A new study using a pig model of heart attack shows that cell-based therapy can improve heart function after damage.
While lower vertebrates can repair their adult hearts after a heart attack, mammals -- including humans -- cannot. The ability to regenerate dead muscle tissue in mammalian hearts disappears just after birth. A pharmaceutical product called TT-10, which spurs proliferation of heart muscle cells, was thought to offer promise to treat heart attacks. In a mouse heart-attack model several years ago, TT-10 treatment improved heart function and reduced scar tissue.
A new study provides evidence that COVID-19 patients' heart damage is caused by the virus invading and replicating inside heart muscle cells, leading to cell death and interfering with heart function. Research in pigs shows that using the exosomes naturally produced from a mixture of heart muscle cells, endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells -- which were all derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells -- improved heart function after a heart attack.
Heart Attack Cell Therapy Regeneration Exosomes Pig Model
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Blood-Based Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise for Treating Childhood Heart FailureA groundbreaking research team in Australia is harnessing the power of blood stem cells to develop a revolutionary therapy for children with heart failure.
Blood-Based Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise for Treating Childhood Heart FailureA groundbreaking research team in Australia is harnessing the power of blood stem cells to develop a revolutionary therapy for children with heart failure.
Read more »
 Corneal Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise in Restoring VisionA groundbreaking clinical trial using reprogrammed stem cells has successfully treated patients with corneal epithelial stem cell deficiency, restoring their vision and offering hope for a new treatment option.
Corneal Stem Cell Therapy Shows Promise in Restoring VisionA groundbreaking clinical trial using reprogrammed stem cells has successfully treated patients with corneal epithelial stem cell deficiency, restoring their vision and offering hope for a new treatment option.
Read more »
 Brain tumor organoids accurately model patient response to CAR T cell therapyResearchers used lab-grown organoids created from tumors of individuals with glioblastoma (GBM) to accurately model a patient's response to CAR T cell therapy in real time. The organoid's response to therapy mirrored the response of the actual tumor in the patient's brain.
Brain tumor organoids accurately model patient response to CAR T cell therapyResearchers used lab-grown organoids created from tumors of individuals with glioblastoma (GBM) to accurately model a patient's response to CAR T cell therapy in real time. The organoid's response to therapy mirrored the response of the actual tumor in the patient's brain.
Read more »
 Early Success Seen With CAR T-Cell Therapy for Systemic SclerosisA case series showed that chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting CD19 halted the progression of fibrotic organ manifestations in six patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis.
Early Success Seen With CAR T-Cell Therapy for Systemic SclerosisA case series showed that chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting CD19 halted the progression of fibrotic organ manifestations in six patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis.
Read more »
 WWI aircraft-inspired tech could transform cell therapy, tissue engineeringTaking inspiration from the mechanics of WWI aircraft, this innovation could redefine approaches to cancer and heart disease treatments.
WWI aircraft-inspired tech could transform cell therapy, tissue engineeringTaking inspiration from the mechanics of WWI aircraft, this innovation could redefine approaches to cancer and heart disease treatments.
Read more »
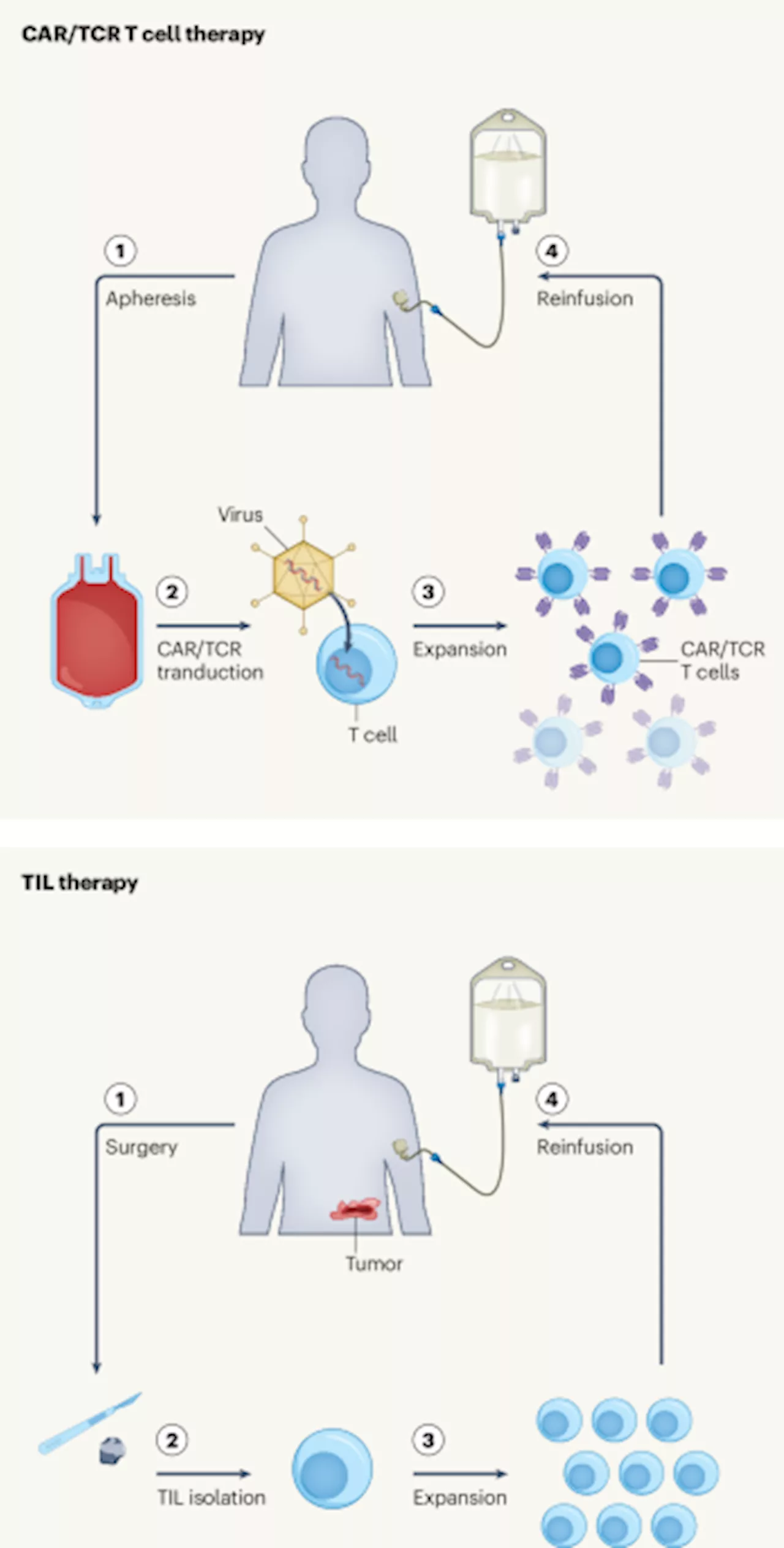 Beyond the blood: expanding CAR T cell therapy to solid tumorsChimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy stands as a transformative advancement in immunotherapy, triumphing against hematological malignancies and, increasingly, autoimmune disorders.
Beyond the blood: expanding CAR T cell therapy to solid tumorsChimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy stands as a transformative advancement in immunotherapy, triumphing against hematological malignancies and, increasingly, autoimmune disorders.
Read more »
