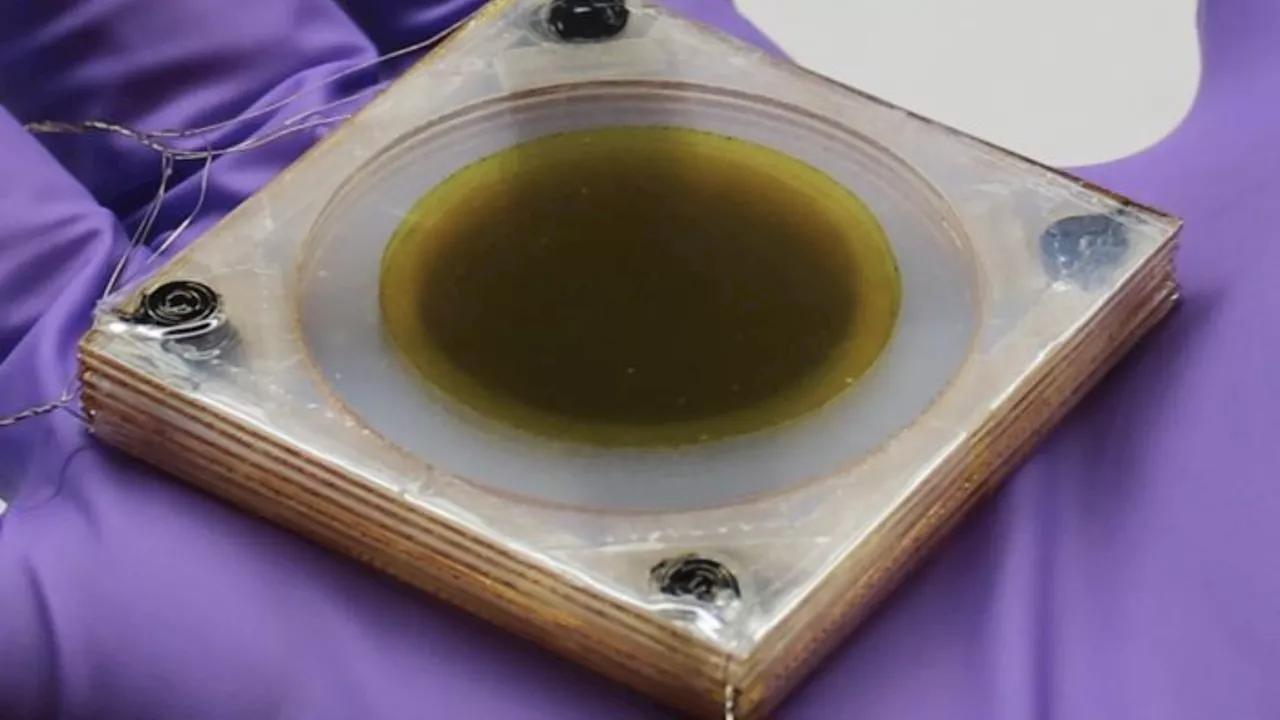
Researchers at UCLA have created a new cooling technology that utilizes the electrocaloric effect to continuously lower temperatures. The innovative design employs layers of flexing thin films that pump away heat when subjected to an electric field. In lab experiments, the prototype successfully reduced ambient temperatures by 16 degrees Fahrenheit continuously and up to 25 degrees at the heat source within 30 seconds.
A new cooling innovation developed by scientists pumps away heat continuously using layers of flexing thin films . The design is based on the electrocaloric effect , in which an electric field causes a temporary change in a material’s temperature, according to researchers.
When the electricity switches off, the stacked pairs come apart to then press against the other neighboring layers. As this alternating process repeats itself, the self-regenerative, accordion-like cascading action continually pumps heat away, layer by layer, according to a press release.
