A person’s brain performs an intricate juggling act while watching a movie, a new study demonstrates.
A person's brain performs an intricate juggling act while watching a movie, a new study demonstrates.
The brain's “executive control” networks -- regions related to planning, solving problems and prioritizing information -- tend to kick in when a movie's content is more difficult to follow or ambiguous. But during more easily understandable scenes, the brain hands off processing to regions with specialized functions.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Omega-3s Linked to Lower Cancer Risk, Better Brain FunctionDana Schulz is an experienced editor, writer, and content strategist who is just as likely to be crunching the latest housing market data as she is to be sharing all the best new kitchen gadgets at Target. She has written about real estate, apartment living, home decor, and history for more than 14 years.
Omega-3s Linked to Lower Cancer Risk, Better Brain FunctionDana Schulz is an experienced editor, writer, and content strategist who is just as likely to be crunching the latest housing market data as she is to be sharing all the best new kitchen gadgets at Target. She has written about real estate, apartment living, home decor, and history for more than 14 years.
Read more »
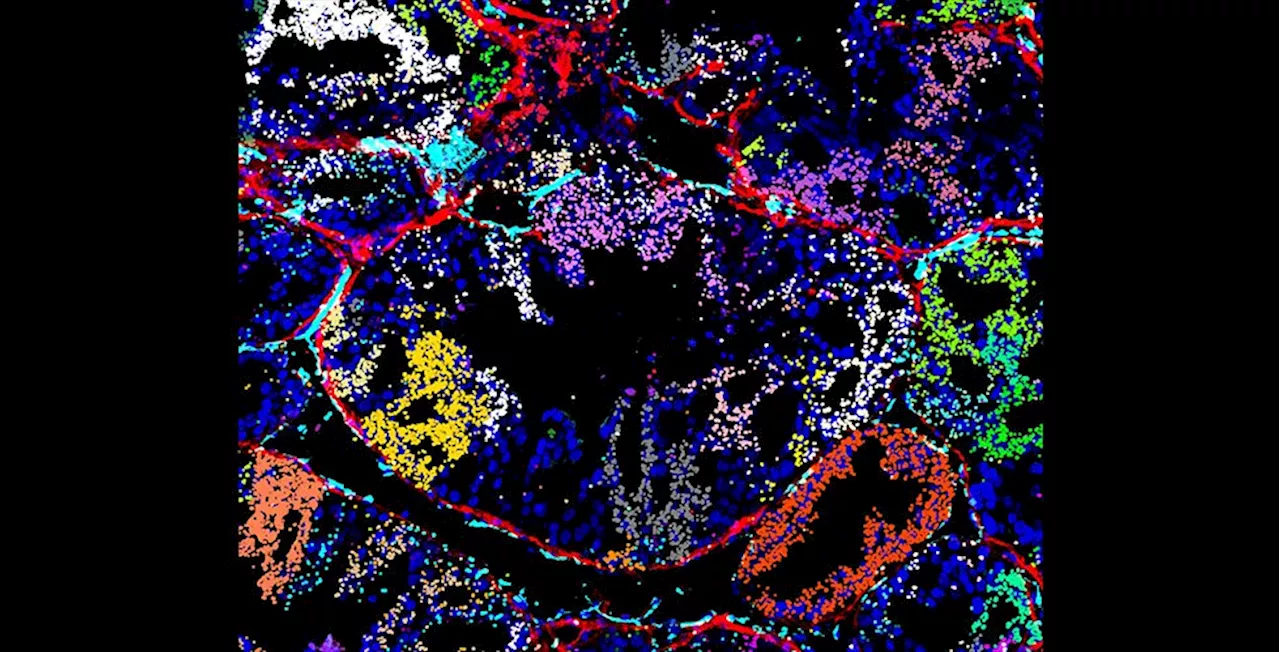 Scientists develop a new method to study gene function in cells and tissueThe Gaublomme lab has developed a new optical pooled screening approach called CRISPRmap, which enables the coupling of optical properties of single cells to targeted genetic perturbations.
Scientists develop a new method to study gene function in cells and tissueThe Gaublomme lab has developed a new optical pooled screening approach called CRISPRmap, which enables the coupling of optical properties of single cells to targeted genetic perturbations.
Read more »
 Cambridge scientists to look at AI in child brain tumour researchAbout 420 children in the UK are diagnosed with brain cancer every year, researchers say.
