A metal alloy composed of niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium has shocked materials scientists with its impressive strength and toughness at both extremely hot and cold temperatures, a combination of properties that seemed so far to be nearly impossible to achieve.
Researchers uncover kinky metal alloy that won't crack at extreme temperatures at the atomic level retrieved 22 April 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-uncover-kinky-metal-alloy-wont.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Apr 18, 2024 Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers Propose Non-Aqueous Manganese Metal BatteriesResearchers in China say they have found a way to make manganese ion batteries that will be much less expensive to manufacture.
Researchers Propose Non-Aqueous Manganese Metal BatteriesResearchers in China say they have found a way to make manganese ion batteries that will be much less expensive to manufacture.
Read more »
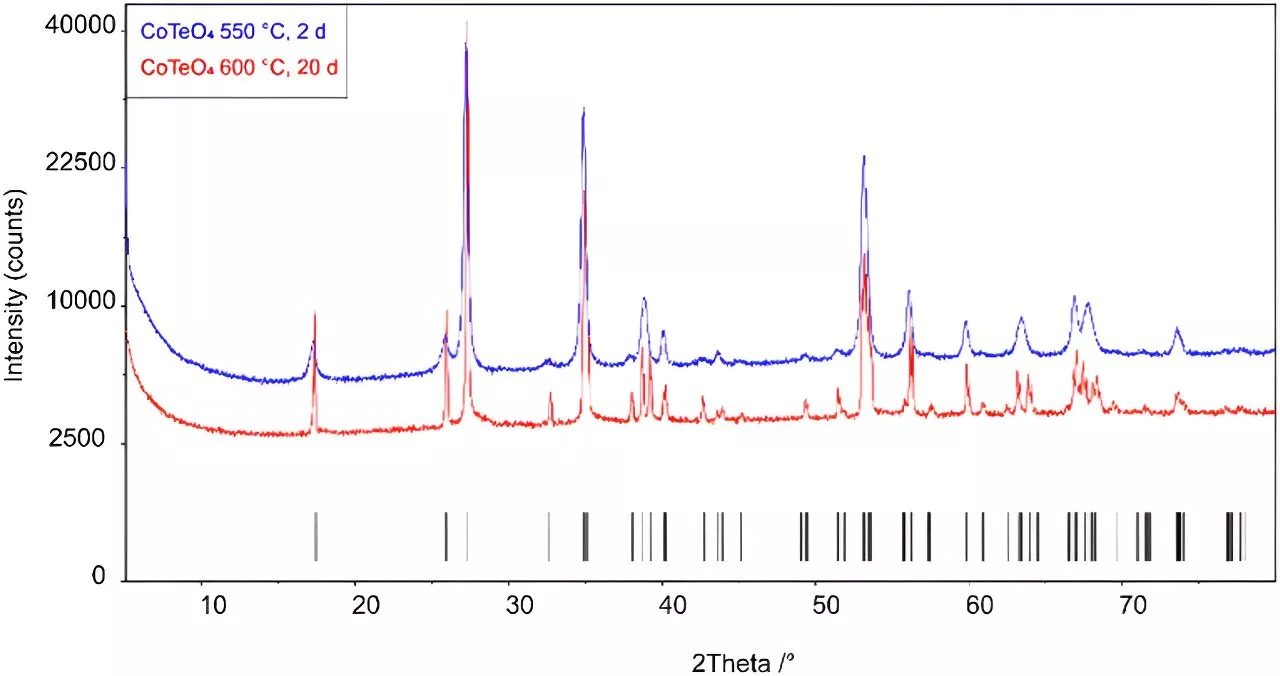 Researchers determine structure of new metal tellurate material with potential uses in solar energy and moreScientists have determined the structure of a new material with the potential to be used in solar energy, batteries, and splitting water to produce hydrogen.
Researchers determine structure of new metal tellurate material with potential uses in solar energy and moreScientists have determined the structure of a new material with the potential to be used in solar energy, batteries, and splitting water to produce hydrogen.
