The Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
"In just a few centuries, the people of Easter Island wiped out their forest, drove their plants and animals to extinction, and saw their complex society spiral into chaos and cannibalism."Nearly two decades later, an international team of geneticists has found evidence that this famous cautionary tale never actually happened.
Instead, ancient genetic data suggests the island was once home to a small population of between 1,500 and 3,000 individuals, who were interbreeding with populations that had Polynesian and Indigenous American ancestry long before Europeans had reached either region. The results are based on the remains of 15 ancient individuals from Rapa Nui, whose bones and teeth were taken by Europeans from the island in the 19th and 20th centuries and kept at several museums in Paris.
Based on the genomic analysis, which reconstructs the population of Rapa Nui over the last 100 generations, the researchers say it is unlikely that these individuals were born after European contact. When the team reanalyzed the ancient genomes from one past study, they detected an Indigenous American-like component in three out of five ancient Rapanui individuals.this interbreeding event or right after it occurred, before the evidence was incorporated into their genome.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
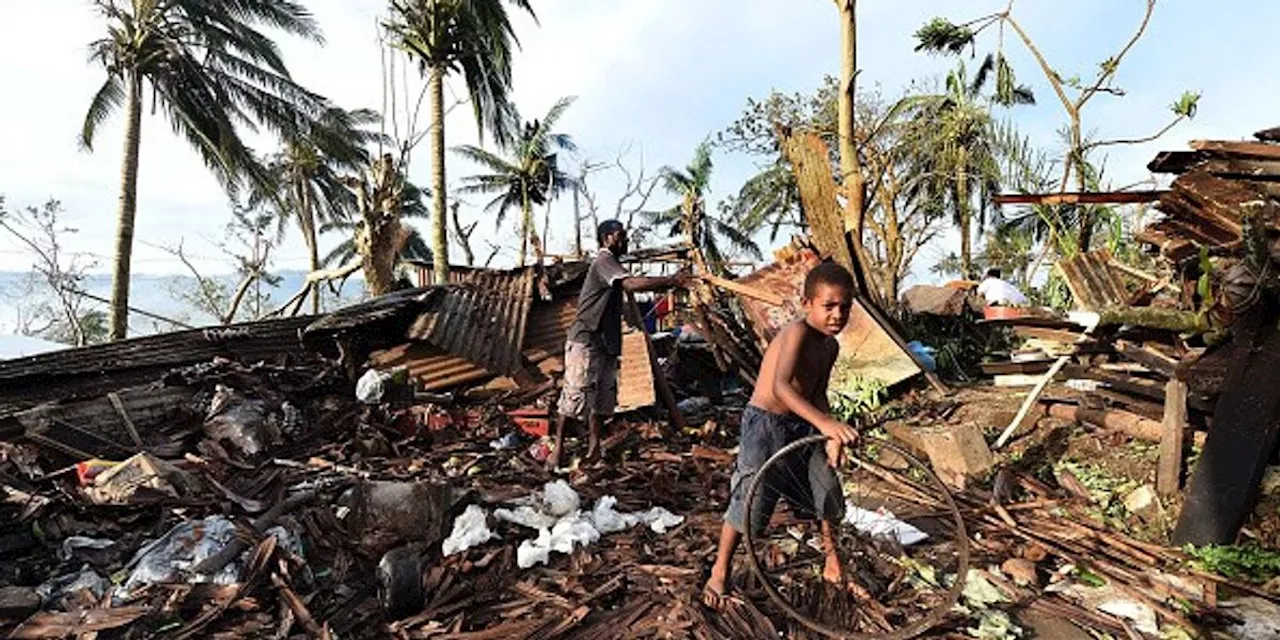 Pacific Islands Push ICC to Recognize Ecocide as International CrimeJulia Conley is a staff writer for Common Dreams.
Pacific Islands Push ICC to Recognize Ecocide as International CrimeJulia Conley is a staff writer for Common Dreams.
Read more »
 EU to Criminalize Acts 'Comparable to Ecocide'Olivia Rosane is a staff writer for Common Dreams.
EU to Criminalize Acts 'Comparable to Ecocide'Olivia Rosane is a staff writer for Common Dreams.
Read more »
 Fighting fungal foes: Walnut's genetic armor against anthracnose revealedA recent study has pinpointed a gene module crucial for enhancing walnut trees' resistance to anthracnose, a widespread fungal disease threatening the walnut industry.
Fighting fungal foes: Walnut's genetic armor against anthracnose revealedA recent study has pinpointed a gene module crucial for enhancing walnut trees' resistance to anthracnose, a widespread fungal disease threatening the walnut industry.
