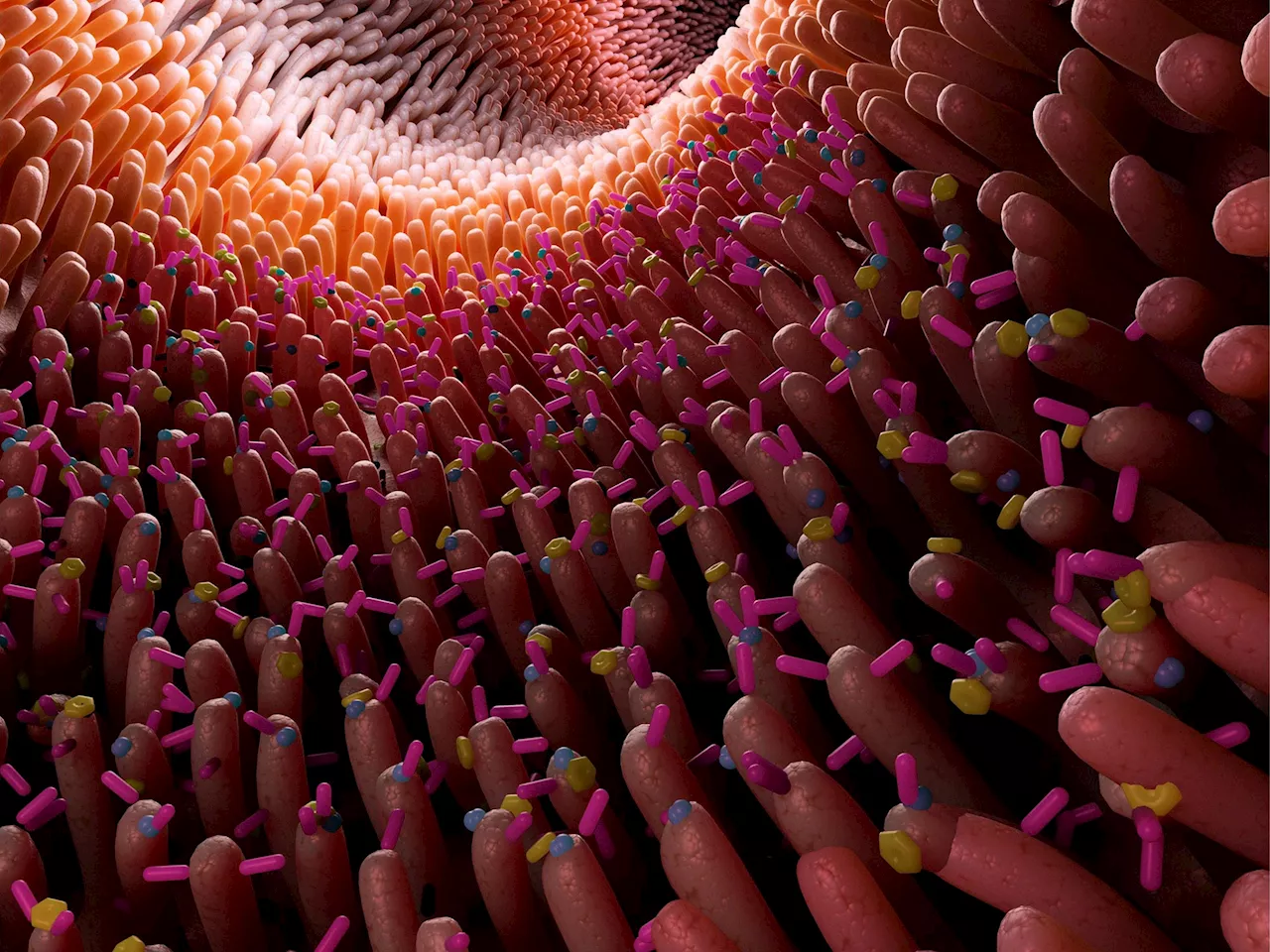
Researchers have discovered that specific gut bacteria can lower cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk. The study identified Oscillibacter bacteria that metabolize cholesterol, potentially paving the way for microbiome-based interventions to decrease cholesterol levels in humans.
Researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital discovered that specific gut bacteria can lower cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk, a finding from the Framingham Heart Study involving over 1,400 participants. Their study, published in Cell, identified Oscillibacter bacteria that metabolize cholesterol, potentially paving the way for microbiome-based interventions to decrease cholesterol levels in humans.
Research identifies multiple types of bacteria that metabolize cholesterol in individuals with reduced cholesterol levels. Alterations in the gut microbiome are associated with a range of diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, and inflammatory bowel disease. Members of Ramnik Xavier’s lab, Broad’s Metabolomics Platform, and collaborators analyzed metabolites and microbial genomes from more than 1,400 participants in the Framingham Heart Study, a decades-long project focused on risk factors for cardiovascular disease. They found that Oscillibacter bacteria in the gut can take up and metabolize cholesterol from their surroundings, and that people carrying higher levels of the microbe in their gut had lower levels of cholesterol. They also identified the mechanism the bacteria likely use to break down cholesterol. The results suggest that interventions that manipulate the microbiome in specific ways could one day help decrease cholesterol in people
Gut Bacteria Cholesterol Heart Disease Microbiome Interventions Framingham Heart Study
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Infants’ Gut Bacteria Create Serotonin To Build A Robust Immune SystemAnuradha Varanasi is a freelance science writer. She writes on the intersection of health/medicine, racial disparities, and climate change. She earned an MA in Science Journalism from Columbia University in New York City.
Infants’ Gut Bacteria Create Serotonin To Build A Robust Immune SystemAnuradha Varanasi is a freelance science writer. She writes on the intersection of health/medicine, racial disparities, and climate change. She earned an MA in Science Journalism from Columbia University in New York City.
Read more »
 Gut bacteria important for overcoming milk allergyResearchers have discovered a link between gut bacteria and the success of milk-allergy oral immunotherapy. The study found that Bifidobacterium -- a genus of beneficial bacteria in the gut -- was associated with a higher chance of successful treatment.
Gut bacteria important for overcoming milk allergyResearchers have discovered a link between gut bacteria and the success of milk-allergy oral immunotherapy. The study found that Bifidobacterium -- a genus of beneficial bacteria in the gut -- was associated with a higher chance of successful treatment.
