Researchers have harnessed the power of baker's yeast to create a cost-effective and highly efficient approach for unraveling how plants synthesize medicinal compounds, and used the new method to identify key enzymes in a kratom tree.
Cornell researchers have harnessed the power of baker's yeast to create a cost-effective and highly efficient approach for unraveling how plants synthesize medicinal compounds, and used the new method to identify key enzymes in a kratom tree.
Once gene candidates are predicted using plant transcriptomics, baker's yeast -- the same kind used for brewing beer and baking bread -- is engineered with the genes inside to see which ones produce proteins that interact with each other. As a result, the number of genes that must then be biochemically screened is significantly reduced.
The yeast-based method led to the identification of six kratom enzymes from 20 candidates predicted by genetic screening to produce mitragynine or other targeted chemicals. Subsequent biochemical testing showed that none of the 14 discarded candidates were functional enzymes, while four of the six identified by the yeast-based method were functional. Li said the method's accuracy opens the door for a more efficient discovery process and continued research on the kratom tree.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Yeast speeds discovery of medicinal compounds in plantsCornell researchers have harnessed the power of baker's yeast to create a cost-effective and highly efficient approach for unraveling how plants synthesize medicinal compounds, and used the new method to identify key enzymes in a kratom tree.
Yeast speeds discovery of medicinal compounds in plantsCornell researchers have harnessed the power of baker's yeast to create a cost-effective and highly efficient approach for unraveling how plants synthesize medicinal compounds, and used the new method to identify key enzymes in a kratom tree.
Read more »
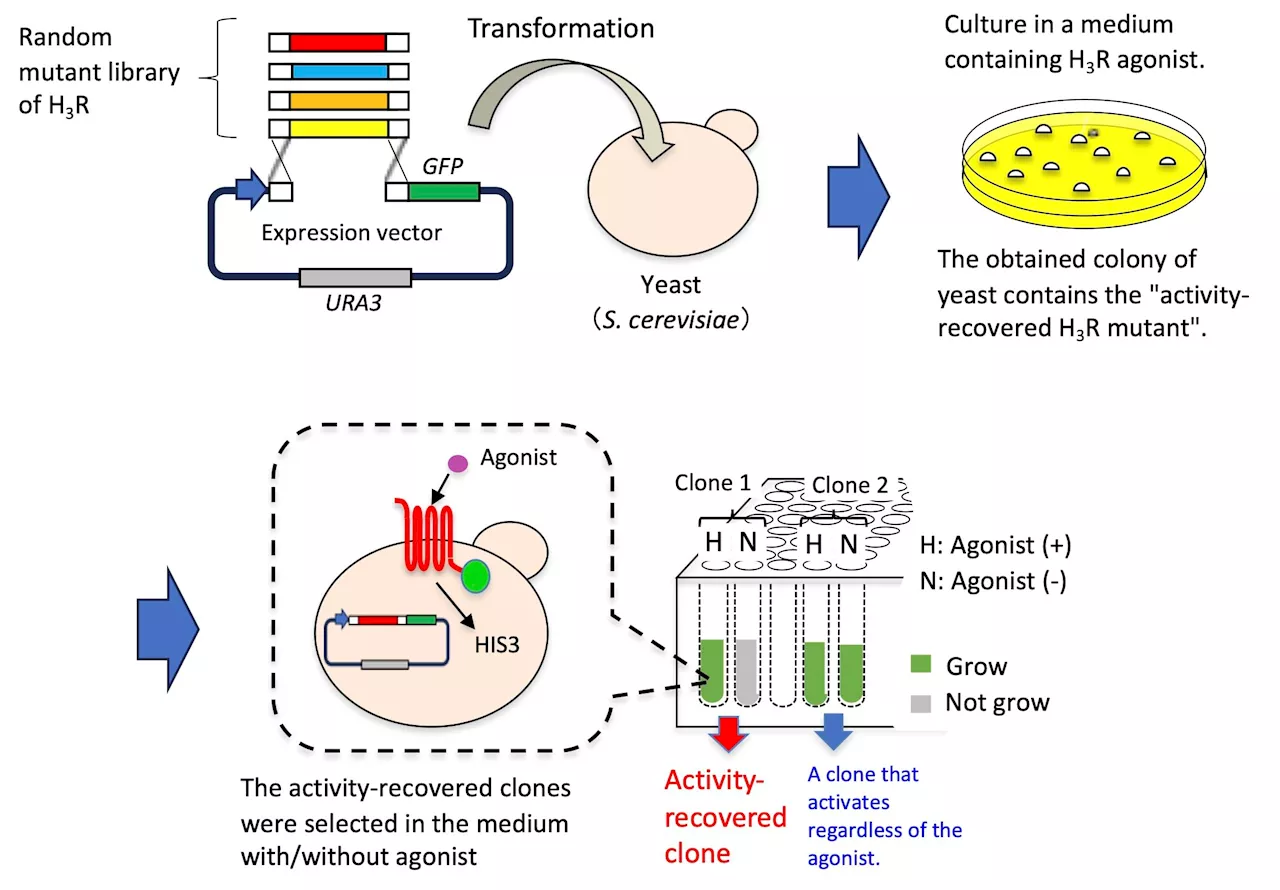 Restoring the function of a human cell surface protein in yeast cellsG protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest and most diverse group of cell surface proteins in humans. These receptors, which can be seen as 'traffic directors,' transmit signals from the outside to the inside of cells and are involved in many physiological processes.