Electrocaloric Effect Cooling Technology Thin Films Wearable Devices Energy Efficiency
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
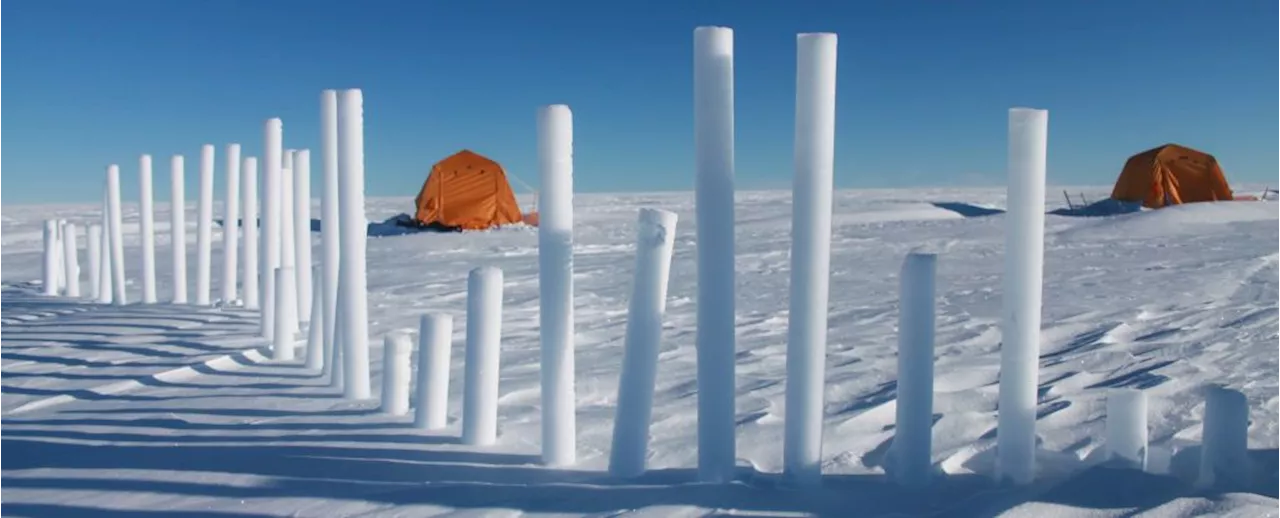 Scientists Unveil Mystery Volcano Behind 1830s Global CoolingVolcanologists have finally identified the volcano responsible for a major eruption in the 1830s that caused global cooling. By analyzing ash trapped in the Greenland ice sheet, researchers pinpointed the culprit to a volcano in the Kuril Islands, a remote chain between Russia and Japan.
Scientists Unveil Mystery Volcano Behind 1830s Global CoolingVolcanologists have finally identified the volcano responsible for a major eruption in the 1830s that caused global cooling. By analyzing ash trapped in the Greenland ice sheet, researchers pinpointed the culprit to a volcano in the Kuril Islands, a remote chain between Russia and Japan.
Read more »
 Scientists Develop Precise Method to Study Plasmonic WavesA new study combines time-resolved electron microscopy and multi-polarization lasers to create a highly accurate method for analyzing plasmonic waves, offering insights into their behavior and potential applications.
Scientists Develop Precise Method to Study Plasmonic WavesA new study combines time-resolved electron microscopy and multi-polarization lasers to create a highly accurate method for analyzing plasmonic waves, offering insights into their behavior and potential applications.
Read more »
 Scientists develop matchbox-sized laser in a bid to boost quantum researchA tiny chip-powered device has the power to replace the bulky lasers scientists use to study quantum applications and atomic clocks.
Scientists develop matchbox-sized laser in a bid to boost quantum researchA tiny chip-powered device has the power to replace the bulky lasers scientists use to study quantum applications and atomic clocks.
Read more »
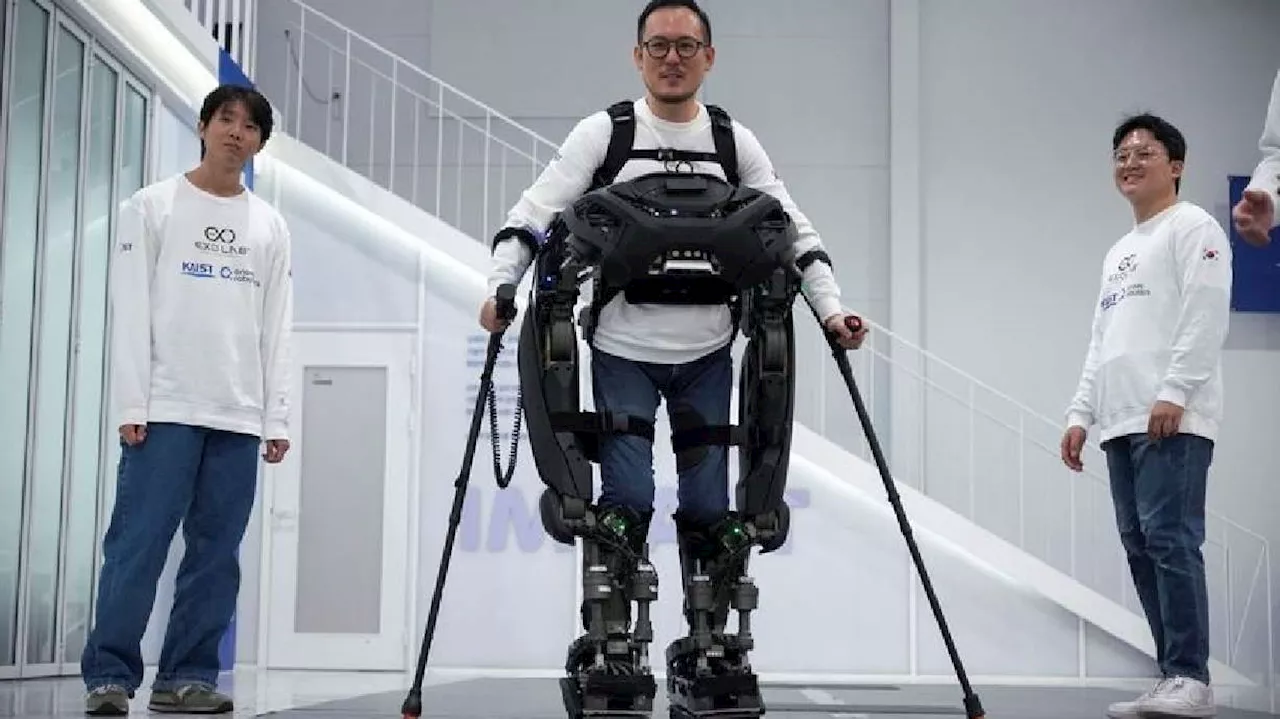 South Korean Scientists Develop a Wearable Robot to Help Paraplegic Users WalkResearchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have created a lightweight, wearable robot that can assist paraplegic individuals in walking, maneuvering obstacles, and climbing stairs. The robot, which can lock onto the user, aims to seamlessly integrate into their daily lives.
