which can selectively bind to target cells and efficiently fulfill cytosolic delivery through membrane fusion.
Read more »