Restoring the function of a human cell surface protein in yeast cellsG protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest and most diverse group of cell surface proteins in humans. These receptors, which can be seen as 'traffic directors,' transmit signals from the outside to the inside of cells and are involved in many physiological processes.
Read more »
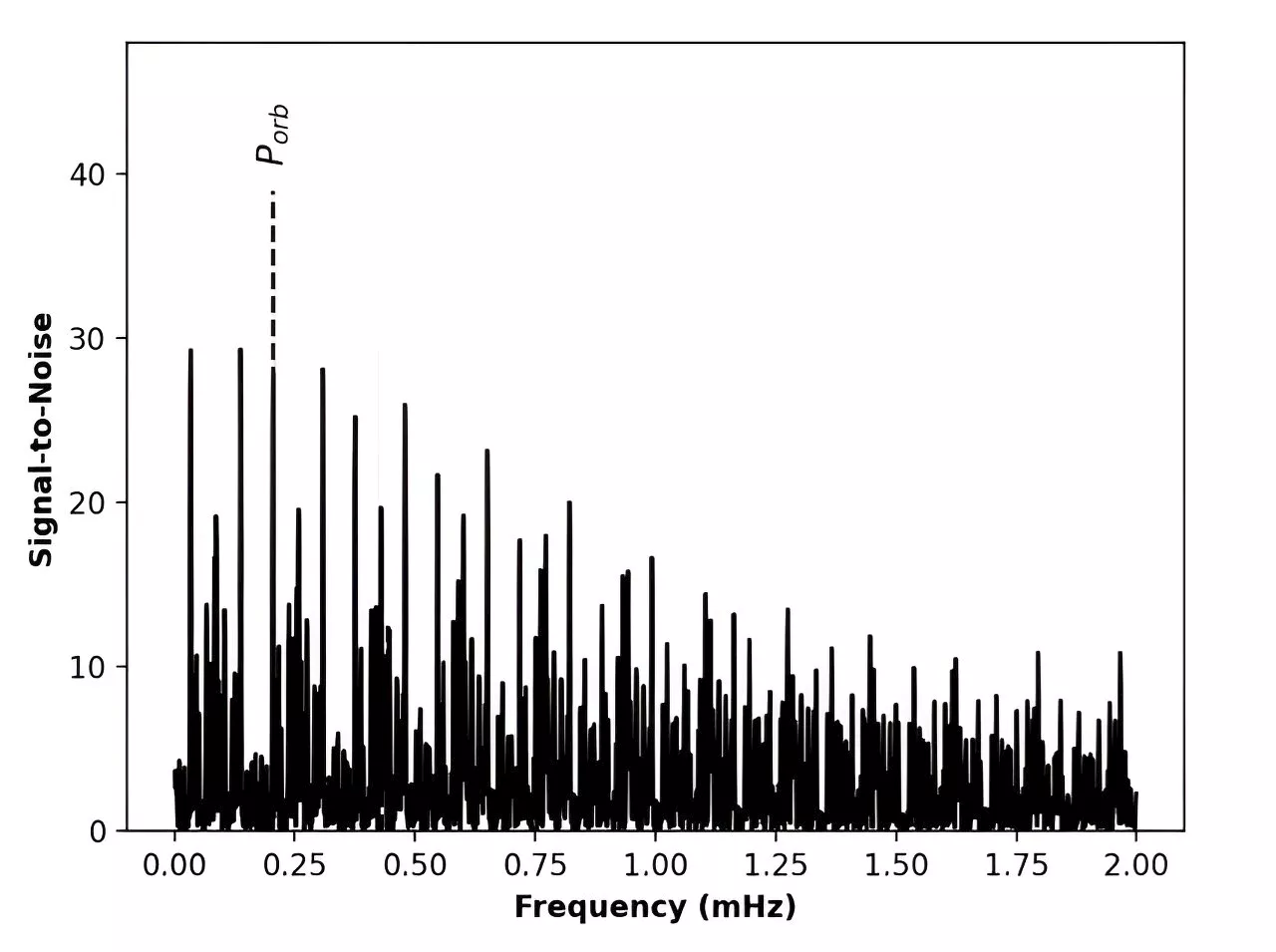 Cataclysmic variable Swift J0503.7-2819 investigated by researchersUsing various spacecraft and ground-based observatories, an international team of astronomers has performed a multi-wavelength study of a cataclysmic variable system known as Swift J0503.7-2819. Results of the study, published October 11 on the pre-print server arXiv, deliver important insights into the nature of this system.
