A new study reveals that AI can accurately replicate a person's personality based on a two-hour conversation. Researchers from Google and Stanford University created AI replicas of over 1,000 individuals using interviews and trained a generative AI model to mimic human behavior. The AI replicas demonstrated 85% accuracy in matching human responses to personality tests, social surveys, and logic games.
Researchers from Google and Stanford University have discovered that a two-hour conversation with an artificial intelligence (AI) model is enough to create an accurate replica of someone's personality. In a new study published on arXiv, they created 'simulation agents' — essentially, AI replicas — of 1,052 individuals based on two-hour interviews with each participant. These interviews were used to train a generative AI model designed to mimic human behavior .
To evaluate the accuracy of the AI replicas, each participant completed two rounds of personality tests, social surveys and logic games, and were asked to repeat the process two weeks later. When the AI replicas underwent the same tests, they matched the responses of their human counterparts with 85% accuracy. The researchers propose that AI models that emulate human behavior could be useful across a variety of research scenarios, such as evaluating the effectiveness of public health policies, understanding responses to product launches, or even modeling reactions to major societal events. They believe that general-purpose simulation of human attitudes and behavior could enable a laboratory for researchers to test a broad set of interventions and theories. Simulations could also help pilot new public interventions, develop theories around causal and contextual interactions, and increase our understanding of how institutions and networks influence people
Artificial Intelligence Personality Simulation AI Research Human Behavior Generative AI
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
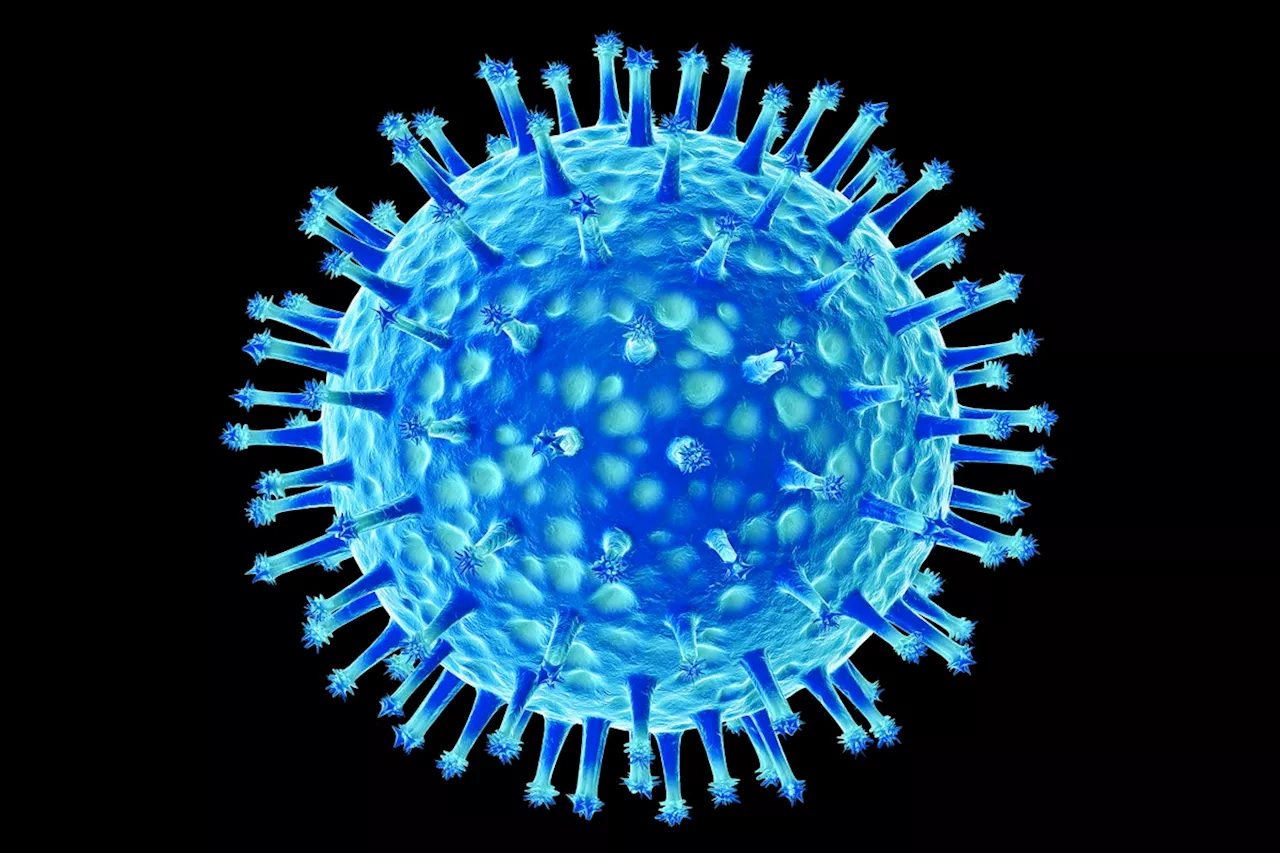 Louisiana Patient's H5N1 Virus Shows Potential for Human-to-Human SpreadThe Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that viral samples from a hospitalized patient in Louisiana with severe H5N1 avian influenza show genetic mutations that could make the virus spread more easily among humans. The mutations were found in the patient's samples but not in those from backyard poultry, suggesting they occurred within the patient. While the CDC maintains the risk to the general public is low, this development highlights the virus's ability to adapt to human airways.
