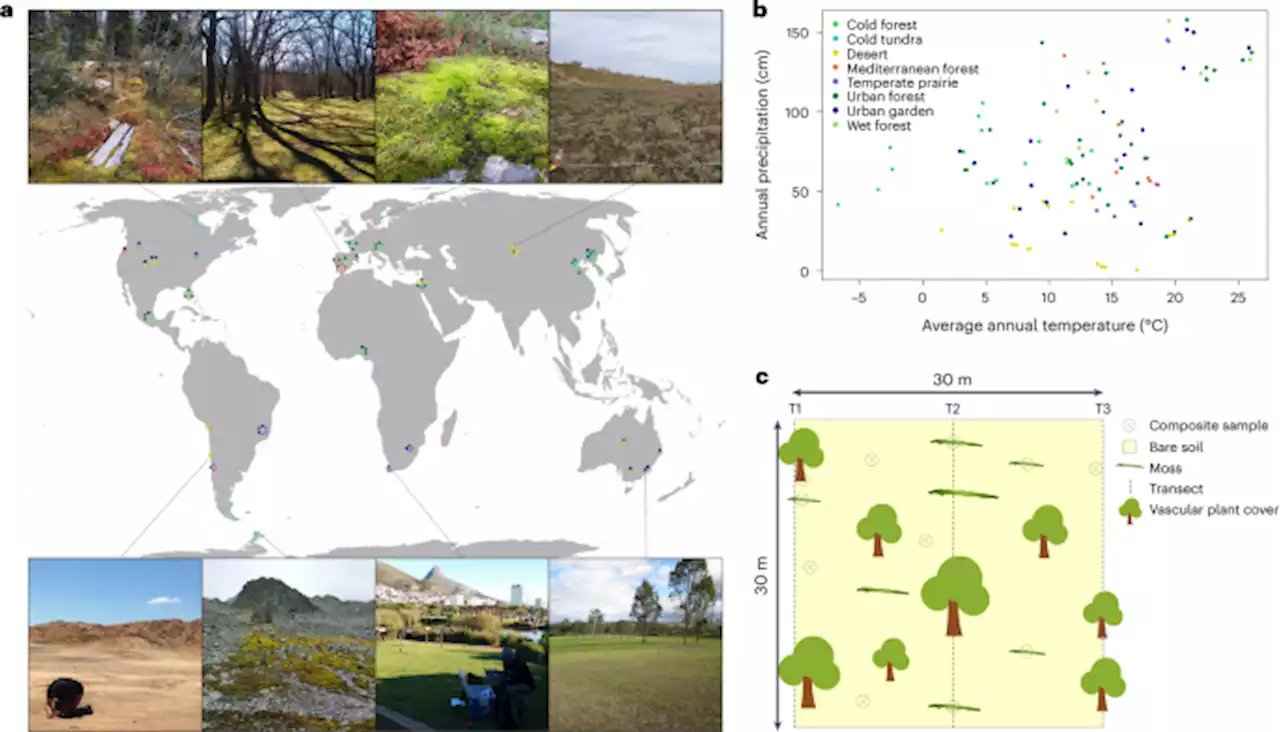
Why mosses are vital for the health of our soil and Earth NatureGeosci
We thank D. Wardle for his insightful comments on an earlier draft and A. Gallardo for his assistance during sample collection. We are grateful to V. Hugonnot, J. G. Segarra-Moragues, F. Müller, S. Stix, I. Charissou, D. Yann, M.-F. Indorf and BRYONET for assistance identifying moss species. We thank S. C. Angorrilla for help with laboratory analyses. The study work associated with this paper was funded by a Large Research Grant from the British Ecological Society . D.J.E.
Laboratório de Sistemática Vegetal, Departamento de Botânica, Instituto de Ciências Biológicas, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Pampulha, Belo Horizonte, BrazilDepartamento de Biología, Instituto Universitario de Ciencias del Mar, Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, SpainInstituto de Geología, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ciudad Universitaria, México D.F.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
You can get paid to take nature walks and learn 'water-wise' waysThe San Antonio Water System manages a precious resource: water. To encourage conservation, it will pay you to take nature walks and learn good habits.