Cataclysmic variable Swift J0503.7-2819 investigated by researchersUsing various spacecraft and ground-based observatories, an international team of astronomers has performed a multi-wavelength study of a cataclysmic variable system known as Swift J0503.7-2819. Results of the study, published October 11 on the pre-print server arXiv, deliver important insights into the nature of this system.
Read more »
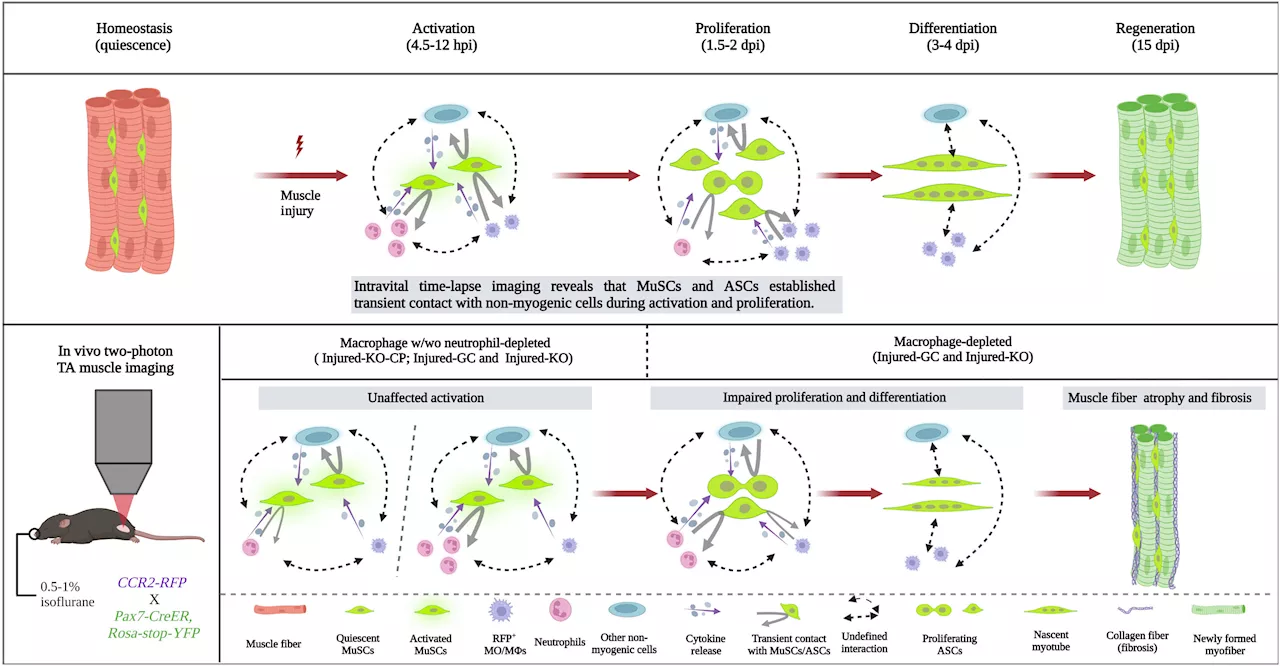 Researchers develop an innovative microscope platform to unveil the intricacies of skeletal muscle regenerationResearchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have created a cutting-edge platform consisting of a dual-laser nonlinear optical microscope to investigate the dynamics of muscle satellite cells (MuSCs) during the process of muscle regeneration.
Researchers develop an innovative microscope platform to unveil the intricacies of skeletal muscle regenerationResearchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have created a cutting-edge platform consisting of a dual-laser nonlinear optical microscope to investigate the dynamics of muscle satellite cells (MuSCs) during the process of muscle regeneration.
Read more »
 Researchers Create Cleaner Alternative To Using Cobalt In BatteriesI am a reporter with experience covering trending tech and business topics. Before joining Forbes as a breaking news reporter, I covered tech and business news at Insider where I started as a fellow on the Careers team. I graduated from UNC Chapel Hill in 2021 with a double degree in journalism and contemporary European studies.
Researchers Create Cleaner Alternative To Using Cobalt In BatteriesI am a reporter with experience covering trending tech and business topics. Before joining Forbes as a breaking news reporter, I covered tech and business news at Insider where I started as a fellow on the Careers team. I graduated from UNC Chapel Hill in 2021 with a double degree in journalism and contemporary European studies.
Read more »
 Oxford researchers’ photonic-electronic AI chip puts apps on steroidsInteresting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
Oxford researchers’ photonic-electronic AI chip puts apps on steroidsInteresting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
Read more »
