Researchers have developed a new technique to view living mammalian cells. The team used a powerful laser, called a soft X-ray free electron laser, to emit ultrafast pulses of illumination at the speed of femtoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second.
With this they could capture images of carbon-based structures in living cells for the first time, before the soft X-ray radiation damaged them.
However, a team of researchers has constructed a new soft X-ray microscope through which they could view live mammalian cells for the first time. They were able to take images of carbon structures within the cells, which had not been seen before through other instruments. Carbon is one of the main elements for life, so this provides a new window into a vital part of ourselves.
Although soft X-ray free electron lasers have previously been used to study smaller viruses and bacteria, mammalian cells were too big to be studied this way. However, by using Wolter mirrors, the team could achieve a wider field of view and use a thicker sample holder which could hold larger cells. The resulting images showed details about carbon content in the cells that had not been seen through other methods, such as electron microscopy and fluorescence microscopy.
Today's Healthcare Medical Devices Biology Molecular Biology Cell Biology Medical Technology Optics Organic Chemistry
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Observing mammalian cells with superfast soft X-raysResearchers have developed a new technique to view living mammalian cells. The team used a powerful laser, called a soft X-ray free electron laser, to emit ultrafast pulses of illumination at the speed of femtoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second.
Observing mammalian cells with superfast soft X-raysResearchers have developed a new technique to view living mammalian cells. The team used a powerful laser, called a soft X-ray free electron laser, to emit ultrafast pulses of illumination at the speed of femtoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second.
Read more »
 Researchers create artificial cells that act like living cellsResearchers describe the steps they took to manipulate DNA and proteins -- essential building blocks of life -- to create cells that look and act like cells from the body. This accomplishment, a first in the field, has implications for efforts in regenerative medicine, drug delivery systems and diagnostic tools.
Researchers create artificial cells that act like living cellsResearchers describe the steps they took to manipulate DNA and proteins -- essential building blocks of life -- to create cells that look and act like cells from the body. This accomplishment, a first in the field, has implications for efforts in regenerative medicine, drug delivery systems and diagnostic tools.
Read more »
 Researchers identify drug compounds that can reduce prion protein levels in infected cellsPrions are the abnormal, pathogenic agents that are transmissible and are able to induce abnormal folding of specific normal cellular proteins.
Researchers identify drug compounds that can reduce prion protein levels in infected cellsPrions are the abnormal, pathogenic agents that are transmissible and are able to induce abnormal folding of specific normal cellular proteins.
Read more »
 Unlocking Cancer’s Code: Johns Hopkins Researchers Reveal How Cells Go RogueScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Unlocking Cancer’s Code: Johns Hopkins Researchers Reveal How Cells Go RogueScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Researchers crack code for more efficient perovskite solar cellsResearchers developed a new strategy to achieve record efficiency (25.82%) and stability in perovskite/organic tandem solar cells.
Researchers crack code for more efficient perovskite solar cellsResearchers developed a new strategy to achieve record efficiency (25.82%) and stability in perovskite/organic tandem solar cells.
Read more »
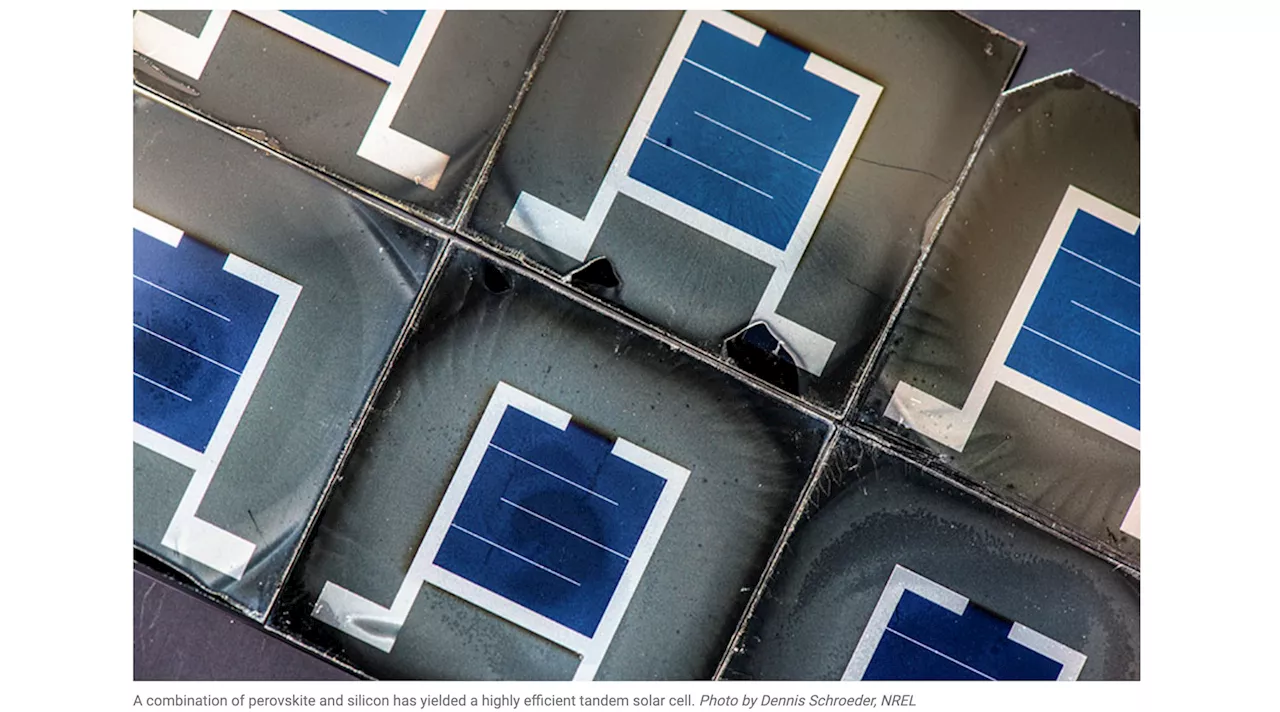 NREL Researchers Outline Path Forward for Tandem Solar CellsSolar,NREL Researchers Outline Path Forward for Tandem Solar Cells
NREL Researchers Outline Path Forward for Tandem Solar CellsSolar,NREL Researchers Outline Path Forward for Tandem Solar Cells
Read more »