Read more »
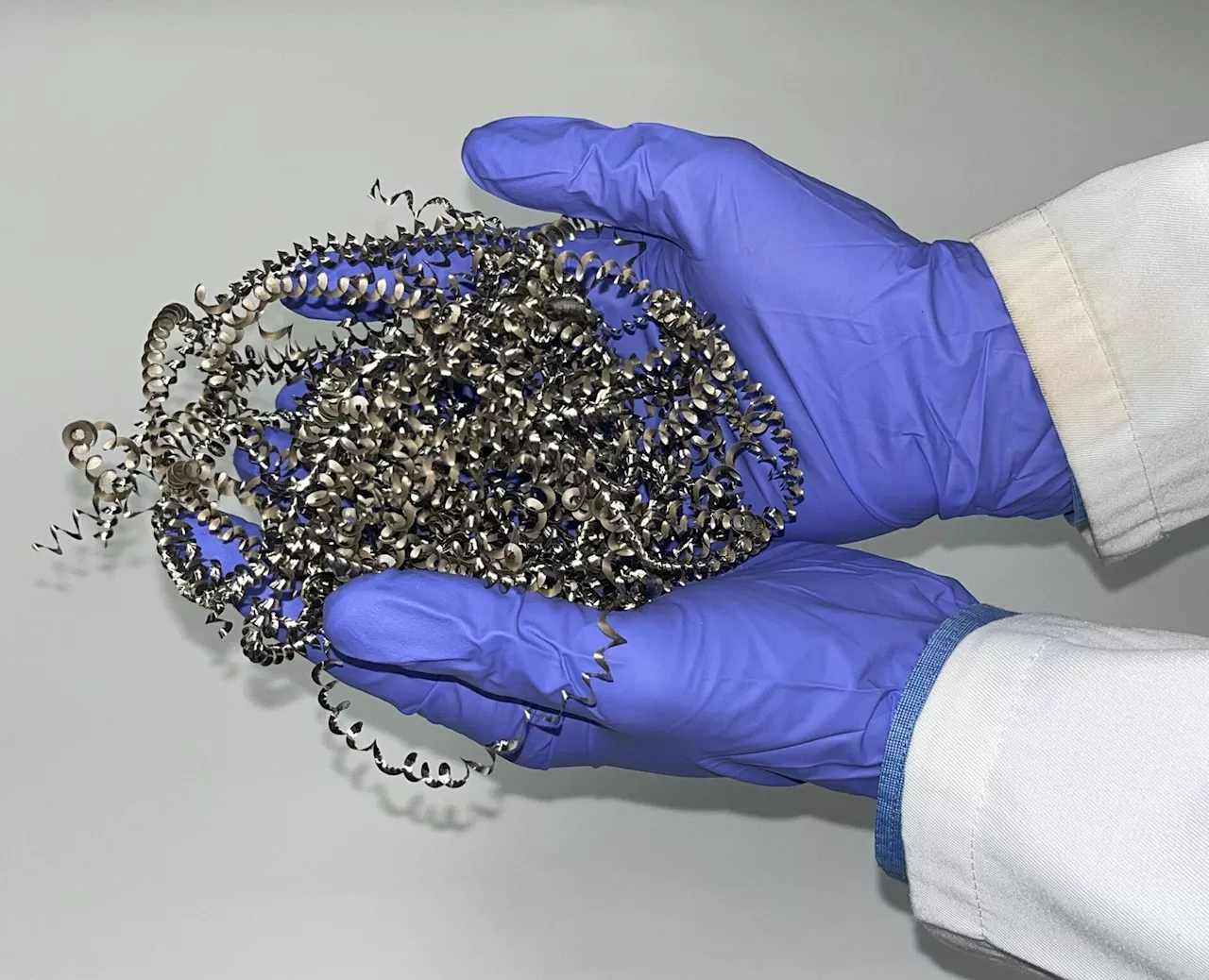 Trash to treasure—Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Trash to treasure—Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Read more »
 Trash to treasure -- researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Trash to treasure -- researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogenScientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that could make hydrogen production more sustainable.
Read more »
 Researchers advance pigment chemistry with moon-inspired reddish magentasA researcher who made color history in 2009 with a vivid blue pigment has developed durable, reddish magentas inspired by lunar mineralogy and ancient Egyptian chemistry.
Researchers advance pigment chemistry with moon-inspired reddish magentasA researcher who made color history in 2009 with a vivid blue pigment has developed durable, reddish magentas inspired by lunar mineralogy and ancient Egyptian chemistry.
Read more »
 Researchers reveal oceanic black carbon sink effect driven by seawater microdropletsPyrogenic carbon is widely produced during the incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels on land. About one-third of pyrogenic carbon is exported to the ocean by rivers, and thereinto, the refractory fraction becomes the source of oceanic black carbon that can provide a long-term sink for atmospheric CO2.
Researchers reveal oceanic black carbon sink effect driven by seawater microdropletsPyrogenic carbon is widely produced during the incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels on land. About one-third of pyrogenic carbon is exported to the ocean by rivers, and thereinto, the refractory fraction becomes the source of oceanic black carbon that can provide a long-term sink for atmospheric CO2.
Read more »
