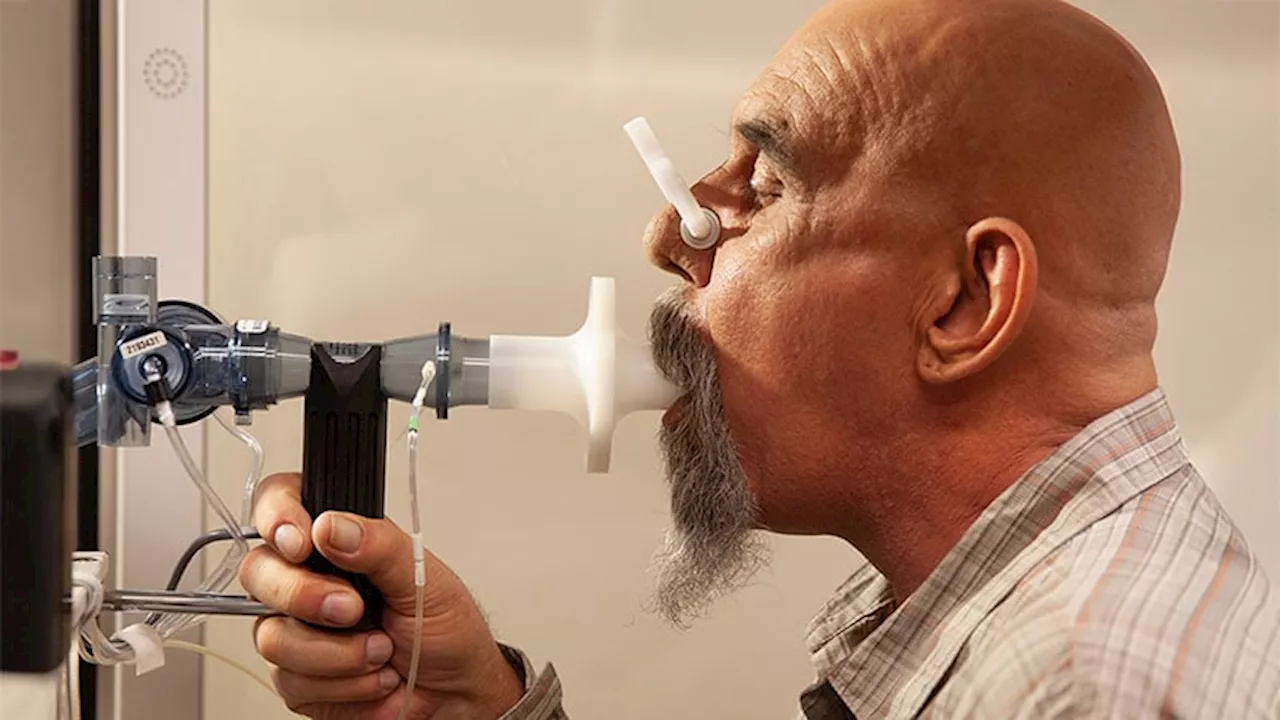
A study found that changes in KL-6 levels after 12 months of treatment with MMF or CYC are associated with the development of progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).
Changes in Krebs von den Lungen 6 (KL-6) levels after 12 months of treatment with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or cyclophosphamide (CYC) are associated with the development of progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) in patients with systemic sclerosis–associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) in the following year.