Cambridge scientists to look at AI in child brain tumour researchAbout 420 children in the UK are diagnosed with brain cancer every year, researchers say.
Read more »
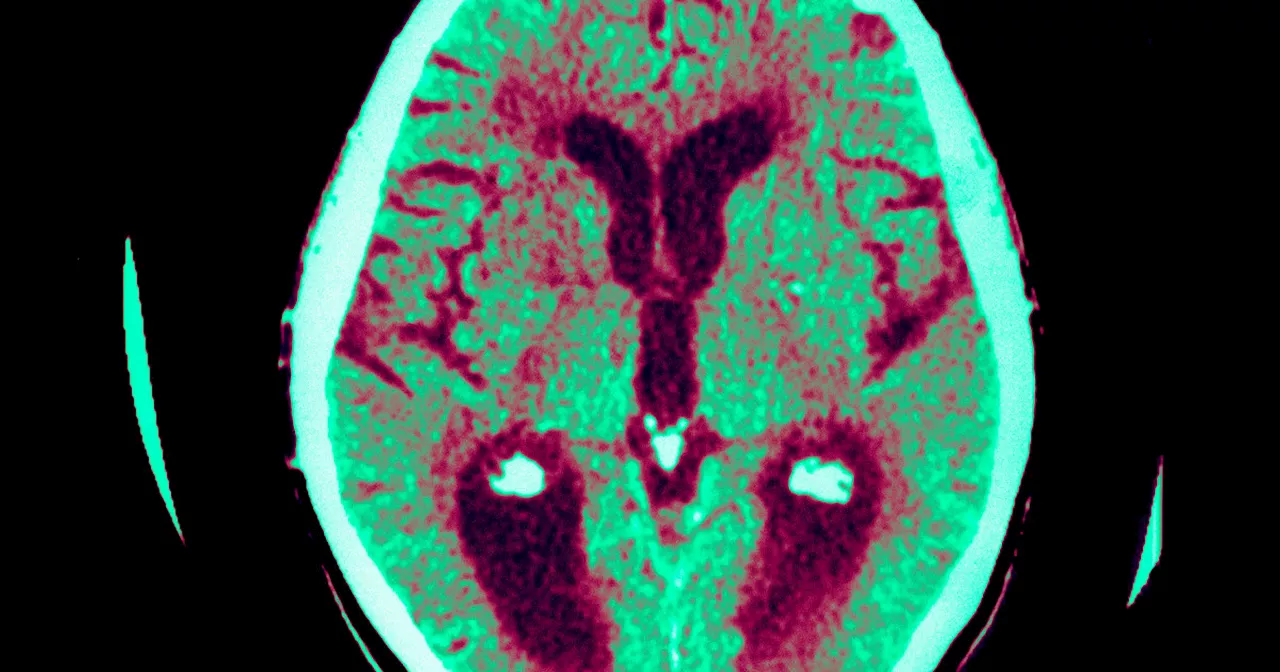 Alzheimer's scientists say brain stimulating device could slow memory lossThe growing cost of elder care is putting an increasing burden on American families. NBC News' Christine Romans profiles one American family dealing with the financial and emotional burdens of Alzheimer's Disease.
Alzheimer's scientists say brain stimulating device could slow memory lossThe growing cost of elder care is putting an increasing burden on American families. NBC News' Christine Romans profiles one American family dealing with the financial and emotional burdens of Alzheimer's Disease.
Read more »
 Scientists Discover 'Deep Brain' Genes Linked to Parkinson's And ADHDThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Scientists Discover 'Deep Brain' Genes Linked to Parkinson's And ADHDThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »
 Scientists can reverse brain aging in fruit flies by preventing buildup of a common proteinBuildup of a protein called filamentous actin, or F-actin, in the brain inhibits the removal of cellular wastes, including DNA, lipids, proteins and organelles. The resulting accumulation of waste diminishes neuronal functions and contributes to cognitive decline.
Scientists can reverse brain aging in fruit flies by preventing buildup of a common proteinBuildup of a protein called filamentous actin, or F-actin, in the brain inhibits the removal of cellular wastes, including DNA, lipids, proteins and organelles. The resulting accumulation of waste diminishes neuronal functions and contributes to cognitive decline.
Read more »