Read more »
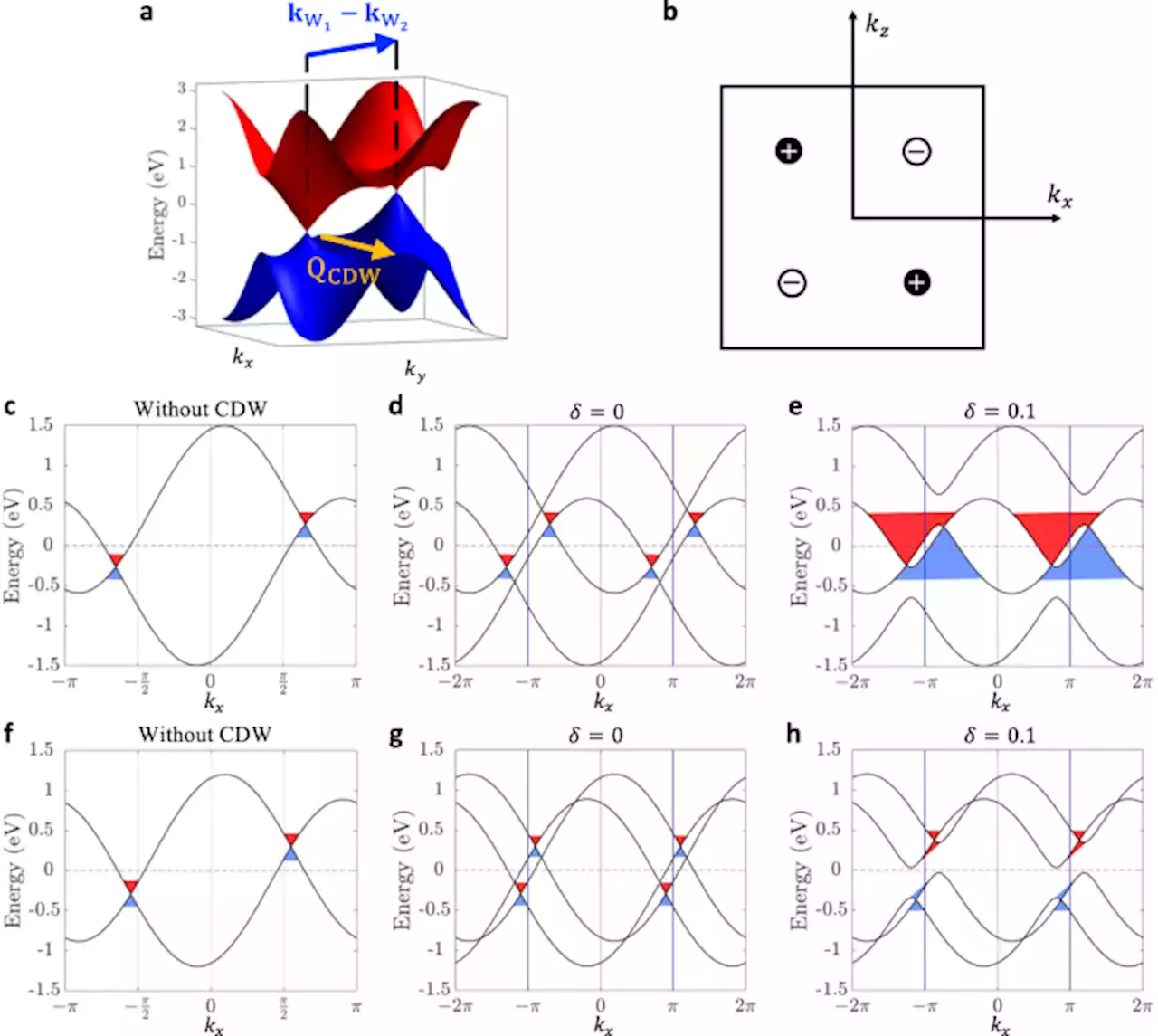 Causal structure of interacting Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems - Nature CommunicationsCausality, the relationship between cause and effect, is a central concept in Einstein’s theory of relativity. Here, authors show that a causality analogue in energy-momentum space plays an important role in describing quasiparticle interactions in quantum matter.