Louisiana Patient's H5N1 Virus Shows Potential for Human-to-Human SpreadThe Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that viral samples from a hospitalized patient in Louisiana with severe H5N1 avian influenza show genetic mutations that could make the virus spread more easily among humans. The mutations were found in the patient's samples but not in those from backyard poultry, suggesting they occurred within the patient. While the CDC maintains the risk to the general public is low, this development highlights the virus's ability to adapt to human airways.
Read more »
 Bird Flu Mutations Raise Concerns, But No Human-to-Human Spread ReportedA concerning development in the ongoing bird flu outbreak: A patient in Louisiana, with underlying health conditions, tested positive for the virus with mutations that could potentially make it more transmissible between humans. However, the CDC reports that there is no evidence of the virus spreading from this patient to others.
Bird Flu Mutations Raise Concerns, But No Human-to-Human Spread ReportedA concerning development in the ongoing bird flu outbreak: A patient in Louisiana, with underlying health conditions, tested positive for the virus with mutations that could potentially make it more transmissible between humans. However, the CDC reports that there is no evidence of the virus spreading from this patient to others.
Read more »
 Postdoc Position at Human Technopole: Modeling Human Neurodiversity with OrganoidsThe Neurogenomics Research Centre at Human Technopole is seeking a highly motivated Postdoctoral Researcher to work on organoid-based projects. The position focuses on modeling human neurodiversity and overcoming categorical distinctions in neuropsychiatric diagnosis using high resolution molecular and clinical phenotyping. Candidates should be passionate about understanding human neuropsychiatric conditions and have experience with single cell technologies, stem cell-based approaches, and bioengineered models.
Postdoc Position at Human Technopole: Modeling Human Neurodiversity with OrganoidsThe Neurogenomics Research Centre at Human Technopole is seeking a highly motivated Postdoctoral Researcher to work on organoid-based projects. The position focuses on modeling human neurodiversity and overcoming categorical distinctions in neuropsychiatric diagnosis using high resolution molecular and clinical phenotyping. Candidates should be passionate about understanding human neuropsychiatric conditions and have experience with single cell technologies, stem cell-based approaches, and bioengineered models.
Read more »
 North Royalton man flips car in Middleburg Heights while trying to mimic Kurt Russell movie stuntPolice arrested an intoxicated North Royalton man Nov. 28 after he flipped a Kia Sportage on Lucerne Drive at Normandie Boulevard.
North Royalton man flips car in Middleburg Heights while trying to mimic Kurt Russell movie stuntPolice arrested an intoxicated North Royalton man Nov. 28 after he flipped a Kia Sportage on Lucerne Drive at Normandie Boulevard.
Read more »
 How plant-based meat alternatives mimic the real thingMeat has a distinct taste, texture, and aroma.
How plant-based meat alternatives mimic the real thingMeat has a distinct taste, texture, and aroma.
Read more »
 AI-Designed Nanocages Mimic Viruses for Enhanced Gene TherapyResearchers develop innovative nanocages using AI to mimic the complex structures of viruses, enabling the delivery of larger amounts of genetic material for gene therapy.
AI-Designed Nanocages Mimic Viruses for Enhanced Gene TherapyResearchers develop innovative nanocages using AI to mimic the complex structures of viruses, enabling the delivery of larger amounts of genetic material for gene therapy.
Read more »
