Researchers hope this discovery with honeybees may open the way for new disease-detection tools based on biological systems and scent analysis.
Have you ever heard of a bee sniffing out cancer? Believe it or not, honeybees can detect lung cancer in human breath.
This isn’t the first time scientists have explored animals’ amazing olfactory abilities for cancer detection. Previous studies have demonstrated that trained canines, rats, insects, and even nematodes may detect cancer.They created a special recipe for a “synthetic breath mixture.” This mixture resembled the chemical composition of a healthy person’s breath and that of someone with lung cancer.
Interestingly, researchers observed a difference in honeybee’s neural firing rates when exposed to the odors. The team saw honeybees activating multiple distinct neurons in their brains, which helped them distinguish between synthetic lung cancer breath and healthy breath.
Energy &Amp Environment Health
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 UC Berkeley researchers to have human subjects in psilocybin studyA UC Berkeley research center seeks to understand why psilocybin alters the visual experience in a study with human subjects.
UC Berkeley researchers to have human subjects in psilocybin studyA UC Berkeley research center seeks to understand why psilocybin alters the visual experience in a study with human subjects.
Read more »
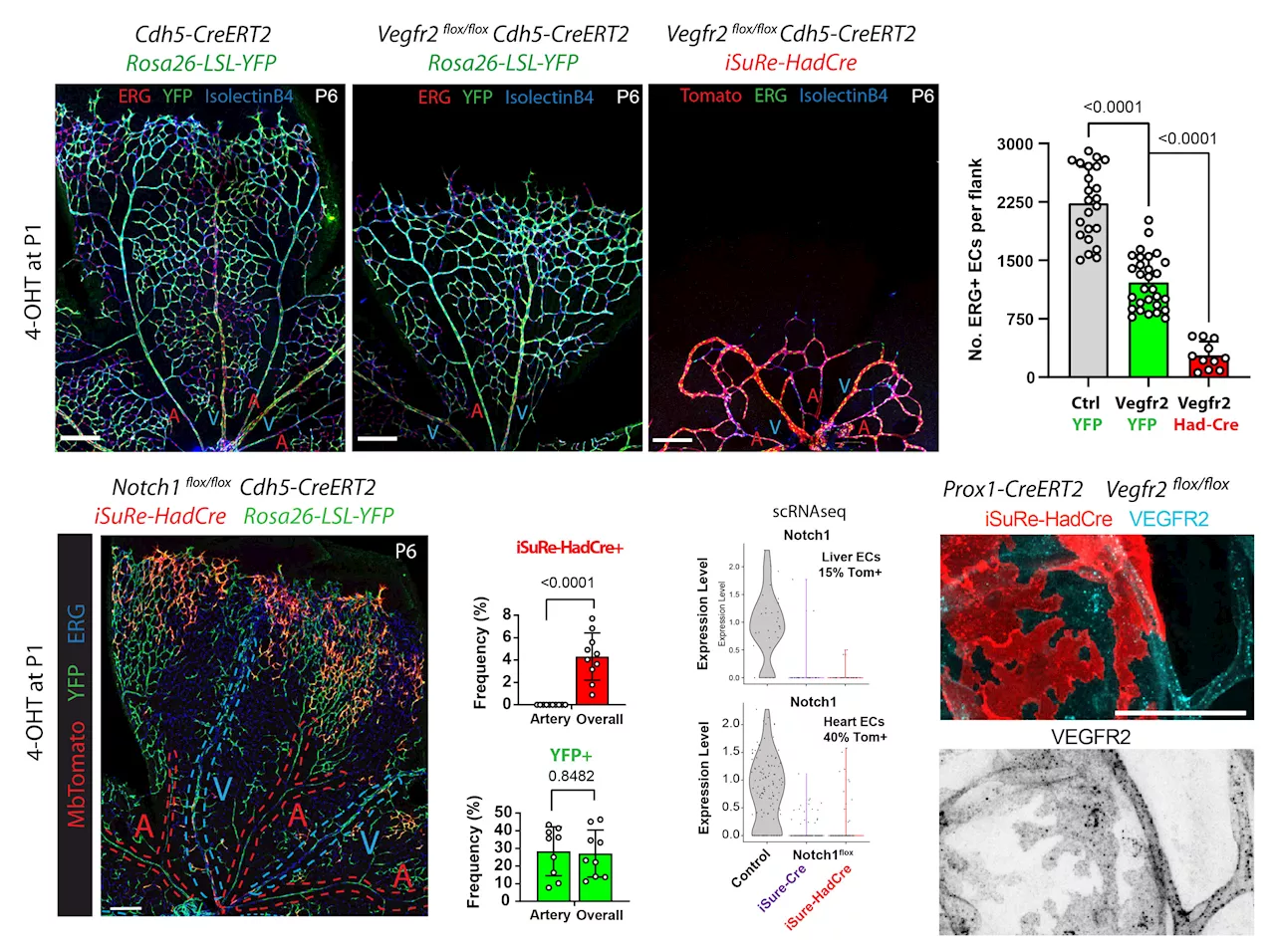 Researchers create an innovative tool for the reliable and efficient study of gene functionA team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Rui Benedito has generated a novel genetic tool, called iSuRe-HadCre, that enables the induction of precise genetic alterations in whole tissues or in individual cells with high efficiency and reliability.
