Science, Space and Technology News 2024
A study from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai indicates that current large language models are not yet effective for medical coding, requiring further development and rigorous testing before clinical implementation. Credit: SciTechDaily.comhave found that state-of-the-art artificial intelligence systems, specifically large language models , are poor at medical coding.
The next best-performing model, GPT-3.5, had the greatest tendency toward being vague. It had the highest proportion of incorrectly generated codes that were accurate but more general in nature compared to the precise codes. In this case, when provided with the ICD-9-CM description “unspecified adverse effect of anesthesia,” GPT-3.5 generated a code for “other specified adverse effects, not elsewhere classified.
“Previous studies indicate that newer large language models struggle with numerical tasks. However, the extent of their accuracy in assigning medical codes from clinical text had not been thoroughly investigated across different models,” says co-senior author Eyal Klang, MD, Director of the D3M’s Generative AI Research Program.
The researchers caution that the study’s artificial task may not fully represent real-world scenarios where LLM performance could be worse.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Challenges And Opportunities In Implementing Large Language ModelsAnkit is an ethical AI and data engineering expert at Google focused on customers' successful data and machine learning journeys. Read Ankit Virmani's full executive profile here.
Challenges And Opportunities In Implementing Large Language ModelsAnkit is an ethical AI and data engineering expert at Google focused on customers' successful data and machine learning journeys. Read Ankit Virmani's full executive profile here.
Read more »
 Large language models respond differently based on user's motivationA new study reveals how large language models (LLMs) respond to different motivational states.
Large language models respond differently based on user's motivationA new study reveals how large language models (LLMs) respond to different motivational states.
Read more »
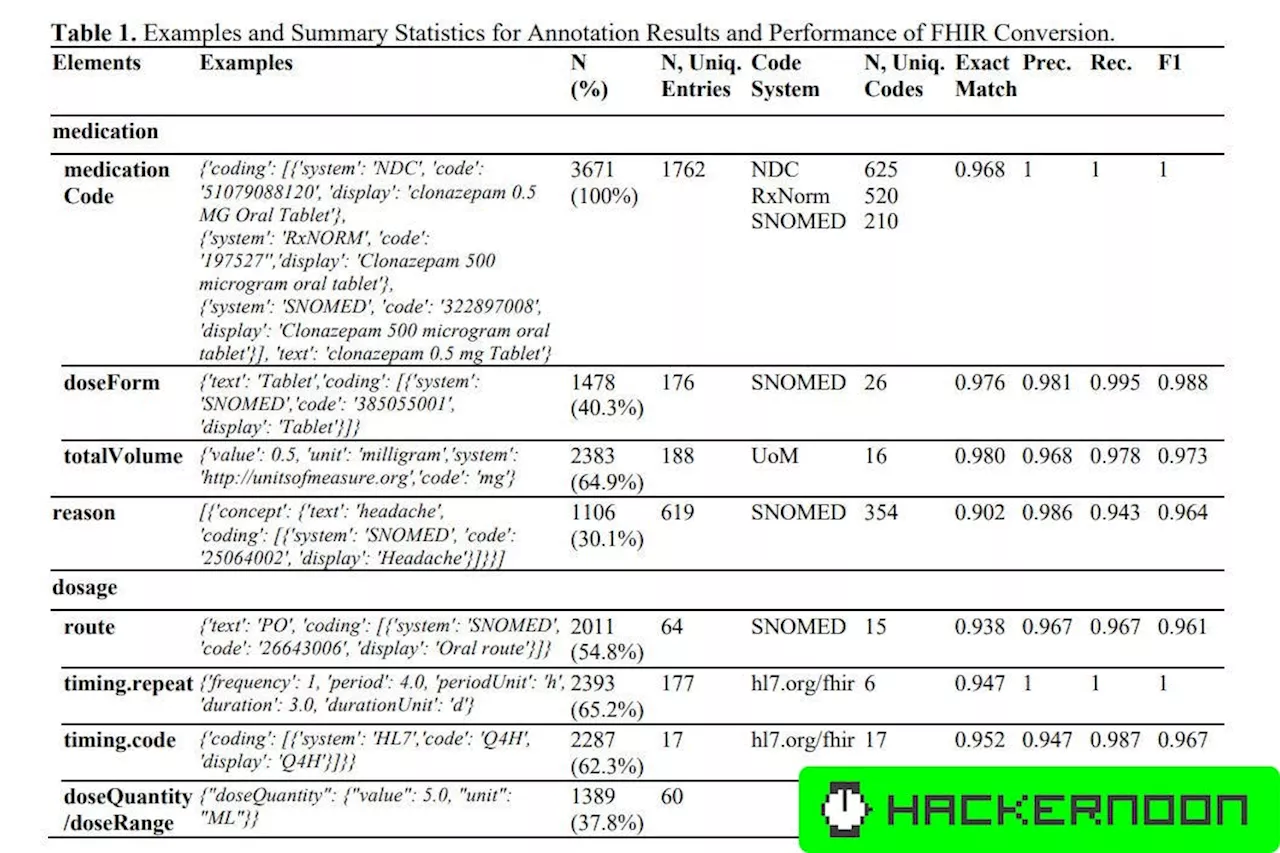 Enhancing Health Data Interoperability with Large Language Models: A FHIR StudyDiscover how LLMs revolutionize healthcare by directly transforming unstructured clinical notes into Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
Enhancing Health Data Interoperability with Large Language Models: A FHIR StudyDiscover how LLMs revolutionize healthcare by directly transforming unstructured clinical notes into Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
Read more »
 Navigation with Large Language Models: LLM Heuristics for Goal-Directed ExplorationIn this paper we study how the “semantic guesswork” produced by language models can be utilized as a guiding heuristic for planning algorithms.
Navigation with Large Language Models: LLM Heuristics for Goal-Directed ExplorationIn this paper we study how the “semantic guesswork” produced by language models can be utilized as a guiding heuristic for planning algorithms.
Read more »
 Navigation with Large Language Models: LFG: Scoring Subgoals by Polling LLMsIn this paper we study how the “semantic guesswork” produced by language models can be utilized as a guiding heuristic for planning algorithms.
Navigation with Large Language Models: LFG: Scoring Subgoals by Polling LLMsIn this paper we study how the “semantic guesswork” produced by language models can be utilized as a guiding heuristic for planning algorithms.
Read more »
 Navigation with Large Language Models: Semantic Guesswork as a Heuristic for Planning: PromptsIn this paper we study how the “semantic guesswork” produced by language models can be utilized as a guiding heuristic for planning algorithms.
Navigation with Large Language Models: Semantic Guesswork as a Heuristic for Planning: PromptsIn this paper we study how the “semantic guesswork” produced by language models can be utilized as a guiding heuristic for planning algorithms.
Read more »