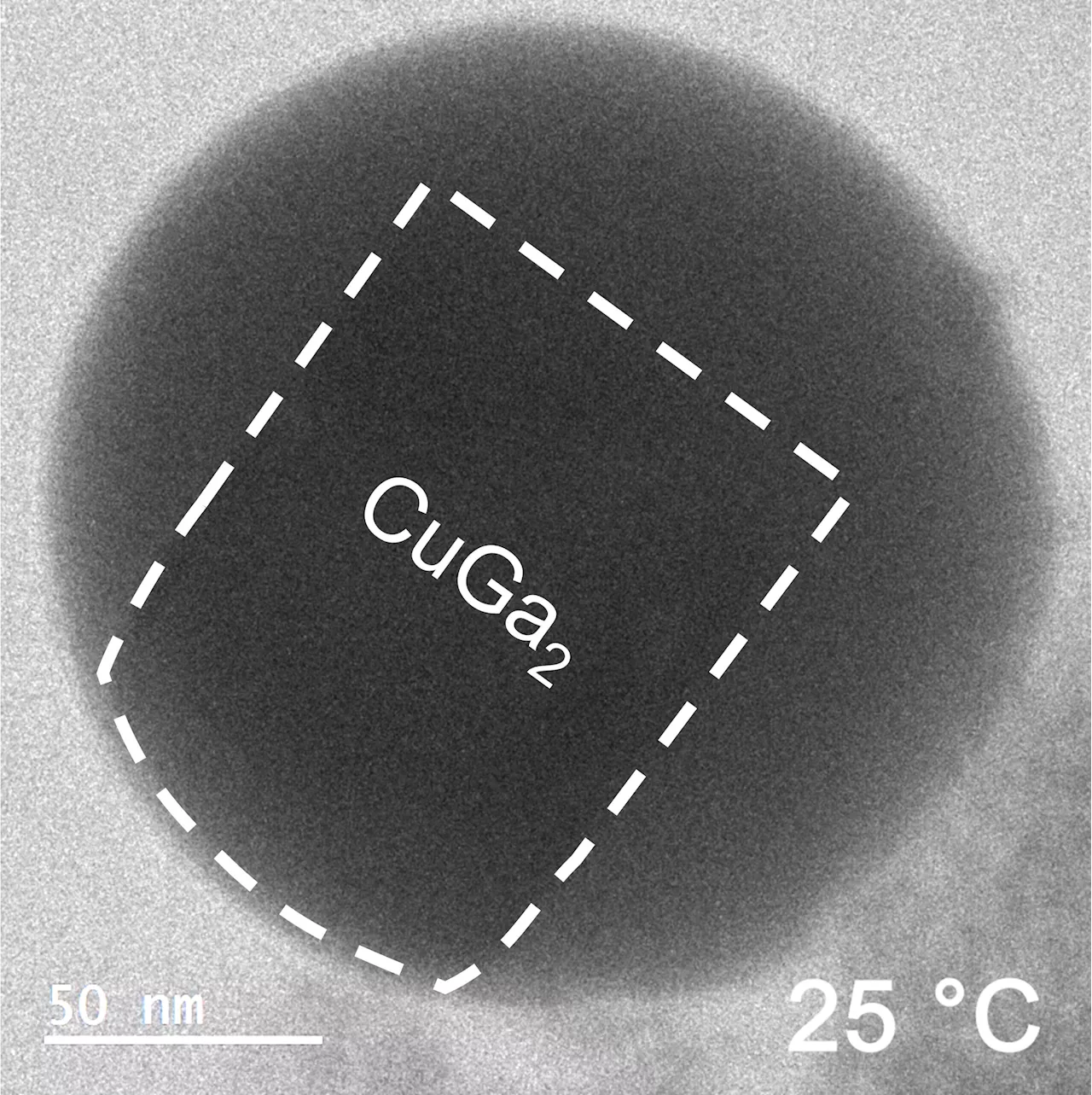
The boundary between solid metal and liquid metal can be much less 'solid' than we ever suspected. RMIT researchers have discovered that the liquid-solid boundary can fluctuate back and forth, with metallic atoms near the surface breaking free from their crystal lattice.
