Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers have developed the highest quality reference genome for the Arabica coffee species, revealing its evolution over 600,000 years and its natural development without human intervention. This new genome sheds light on Arabica’s susceptibility to climate change and pests due to its low genetic diversity, and offers potential for breeding new varieties that are more resistant to environmental stresses.
Coffee giants like Starbucks and Tim Hortons exclusively use beans from Arabica plants to brew the millions of cups of coffee they serve everyday, yet, in part due to a low genetic diversity stemming from a history of inbreeding and small population size, Arabica is susceptible to many pests and diseases and can only be cultivated in a few places in the world where pathogen threats are lower and climate conditions are more favorable.
The models show three population bottlenecks during Arabica’s history, with the oldest happening some 29,000 generations — or 610,000 years — ago. This suggests Arabica formed sometime before that, anywhere from 610,000 to 1 million years ago, researchers say. That would align with evidence that coffee cultivation may have started principally in Yemen, around the 15th century. Indian monk Baba Budan is believed to have smuggled the fabled “seven seeds” out of Yemen around 1600, establishing Indian Arabica cultivars and setting the stage for coffee’s global reach today.
During this same time, around 30,000 years ago, the wild varieties and the varieties that would eventually become cultivated by humans split from each other. The Timor variety formed in Southeast Asia as a spontaneous hybrid between Arabica and one of its parents,. Also known as Robusta and used primarily for instant coffee, this species is more resistant to disease than Arabica“Thus, when Robusta hybridized itself back into Arabica on Timor, it brought some of its pathogen defense genes along with it,” says Albert, who also co-led
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Millennia-old Egyptian skull shows signs of surgical treatment for cancerA team of European researchers found cut marks near lesions on the skull of an Egyptian man dating back thousands of years. The marks suggest a form of cancer treatment.
Millennia-old Egyptian skull shows signs of surgical treatment for cancerA team of European researchers found cut marks near lesions on the skull of an Egyptian man dating back thousands of years. The marks suggest a form of cancer treatment.
Read more »
 15-Year-Old Arrested for Shooting 13-Year-Old Boy Dead, Wounding 16-Year-Old GirlSource of breaking news and analysis, insightful commentary and original reporting, curated and written specifically for the new generation of independent and conservative thinkers.
15-Year-Old Arrested for Shooting 13-Year-Old Boy Dead, Wounding 16-Year-Old GirlSource of breaking news and analysis, insightful commentary and original reporting, curated and written specifically for the new generation of independent and conservative thinkers.
Read more »
 Scientists Reveal the First Sign of Autism: 'Key Discovery'The spectrum of autism disorders varies widely but the exact mechanisms behind this disparity have been a long-standing mystery, until now.
Scientists Reveal the First Sign of Autism: 'Key Discovery'The spectrum of autism disorders varies widely but the exact mechanisms behind this disparity have been a long-standing mystery, until now.
Read more »
 Scientists Reveal Origins of Plant-Ant Partnerships 135 Million Years AgoScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Scientists Reveal Origins of Plant-Ant Partnerships 135 Million Years AgoScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 500-Pound Prehistoric Bird Was a ‘Giga-Goose,’ Fossils RevealScientists reveal the face of Australia’s massive, extinct “giga-goose”
500-Pound Prehistoric Bird Was a ‘Giga-Goose,’ Fossils RevealScientists reveal the face of Australia’s massive, extinct “giga-goose”
Read more »
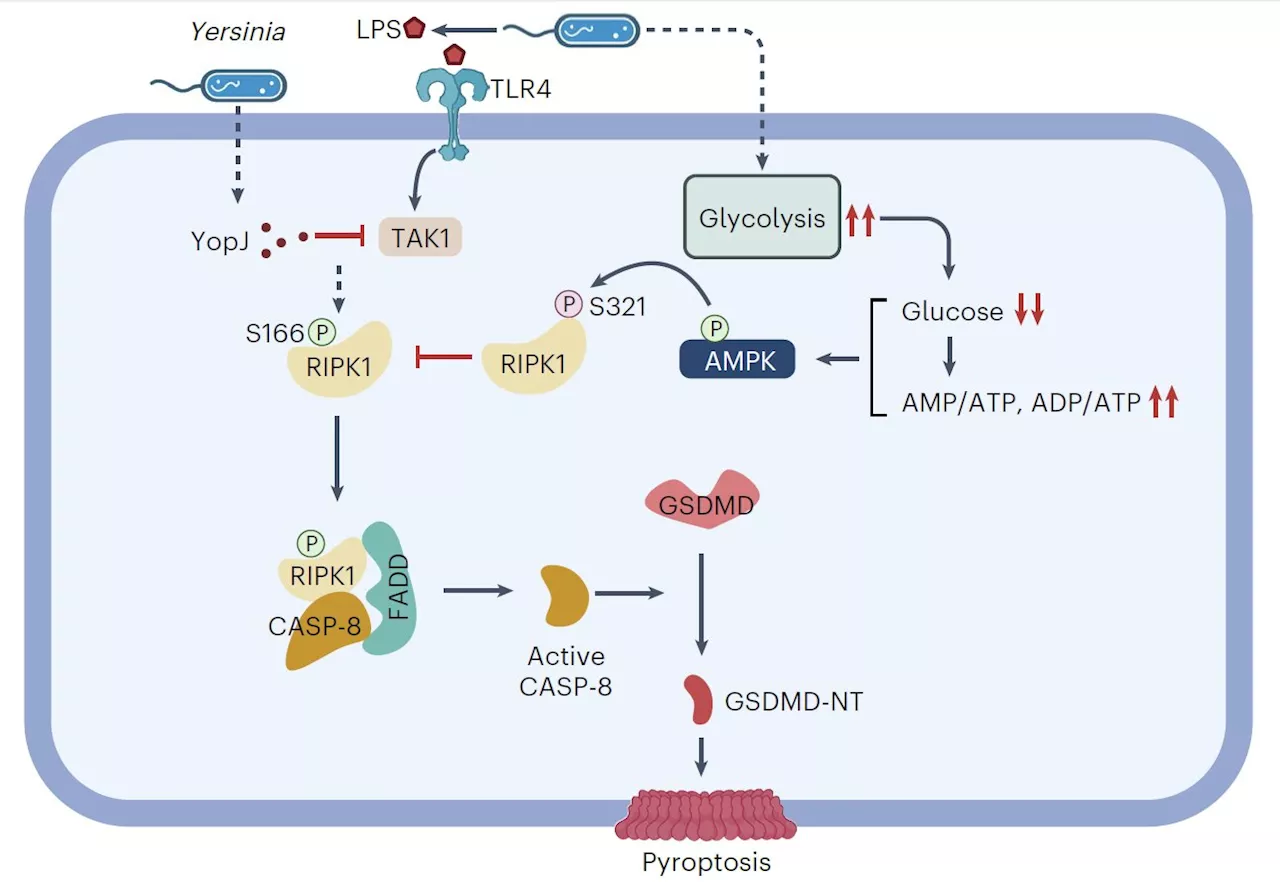 Scientists reveal molecular link between glucose sensing and pyroptosis cell deathAccording to a study published in Nature Microbiology on June 6, researchers led by Prof. Xu Daichao from the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have uncovered the molecular link between glucose sensing and non-classical pyroptosis.
Scientists reveal molecular link between glucose sensing and pyroptosis cell deathAccording to a study published in Nature Microbiology on June 6, researchers led by Prof. Xu Daichao from the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have uncovered the molecular link between glucose sensing and non-classical pyroptosis.
Read more »