Researchers create an innovative tool for the reliable and efficient study of gene functionA team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) led by Rui Benedito has generated a novel genetic tool, called iSuRe-HadCre, that enables the induction of precise genetic alterations in whole tissues or in individual cells with high efficiency and reliability.
Read more »
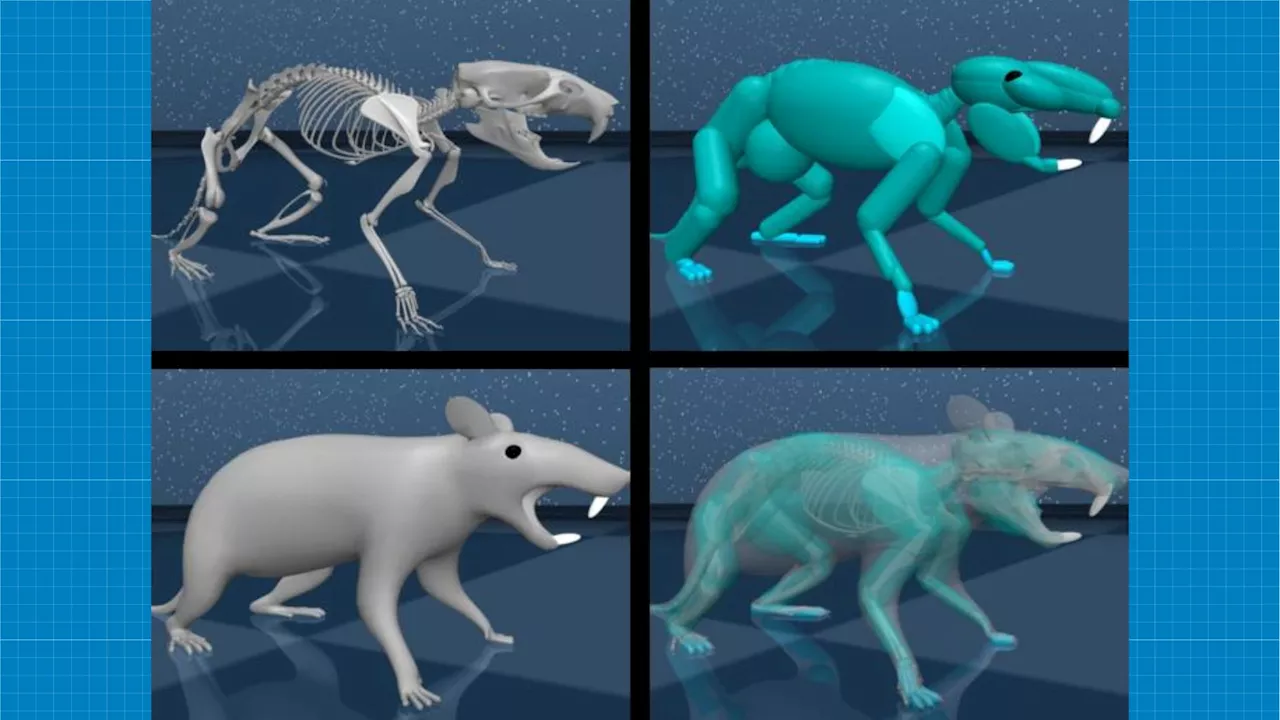 Harvard researchers create virtual rat model to study brain controlHarvard scientists, with Google's DeepMind AI lab, crafted a virtual rat model with an artificial brain mimicking natural movements.
Harvard researchers create virtual rat model to study brain controlHarvard scientists, with Google's DeepMind AI lab, crafted a virtual rat model with an artificial brain mimicking natural movements.
Read more »
 Protein study could help researchers develop new antibioticsA team has found a way to make the bacterial enzyme histidine kinase water-soluble, which could make it possible to rapidly screen potential antibiotics that might interfere with its functions.
Protein study could help researchers develop new antibioticsA team has found a way to make the bacterial enzyme histidine kinase water-soluble, which could make it possible to rapidly screen potential antibiotics that might interfere with its functions.
Read more »
 Researchers conduct Wikipedia study to motivate experts to contribute to open contentGetting experts to contribute to open content, such as Wikipedia, is not an easy task as experts often have high demands on their time. But one way to increase expert contributions is to understand what motivates them to contribute, a University of Michigan study shows.
Researchers conduct Wikipedia study to motivate experts to contribute to open contentGetting experts to contribute to open content, such as Wikipedia, is not an easy task as experts often have high demands on their time. But one way to increase expert contributions is to understand what motivates them to contribute, a University of Michigan study shows.
Read more »
 Researchers at USF using virtual reality to study how brains are developedCrews responded to The Abbey at Medical Center apartments on Rowley Road Tuesday morning where multiple units were damaged. No injuries were reported.
Researchers at USF using virtual reality to study how brains are developedCrews responded to The Abbey at Medical Center apartments on Rowley Road Tuesday morning where multiple units were damaged. No injuries were reported.
Read more »