Causal structure of interacting Weyl fermions in condensed matter systems - Nature CommunicationsCausality, the relationship between cause and effect, is a central concept in Einstein’s theory of relativity. Here, authors show that a causality analogue in energy-momentum space plays an important role in describing quasiparticle interactions in quantum matter.
Read more »
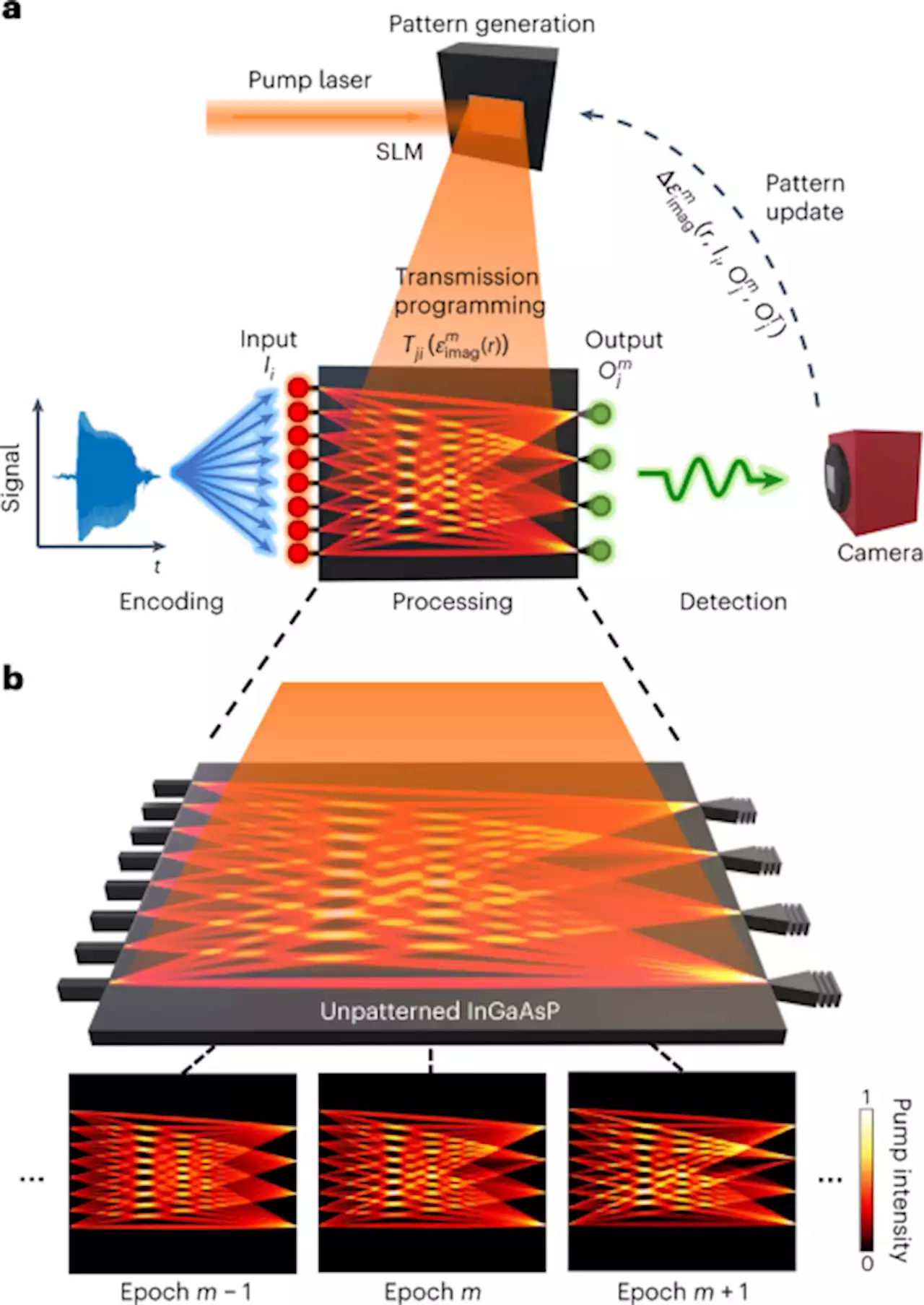 Lithography-free reconfigurable integrated photonic processor - Nature PhotonicsSpatial light modulator-based lithography-free programmable light transmission through optical gain medium is demonstrated for optical switching and a rudimentary photonic neural network.