Despite available treatments, about 25% of patients with SSc-ILD develop PPF, highlighting the need for reliable early treatment response indicators, such as blood biomarkers, which may help predict the risk for PPF. Researchers conducted post hoc analyses of a randomized control trial that compared treatment responses to MMF with those to CYC in patients with SSc-ILD. Patients received either oral CYC for 12 months followed by placebo for 12 months or MMF for 24 months. A total of 92 patients with complete biomarker measurements at baseline and 12 months were included in the analysis (mean age, 52.2 years; 73.9% women; 68.5% White). The analysis included measurement of multiple blood biomarker levels, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6, chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4), chemokine ligand 18, and KL-6. Changes in these levels were evaluated from baseline to 12 months. The primary outcome was the development of PPF between 12 and 24 months, defined by meeting at least two of these following conditions: Worsening respiratory symptoms, a decline in forced vital capacity ≥ 5% and/or a decline in diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide ≥ 10%, or radiological disease progression.Among 92 patients, 19 developed PPF between 12 and 24 months, with 10 patients in the MMF arm and 9 patients in the CYC arm. KL-6 levels increased from baseline to 12 months in patients who developed PPF and decreased in those who did not (mean change, 365.68 vs −207.45 u/mL;A 0.10-unit increase in KL-6 levels was associated with a 40% increase in the odds of developing PPF in an adjusted analysis (In the MMF group, levels of KL-6, CRP, and CXCL4 differed significantly between patients who developed PPF and those who did not ('Reliable response biomarkers detectable early in the course of SSc-ILD treatment could minimize exposure to toxic therapies that are not conferring benefit and maximize exposure to alternative therapies that do confer benefit,' the authors wrote.The study was led by Elizabeth R. Volkmann, MD, MS, University of California, Los Angeles David Geffen School of Medicine. It wasThe study population consisted of patients who were treatment-naive to MMF and CYC and had a relatively early disease course, potentially limiting generalizability to patients at later disease stages or with different treatment histories. Additionally, biomarker measurements were conducted at 12 months, when treatment response may be detectable through currently available methods, rather than at earlier timepoints.The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Department of Defense. MMF was supplied by Hoffmann-La Roche. Some authors reported having financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies, including Hoffmann-La Roche. This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.All material on this website is protected by copyright, Copyright © 1994-2025 by WebMD LLC. This website also contains material copyrighted by 3rd parties
SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE PULMONARY FIBROSIS BLOOD BIOMARKERS MYCOPHENOLATE MOFETIL CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New travel alerts: U.S. issues 2 new tourist warnings, including a ‘level 3’ reconsider travel levelThe U.S. State Department has updated two travel alerts for Central American countries.
New travel alerts: U.S. issues 2 new tourist warnings, including a ‘level 3’ reconsider travel levelThe U.S. State Department has updated two travel alerts for Central American countries.
Read more »
 Secret Level Episode 14 Explores Honor of Kings in a 'Hidden Level' AdventureSecret Level episode 14 dives into the world of Honor of Kings, focusing on the character Yi Xing's quest to challenge the city's tyrannical machine, Tiangong.
Secret Level Episode 14 Explores Honor of Kings in a 'Hidden Level' AdventureSecret Level episode 14 dives into the world of Honor of Kings, focusing on the character Yi Xing's quest to challenge the city's tyrannical machine, Tiangong.
Read more »
 New Study Shows Changes in Coffee Drinkers' Gut Microbiome—What It Means for YouWhat you need to know.
New Study Shows Changes in Coffee Drinkers' Gut Microbiome—What It Means for YouWhat you need to know.
Read more »
 Staying sharp: Study explores how brain changes may affect financial skillsA new article sheds light on how age-related changes may affect the way we handle finances -- and how we can stay sharp as we age.
Staying sharp: Study explores how brain changes may affect financial skillsA new article sheds light on how age-related changes may affect the way we handle finances -- and how we can stay sharp as we age.
Read more »
 MLB study: Max velocity, ‘stuff’ likely causing pitching injuries; rule changes should be consideredMichael is a digital sports strategist for Bay Area News Group. The Denver-area native went to Arizona State's Cronkite School of Journalism and worked several years in Phoenix before coming to Northern California, mostly for the fish tacos.
MLB study: Max velocity, ‘stuff’ likely causing pitching injuries; rule changes should be consideredMichael is a digital sports strategist for Bay Area News Group. The Denver-area native went to Arizona State's Cronkite School of Journalism and worked several years in Phoenix before coming to Northern California, mostly for the fish tacos.
Read more »
 MLB study: Velocity, max efforts likely causing pitching injuries; rule changes should be consideredThe study also shows the trend extends to high school and youth baseball because of the incentive to get noticed by professional scouts.
MLB study: Velocity, max efforts likely causing pitching injuries; rule changes should be consideredThe study also shows the trend extends to high school and youth baseball because of the incentive to get noticed by professional scouts.
Read more »