Researchers have discovered a new class of quantum critical metal that could enhance electronic devices like highly sensitive sensors.
The unusual properties could lead to the development of new types of electronic devices, such as sensors with extreme sensitivity.A new study led by Rice University’s Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials.
But unlike water, these electrons follow the rules of quantum mechanics, leading to much more complex behaviors.Even at absolute zero, where thermal fluctuations disappear, quantum fluctuations can still cause changes in the organization of electrons, leading to quantum phase transitions. These transitions often result in extreme physical properties known as quantum criticality.
The research team discovered that this coupling also triggers a transition into a Kondo phase, where the spins of the slow electrons lock onto the fast ones. The study reveals the complex interplay between electronic topology and quantum phase transitions.
Health Inventions And Machines Physics Sustainability
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers present new diagnostic tool for laser-plasma accelerator using metal foil as 3D scannerLaser-plasma accelerators take up less space than conventional facilities, which are sometimes kilometers long. Such compact particle sources can accelerate electron bunches efficiently, enabling X-ray lasers that fit in the basement of a university institute.
Researchers present new diagnostic tool for laser-plasma accelerator using metal foil as 3D scannerLaser-plasma accelerators take up less space than conventional facilities, which are sometimes kilometers long. Such compact particle sources can accelerate electron bunches efficiently, enabling X-ray lasers that fit in the basement of a university institute.
Read more »
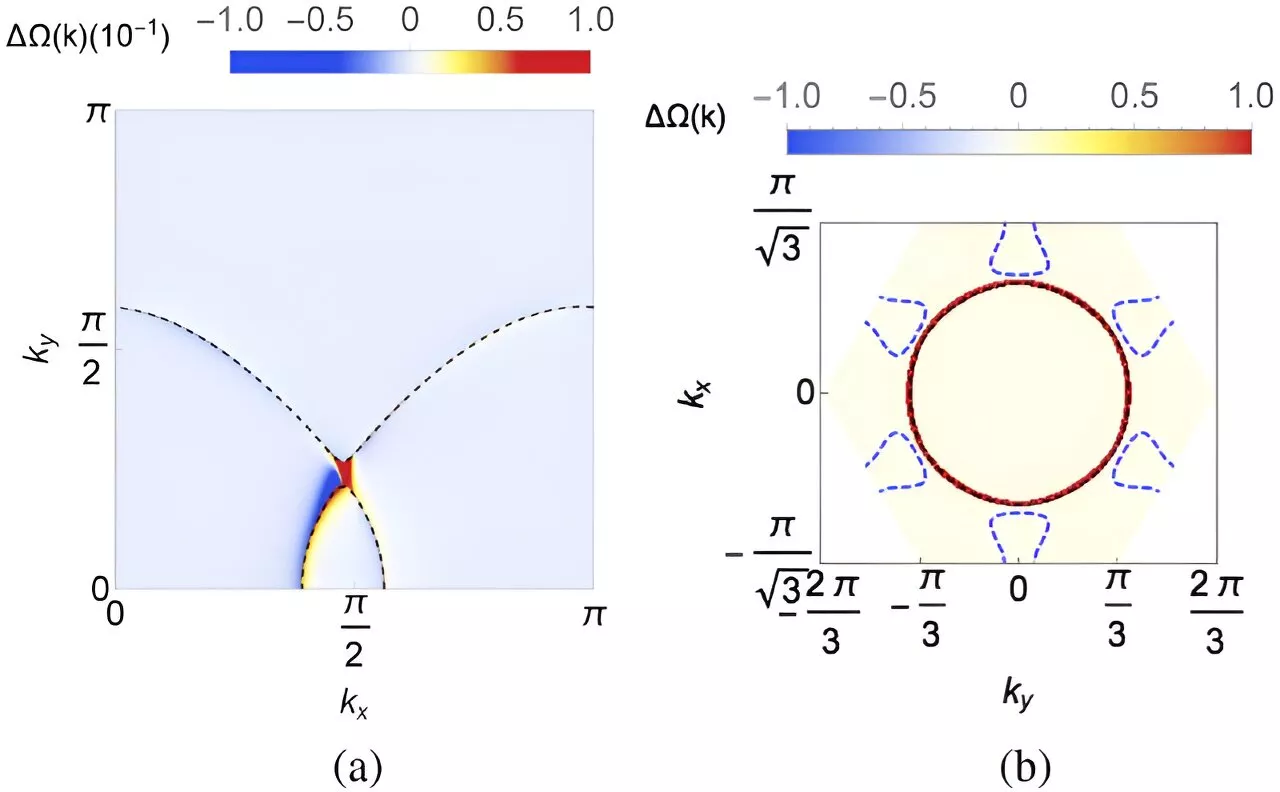 Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devicesA new study led by Rice University's Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on Sept. 6, the research explores the effects of Kondo coupling and chiral spin liquids within specific lattice structures.
Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devicesA new study led by Rice University's Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on Sept. 6, the research explores the effects of Kondo coupling and chiral spin liquids within specific lattice structures.
Read more »
 UT Austin researchers help predict local weather during 2024 Paris OlympicsThe team is part of an international project using the Games to develop tools for making hyperlocal climate predictions. UT researchers plan to apply what they learn in Austin.
UT Austin researchers help predict local weather during 2024 Paris OlympicsThe team is part of an international project using the Games to develop tools for making hyperlocal climate predictions. UT researchers plan to apply what they learn in Austin.
Read more »
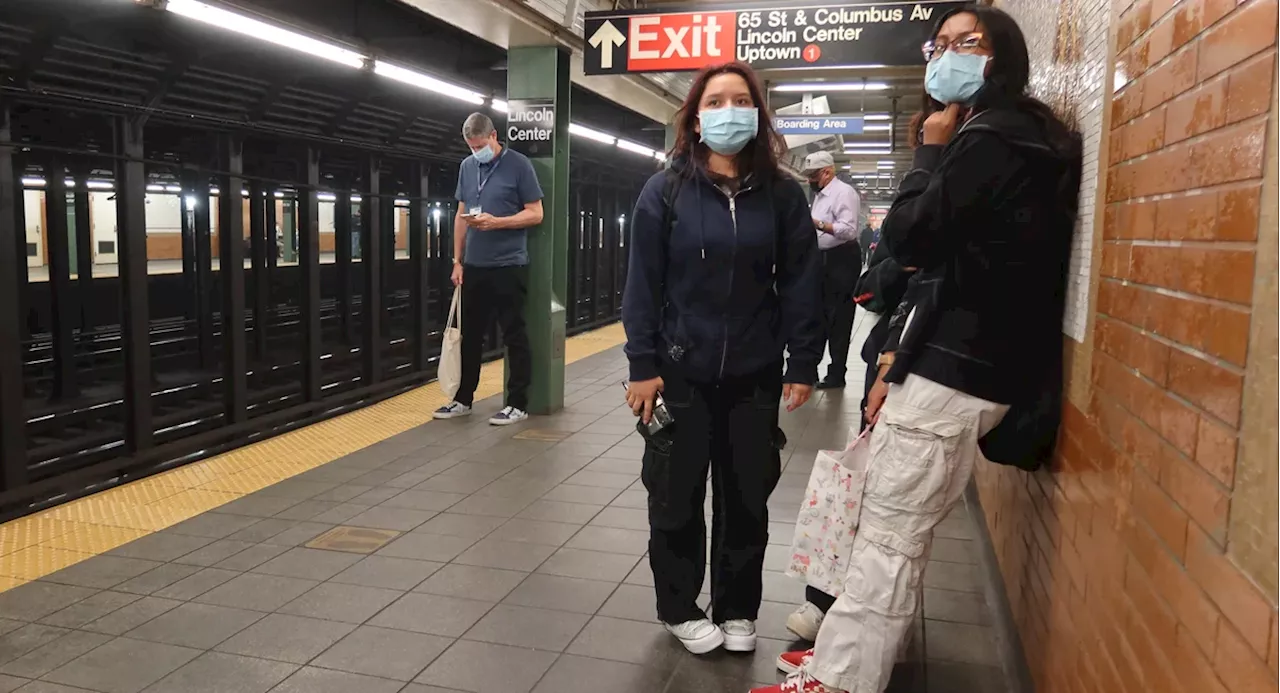 Toxic subway air is worse for Black, Hispanic riders with longer commutes, NYU researchers sayA new study finds that the city’s subway system is more harmful to those with more transfers and longer commutes.
Toxic subway air is worse for Black, Hispanic riders with longer commutes, NYU researchers sayA new study finds that the city’s subway system is more harmful to those with more transfers and longer commutes.
Read more »
 In rare opportunity, researchers observe formation of Icelandic valleysOn 10 November 2023, authorities evacuated the city of Grindavík on Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula.
In rare opportunity, researchers observe formation of Icelandic valleysOn 10 November 2023, authorities evacuated the city of Grindavík on Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula.
Read more »
 Researchers identify seasonal sources of Beijing smogAn international study led by researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has used a new method to identify the various sources of aerosols that create smog in Beijing.
Researchers identify seasonal sources of Beijing smogAn international study led by researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has used a new method to identify the various sources of aerosols that create smog in Beijing.
Read more »
