Researchers developed a technique guaranteeing that data remain secure during multiparty, cloud-based computation. This method, which leverages the quantum properties of light, could enable organizations like hospitals or financial companies to use deep learning to securely analyze confidential patient or customer data.
Deep-learning models are being used in many fields, from health care diagnostics to financial forecasting. However, these models are so computationally intensive that they require the use of powerful cloud-based servers.
Moreover, the technique guarantees security without compromising the accuracy of the deep-learning models. In tests, the researcher demonstrated that their protocol could maintain 96 percent accuracy while ensuring robust security measures. In this scenario, sensitive data must be sent to generate a prediction. However, during the process the patient data must remain secure.
A neural network is a deep-learning model that consists of layers of interconnected nodes, or neurons, that perform computation on data. The weights are the components of the model that do the mathematical operations on each input, one layer at a time. The output of one layer is fed into the next layer until the final layer generates a prediction.
"Instead of measuring all the incoming light from the server, the client only measures the light that is necessary to run the deep neural network and feed the result into the next layer. Then the client sends the residual light back to the server for security checks," Sulimany explains.
Optics Physics Hacking Encryption Information Technology Privacy Issues Security And Defense Surveillance
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers give adult zebra finches back their ability to learn new songsWe all know the adage, 'You can't teach an old dog new tricks.' As we age, our ability to learn new skills, like mastering a foreign language or picking up a musical instrument, seems to fade. The culprit? A decline in brain plasticity - the brain's capacity to rewire itself and adapt to new challenges.
Researchers give adult zebra finches back their ability to learn new songsWe all know the adage, 'You can't teach an old dog new tricks.' As we age, our ability to learn new skills, like mastering a foreign language or picking up a musical instrument, seems to fade. The culprit? A decline in brain plasticity - the brain's capacity to rewire itself and adapt to new challenges.
Read more »
 Researchers create new tool to analyze embodied carbon in more than 1 million buildings in ChicagoThe built environment—which includes the construction and operation of buildings, highways, bridges and other infrastructure—is responsible for close to 40% of the global greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change.
Researchers create new tool to analyze embodied carbon in more than 1 million buildings in ChicagoThe built environment—which includes the construction and operation of buildings, highways, bridges and other infrastructure—is responsible for close to 40% of the global greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change.
Read more »
 Researchers find new way to forecast hurricanes weeks ahead using Kelvin wavesA new research led by NSF NCAR reveals that Kelvin waves can predict increased hurricane activity weeks in advance.
Researchers find new way to forecast hurricanes weeks ahead using Kelvin wavesA new research led by NSF NCAR reveals that Kelvin waves can predict increased hurricane activity weeks in advance.
Read more »
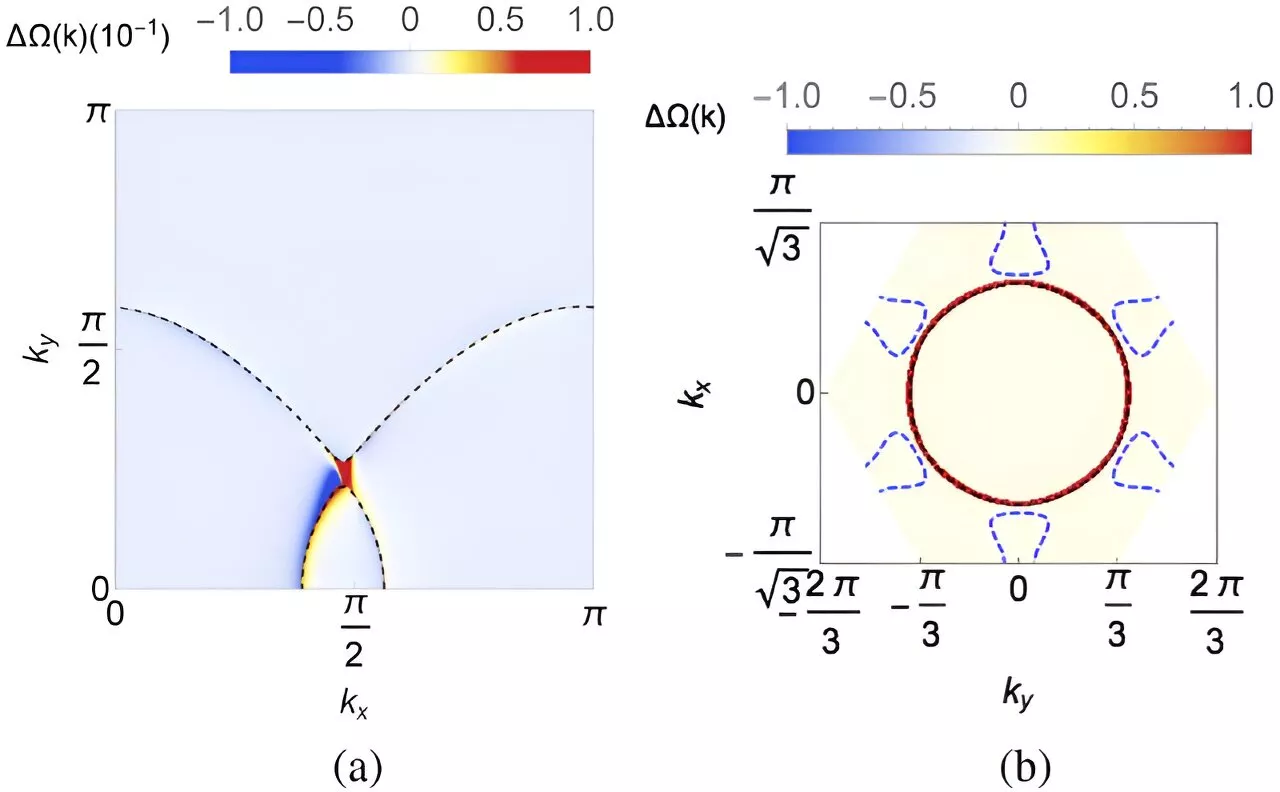 Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devicesA new study led by Rice University's Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on Sept. 6, the research explores the effects of Kondo coupling and chiral spin liquids within specific lattice structures.
Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devicesA new study led by Rice University's Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on Sept. 6, the research explores the effects of Kondo coupling and chiral spin liquids within specific lattice structures.
Read more »
 SC27: Researchers discover new antibody effective against all COVID-19 strainsResearchers have discovered SC27, a new antibody that can neutralize all known COVID-19 variants and SARS-like coronaviruses.
SC27: Researchers discover new antibody effective against all COVID-19 strainsResearchers have discovered SC27, a new antibody that can neutralize all known COVID-19 variants and SARS-like coronaviruses.
Read more »
 Researchers find new quantum metal to elevate sensor tech in medical diagnosticsResearchers have discovered a new class of quantum critical metal that could enhance electronic devices like highly sensitive sensors.
Researchers find new quantum metal to elevate sensor tech in medical diagnosticsResearchers have discovered a new class of quantum critical metal that could enhance electronic devices like highly sensitive sensors.
Read more »