Lithography-free reconfigurable integrated photonic processor - Nature PhotonicsSpatial light modulator-based lithography-free programmable light transmission through optical gain medium is demonstrated for optical switching and a rudimentary photonic neural network.
Read more »
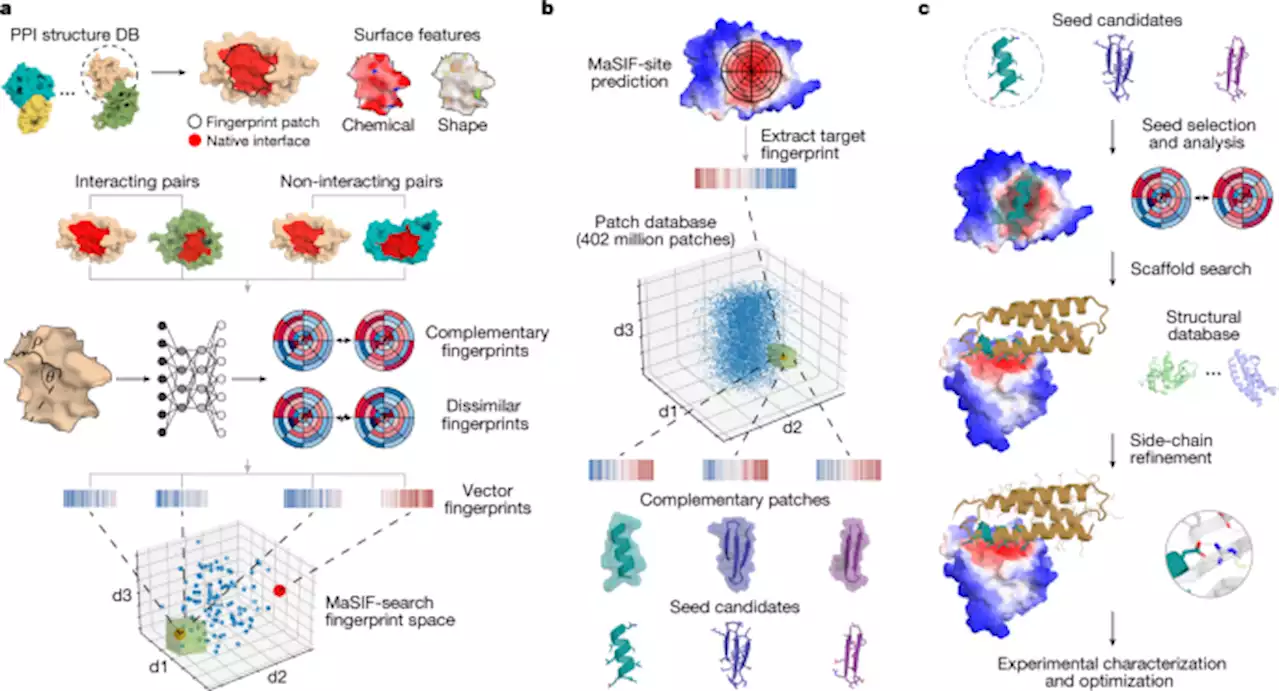 De novo design of protein interactions with learned surface fingerprints - NatureA surface-centric approach captures the physical and chemical determinants of molecular recognition, enabling the de novo design of protein interactions and of artificial proteins with function.
De novo design of protein interactions with learned surface fingerprints - NatureA surface-centric approach captures the physical and chemical determinants of molecular recognition, enabling the de novo design of protein interactions and of artificial proteins with function.