Researchers discover spontaneous liquefaction of solid metal–liquid metal interfaces in colloidal binary alloys retrieved 6 May 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-05-spontaneous-liquefaction-solid-metalliquid-metal.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.59 minutes ago Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
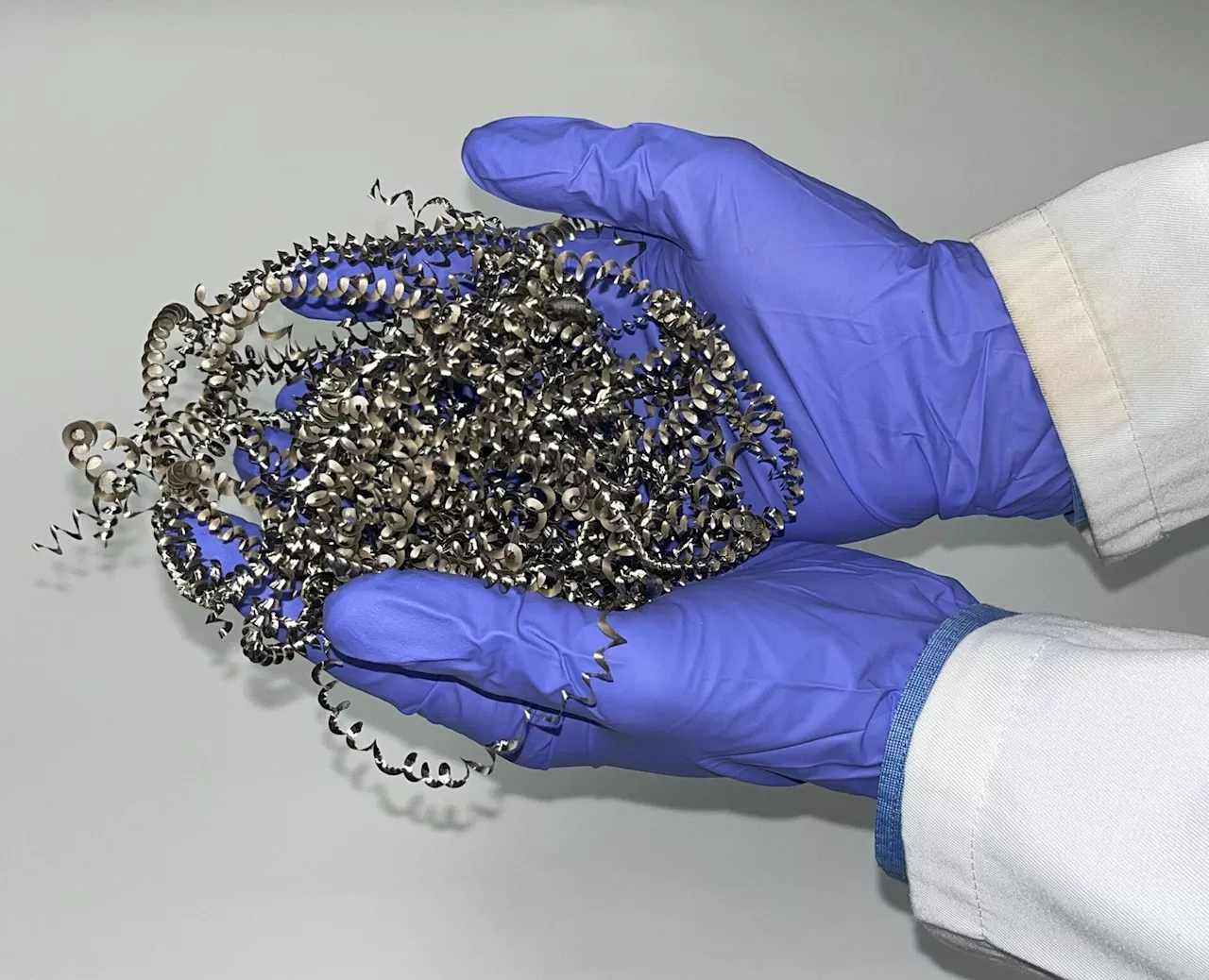 Trash to treasure—Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Trash to treasure—Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Read more »
 Trash to treasure -- researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Trash to treasure -- researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Read more »
 Researchers uncover kinky metal alloy that won't crack at extreme temperatures at the atomic levelA metal alloy composed of niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium has shocked materials scientists with its impressive strength and toughness at both extremely hot and cold temperatures, a combination of properties that seemed so far to be nearly impossible to achieve.
Researchers uncover kinky metal alloy that won't crack at extreme temperatures at the atomic levelA metal alloy composed of niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium has shocked materials scientists with its impressive strength and toughness at both extremely hot and cold temperatures, a combination of properties that seemed so far to be nearly impossible to achieve.
