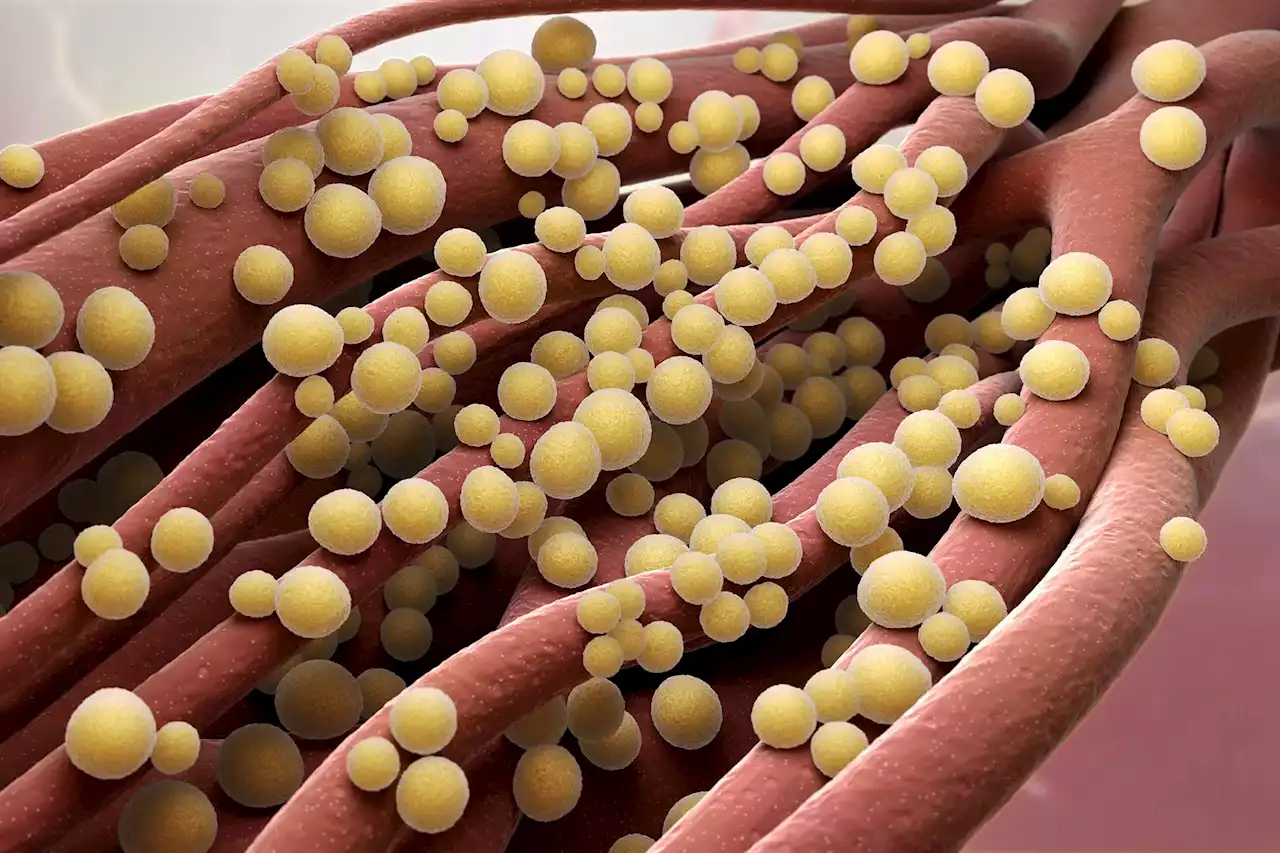
A new analysis reveals how Staphylococcus aureus gains mutations that allow it to colonize eczema patches. Human skin is home to millions of microbes. One of these microbes, Staphylococcus aureus, is an opportunistic pathogen that can invade patches of skin affected by eczema, also known as atopi
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from MIT and other institutions discovered that the microbe Staphylococcus aureus, commonly found on human skin, can rapidly evolve within a person’s microbiome, especially in those with eczema. The microbe evolves into a variant with a mutation in a specific gene, allowing it to grow faster on the skin, making eczema symptoms worse.
Lieberman and Maria Teresa García-Romero, a dermatologist and assistant professor at the National Institute of Pediatrics in Mexico, are the senior authors of the study, which appears on April 12 in the scientific journal. Felix Key, a former MIT postdoc who is now a group leader at the Max Planck Institute for Infection Biology, is the lead author of the paper.in their nostrils, where it is usually harmless.
To answer those questions, the researchers recruited patients aged 5 to 15 who were being treated for moderate to severe eczema. They took samples of the microbes on their skin once a month for three months, and then again at nine months. Samples were taken from the backs of the knees and inside of the elbows , the forearms, which are usually not affected, and the nostrils.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
![]() Ancient 'Hidden Chapter' of the Bible Uncovered with UV PhotographyA researcher has used ultraviolet photography to locate a lost fragment of Biblical text nearly 1,500 years after it was originally written.
Ancient 'Hidden Chapter' of the Bible Uncovered with UV PhotographyA researcher has used ultraviolet photography to locate a lost fragment of Biblical text nearly 1,500 years after it was originally written.
Read more »
 In a first, scientists create embryos in a lab from stem cells of monkeyLab-grown monkey embryos can help us understand embryonic development in detail. However, does this approach also resolves embryo-related ethical concerns?
In a first, scientists create embryos in a lab from stem cells of monkeyLab-grown monkey embryos can help us understand embryonic development in detail. However, does this approach also resolves embryo-related ethical concerns?
Read more »
 Perspective | Scientists identify two new species of a big, strange flying squirrelScientists identify two new species of a big, strange flying squirrel
Perspective | Scientists identify two new species of a big, strange flying squirrelScientists identify two new species of a big, strange flying squirrel
Read more »
 In a first, scientists plan to submerge pendulums in the ocean to reduce coastal erosionThe team highlights that the system could easily absorb ocean waves, and reduce the risk of coastal erosion in the near future.
In a first, scientists plan to submerge pendulums in the ocean to reduce coastal erosionThe team highlights that the system could easily absorb ocean waves, and reduce the risk of coastal erosion in the near future.
Read more »
 Scientists create 'slits in time' in mind-bending physics experimentResearchers replicated the classic double slit experiment using lasers, but their slits are in time not space.
Scientists create 'slits in time' in mind-bending physics experimentResearchers replicated the classic double slit experiment using lasers, but their slits are in time not space.
Read more »
Houston faces increased flooding risks as scientists observe 'unprecedented' Gulf Coast sea level riseScientists: 'Unprecedented' Gulf Coast sea level rise could increase Houston flood risk
Read more »