Read more »
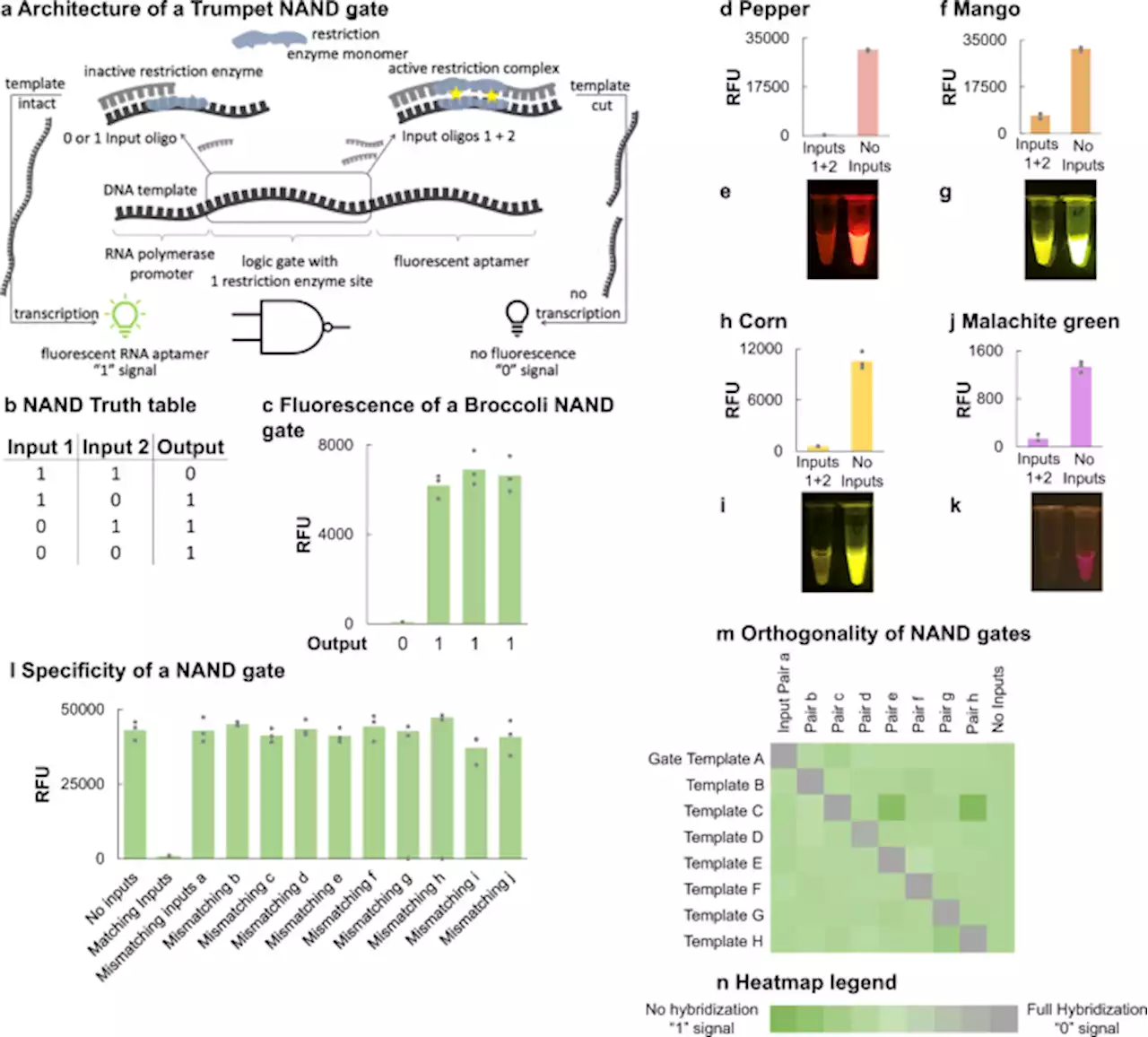 Trumpet is an operating system for simple and robust cell-free biocomputing - Nature CommunicationsBiological computation is becoming a viable and fast-growing alternative to traditional electronic computing. Here the authors present Trumpet, which uses DNA and enzymes to build logic gate circuits with amplified fluorescent readout.
Trumpet is an operating system for simple and robust cell-free biocomputing - Nature CommunicationsBiological computation is becoming a viable and fast-growing alternative to traditional electronic computing. Here the authors present Trumpet, which uses DNA and enzymes to build logic gate circuits with amplified fluorescent readout.