Read more »
 Scientists Crack Lyme Disease’s Genetic Code, Paving the Way for Better Diagnosis and TreatmentScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Scientists Crack Lyme Disease’s Genetic Code, Paving the Way for Better Diagnosis and TreatmentScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
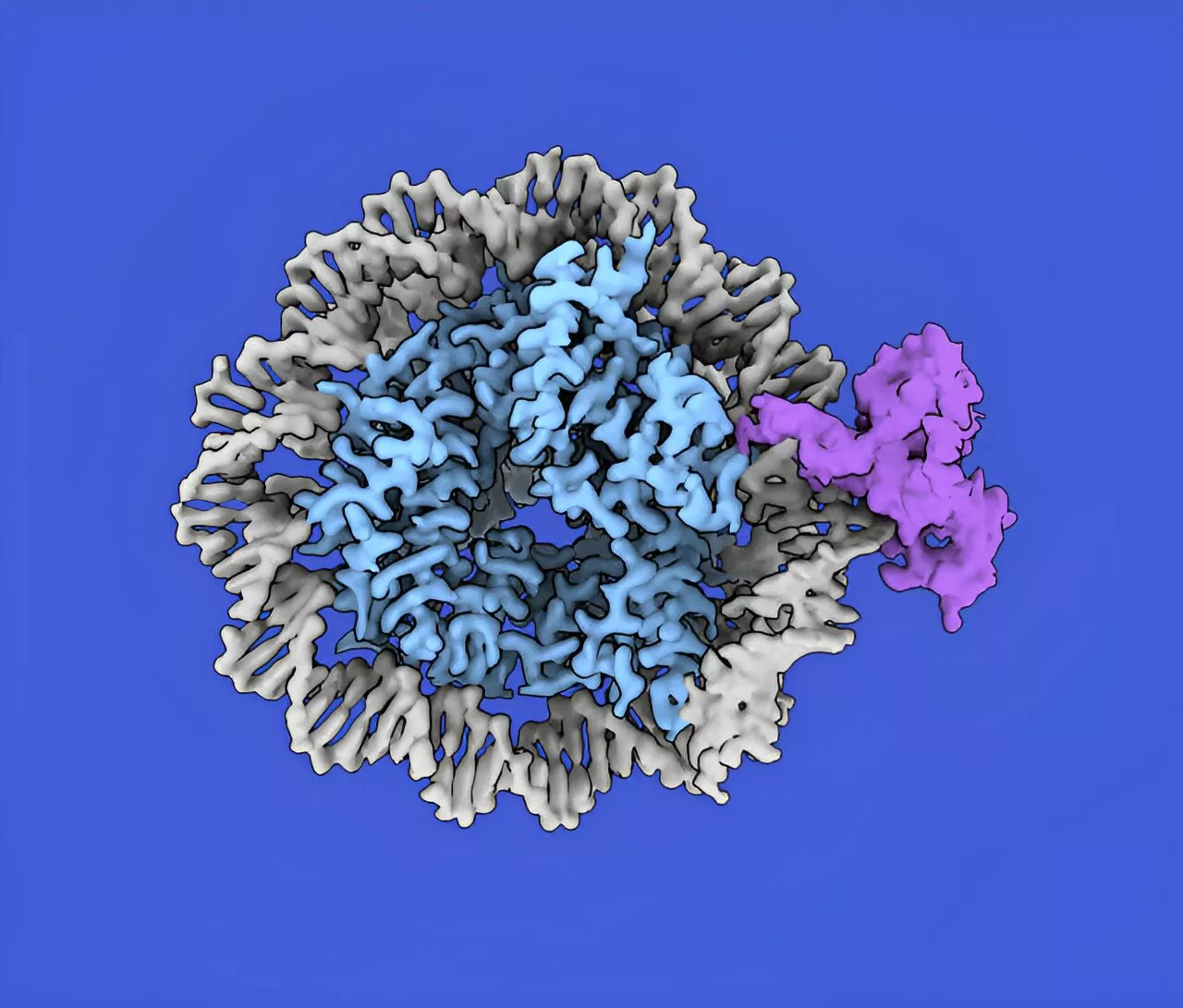 New genetic sensor for DNA methylation discoveredDNA methylation is a process in which a methyl group is attached to the cytosine base of the DNA molecule, and is a major way that DNA is epigenetically marked. Epigenetic modifications can act as on–off switches to regulate gene expression and help generate diverse cell types without changing the underlying DNA sequence.
New genetic sensor for DNA methylation discoveredDNA methylation is a process in which a methyl group is attached to the cytosine base of the DNA molecule, and is a major way that DNA is epigenetically marked. Epigenetic modifications can act as on–off switches to regulate gene expression and help generate diverse cell types without changing the underlying DNA sequence.
Read more »
 From antiquity to adaptation: Tracing the genetic journey of east Asian chestnut varietiesUncovering the genetic saga of Castanea trees, a study maps their evolutionary journey and local climate adaptations. This research reveals the genetic markers and molecular mechanisms that have allowed these nut fruit trees to adapt and flourish across East Asia, offering precious insights for their future in the face of environmental challenges.
From antiquity to adaptation: Tracing the genetic journey of east Asian chestnut varietiesUncovering the genetic saga of Castanea trees, a study maps their evolutionary journey and local climate adaptations. This research reveals the genetic markers and molecular mechanisms that have allowed these nut fruit trees to adapt and flourish across East Asia, offering precious insights for their future in the face of environmental challenges.
Read more »