Read more »
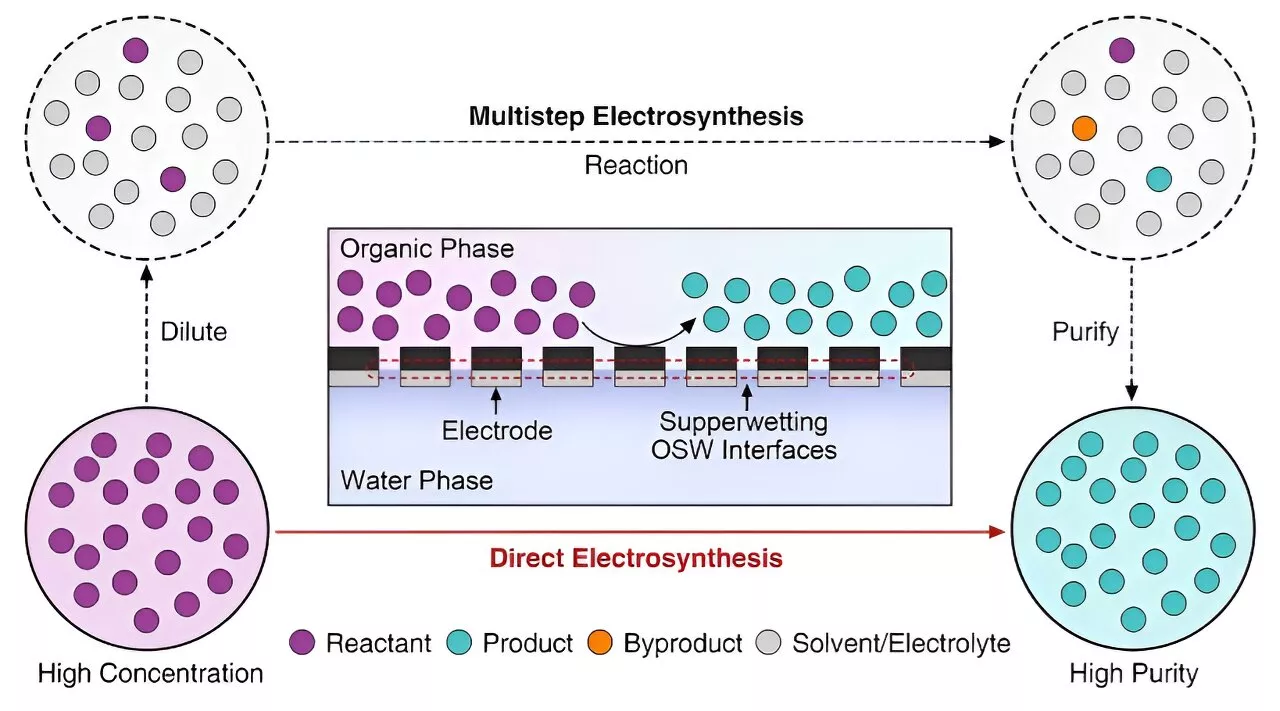 Researchers achieve electrosynthesis via superwetting organic-solid-water interfacesChinese scientists have recently achieved the direct synthesis of high-purity benzaldehyde chemicals from the selective electrooxidation of benzyl alcohol.
Researchers achieve electrosynthesis via superwetting organic-solid-water interfacesChinese scientists have recently achieved the direct synthesis of high-purity benzaldehyde chemicals from the selective electrooxidation of benzyl alcohol.
Read more »
 Researchers reveal water-assisted oxidative redispersion of metal nanoparticlesOxidative redispersion at elevated temperatures has long been utilized in heterogeneous catalysis for the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts and the synthesis of metal single atom and cluster catalysts. These redispersion processes require a considerable energy input.
Researchers reveal water-assisted oxidative redispersion of metal nanoparticlesOxidative redispersion at elevated temperatures has long been utilized in heterogeneous catalysis for the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts and the synthesis of metal single atom and cluster catalysts. These redispersion processes require a considerable energy input.
Read more »
 Researchers suggest that mechanical pressure triggers a key event in HIV infectionIt has been more than 40 years since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic and scientists still don't fully understand how HIV enters and replicates in human cells, which has hindered the development of treatments.
Researchers suggest that mechanical pressure triggers a key event in HIV infectionIt has been more than 40 years since the beginning of the HIV/AIDS epidemic and scientists still don't fully understand how HIV enters and replicates in human cells, which has hindered the development of treatments.
Read more »