Read more »
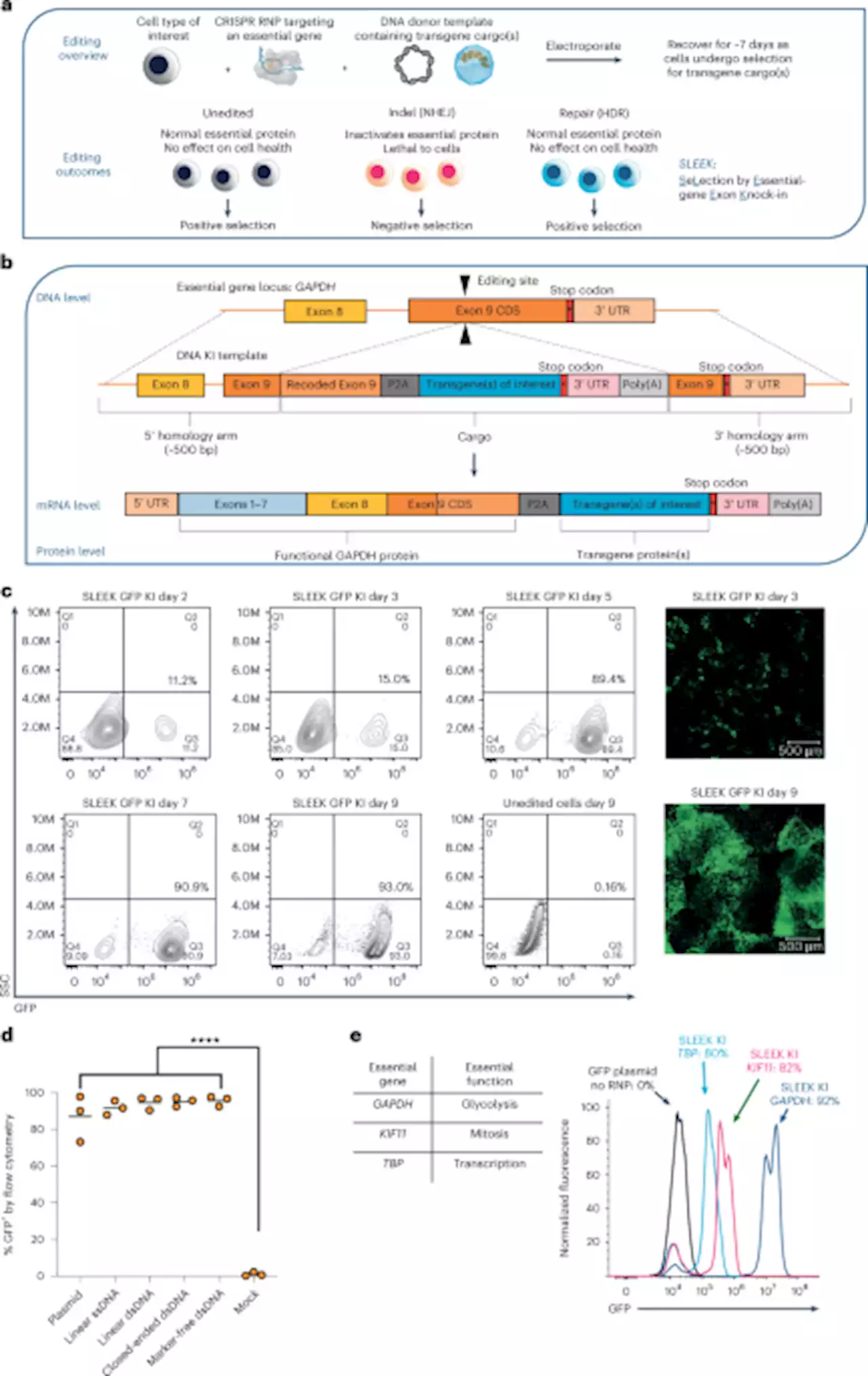 A highly efficient transgene knock-in technology in clinically relevant cell types - Nature BiotechnologyTransgene knock-ins into housekeeping genes lead to high efficiency of cell selection.
A highly efficient transgene knock-in technology in clinically relevant cell types - Nature BiotechnologyTransgene knock-ins into housekeeping genes lead to high efficiency of cell selection.
Read more »