Read more »
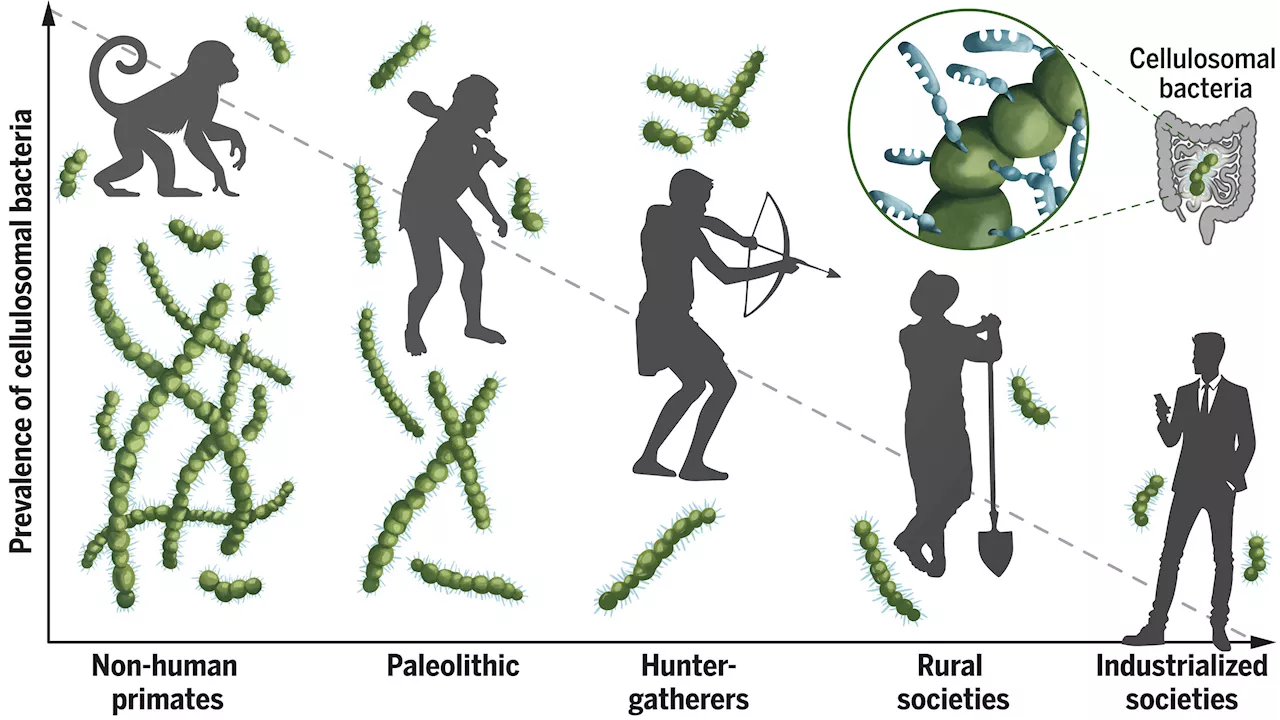 Research team identifies three bacteria species in the human gut that can break down celluloseAn international team of biotechnologists and evolutionary specialists has discovered three types of bacteria in the human gut that help to break down cellulose. In their project, reported in the journal Science, the group studied the genomes of bacteria found in human and ruminates.
Research team identifies three bacteria species in the human gut that can break down celluloseAn international team of biotechnologists and evolutionary specialists has discovered three types of bacteria in the human gut that help to break down cellulose. In their project, reported in the journal Science, the group studied the genomes of bacteria found in human and ruminates.
Read more »
 Gut bacteria make neurotransmitters to shape the newborn immune systemInvestigators discovered that unique bacteria colonize the gut shortly after birth and make the neurotransmitter serotonin to educate gut immune cells. This prevents allergic reactions to food and the bacteria themselves during early development.
Gut bacteria make neurotransmitters to shape the newborn immune systemInvestigators discovered that unique bacteria colonize the gut shortly after birth and make the neurotransmitter serotonin to educate gut immune cells. This prevents allergic reactions to food and the bacteria themselves during early development.
Read more »
 Tryptophan in diet, gut bacteria protect against E. coli infectionGut bacteria and a diet rich in the amino acid tryptophan can play a protective role against pathogenic E. coli, which can cause severe stomach upset, cramps, fever, intestinal bleeding and renal failure.
Tryptophan in diet, gut bacteria protect against E. coli infectionGut bacteria and a diet rich in the amino acid tryptophan can play a protective role against pathogenic E. coli, which can cause severe stomach upset, cramps, fever, intestinal bleeding and renal failure.
Read more »
 Cholesterol-gobbling gut bacteria could protect against heart diseaseSneha Khedkar is a biologist-turned-freelance-science-journalist from India. She holds a master's degree in biochemistry and a bachelor's degree in microbiology and biochemistry. After her master's, she worked as a research fellow for four years, studying stem cell biology.
Cholesterol-gobbling gut bacteria could protect against heart diseaseSneha Khedkar is a biologist-turned-freelance-science-journalist from India. She holds a master's degree in biochemistry and a bachelor's degree in microbiology and biochemistry. After her master's, she worked as a research fellow for four years, studying stem cell biology.
Read more »