In the largest study to date exploring the relationship between severe psoriasis and coronary microvascular dysfunction, researchers have found further evidence that patients with severe psoriasis are at higher cardiovascular risk.
Reviewed by Lily Ramsey, LLMSep 20 2023 The results are published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier.
Lead investigator Stefano Piaserico, MD, PhD, Dermatology Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Padova, explained, "Previous studies have shown that patients with severe psoriasis have an increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. However, there has been limited research on the specific mechanisms underlying this increased risk, particularly regarding coronary microvascular dysfunction.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study sheds light on the neural underpinning of subjective odor perceptionsDifferent people can have varying perceptions of the same scents and odors, for instance perceiving the same perfume as 'fruity' or 'musky.' Studies have suggested that the ways in which the same odors are mapped in the brain of different individuals are highly flexible, particularly compared to visual stimuli, which are typically represented similarly.
Study sheds light on the neural underpinning of subjective odor perceptionsDifferent people can have varying perceptions of the same scents and odors, for instance perceiving the same perfume as 'fruity' or 'musky.' Studies have suggested that the ways in which the same odors are mapped in the brain of different individuals are highly flexible, particularly compared to visual stimuli, which are typically represented similarly.
Read more »
 New study sheds light on vitamin D's role in cardiovascular healthResearchers conducted a prospective population-based analysis to understand whether vitamin D levels were associated with cardiovascular disease events and mortality, and overall mortality.
New study sheds light on vitamin D's role in cardiovascular healthResearchers conducted a prospective population-based analysis to understand whether vitamin D levels were associated with cardiovascular disease events and mortality, and overall mortality.
Read more »
 Nitrous oxide helps relieve kids' pain and distress in emergency rooms, study showsInhaled nitrous oxide, better known as laughing gas, should be used more widely to manage children's pain and distress when they undergo emergency treatment in hospitals, says a University of Alberta expert.
Nitrous oxide helps relieve kids' pain and distress in emergency rooms, study showsInhaled nitrous oxide, better known as laughing gas, should be used more widely to manage children's pain and distress when they undergo emergency treatment in hospitals, says a University of Alberta expert.
Read more »
 Alcohol and other drug use more prevalent in non-car injuries, shows studyA higher percentage of people admitted to hospital for falls, self-harm and violence have used alcohol and other drugs than drivers admitted after car crashes, new research has found.
Alcohol and other drug use more prevalent in non-car injuries, shows studyA higher percentage of people admitted to hospital for falls, self-harm and violence have used alcohol and other drugs than drivers admitted after car crashes, new research has found.
Read more »
 Animal study reveals bittersweet brain chemical clue that may help women stop binge drinkingDr. Leigh Walker led a study that showed that when a certain chemical is removed from the brain, males drink more and females drink less. But when the alcoholic drinks are sweetened, female consumption goes up.
Animal study reveals bittersweet brain chemical clue that may help women stop binge drinkingDr. Leigh Walker led a study that showed that when a certain chemical is removed from the brain, males drink more and females drink less. But when the alcoholic drinks are sweetened, female consumption goes up.
Read more »
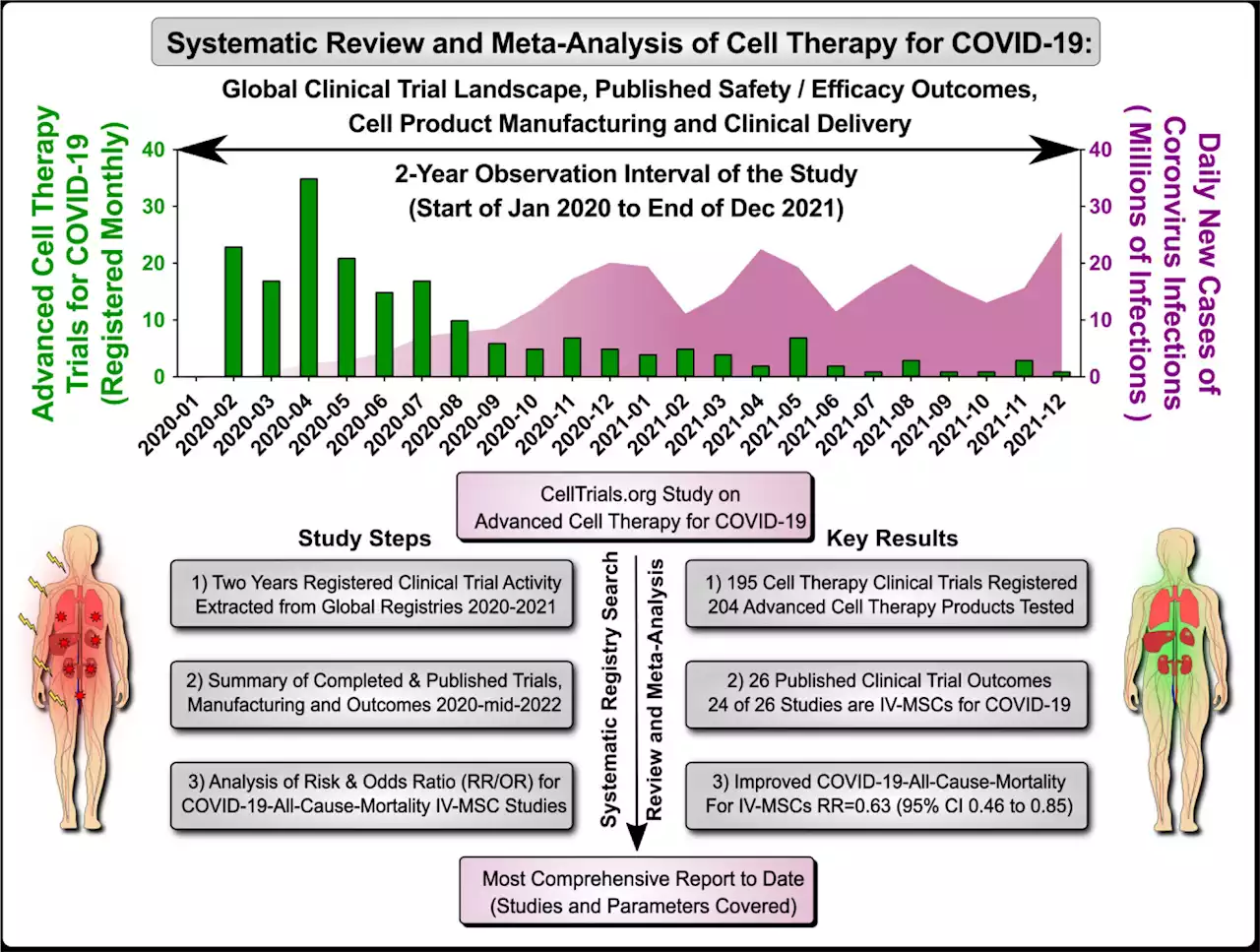 Cell therapy can reduce risk of death from COVID-19 by 60%, study findsThe use of cell therapy to treat COVID-19 patients can reduce the risk of death from the disease by 60%, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, in partnership with colleagues in Germany and the United States.
Cell therapy can reduce risk of death from COVID-19 by 60%, study findsThe use of cell therapy to treat COVID-19 patients can reduce the risk of death from the disease by 60%, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, in partnership with colleagues in Germany and the United States.
Read more »