South Korean Scientists Develop a Wearable Robot to Help Paraplegic Users WalkResearchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have created a lightweight, wearable robot that can assist paraplegic individuals in walking, maneuvering obstacles, and climbing stairs. The robot, which can lock onto the user, aims to seamlessly integrate into their daily lives.
Read more »
 Scientists develop 3D concrete printing method that captures carbon dioxideScientists have developed a 3D concrete printing method that captures carbon, demonstrating a new pathway to reduce the environmental impact of the construction industry.
Scientists develop 3D concrete printing method that captures carbon dioxideScientists have developed a 3D concrete printing method that captures carbon, demonstrating a new pathway to reduce the environmental impact of the construction industry.
Read more »
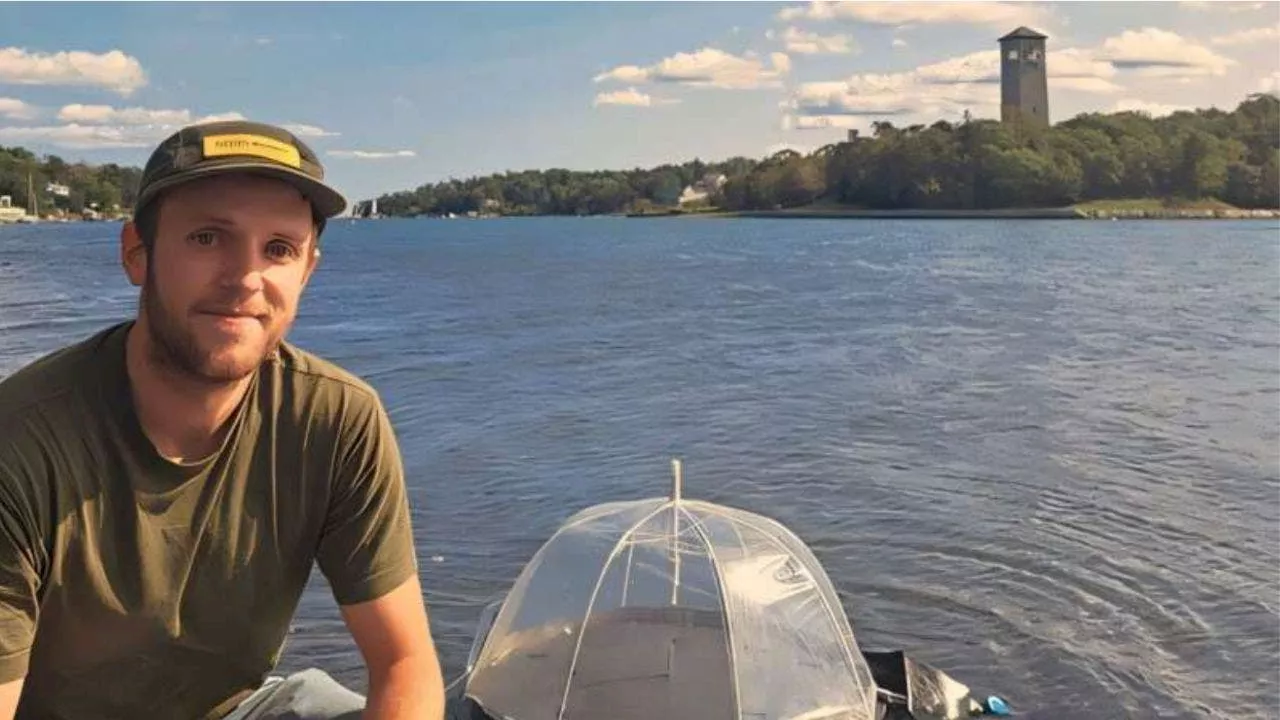 Scientists Develop Groundbreaking Device for Water Desalination Using Solar Power and Recycled TiresA new invention from Dalhousie University could provide a sustainable solution to global water scarcity.
Scientists Develop Groundbreaking Device for Water Desalination Using Solar Power and Recycled TiresA new invention from Dalhousie University could provide a sustainable solution to global water scarcity.
Read more »