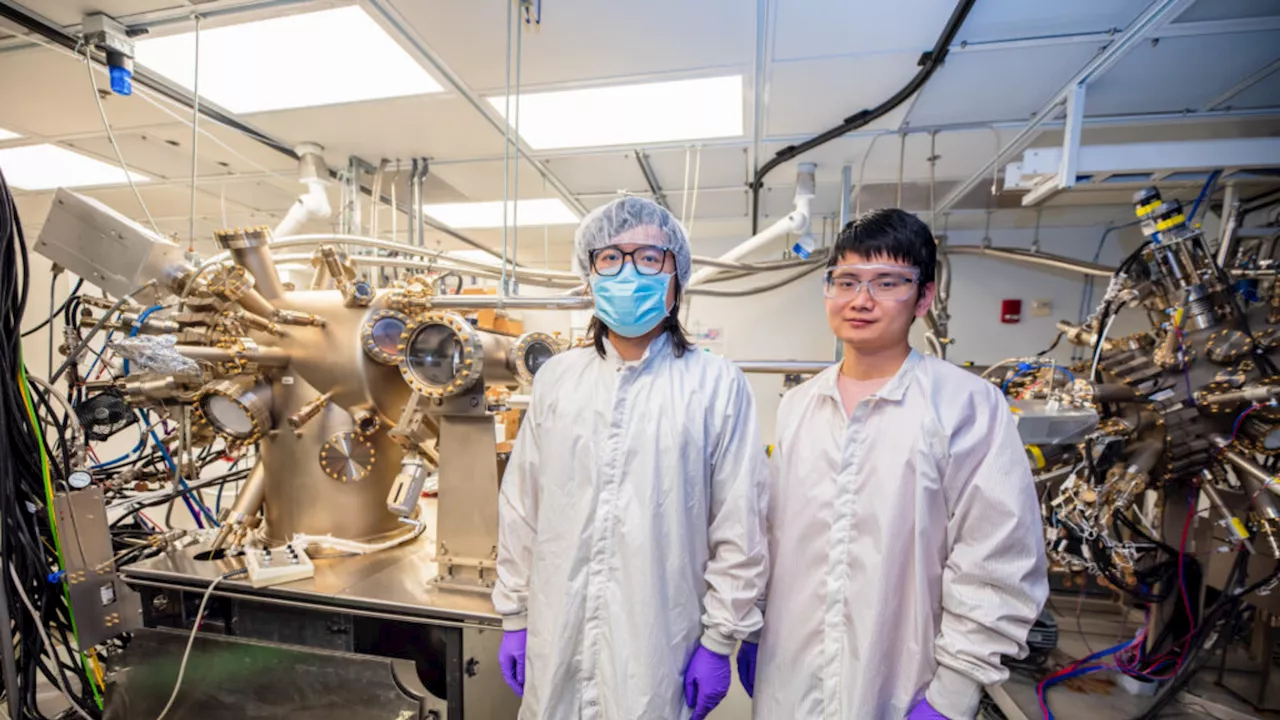
Researchers from the University of Waterloo have devised a way to precisely control the laser light used to manipulate qubits.
When a qubit is measured using laser light, the process often ends up damaging the neighboring qubits. Holograms can solve this problem.
A new study from the University of Waterloo researchers proposes a solution to this problem. The study authors have devised a way to precisely control the laser light used to manipulate qubits.“This demonstration has the potential to significantly impact future research in the field, including advancing quantum processors, enhancing speed and capabilities for tasks like quantum simulations in machines that already exist today, and implementing error correction.
The former is employed to readout, reset, and manipulate qubits using laser light. During this process, qubits are represented by ions that are confined in electromagnetic fields. The latter is used for shaping and manipulating laser light through optical elements However, “The target ion scatters photons in all directions during this process. Even with perfect control over light, there is still a risk that these scattered photons could disturb the quantum states of nearby qubits, which limits how well we can protect them,” Rajibul Islam, senior study author and a professor at the University of Waterloo, said.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 University of Exeter joins centre to train dementia researchersNewcastle University will lead the centre after choosing to partner with the University of Exeter.
University of Exeter joins centre to train dementia researchersNewcastle University will lead the centre after choosing to partner with the University of Exeter.
Read more »
 University of South Alabama researchers studying mitochondrial DNA phenomenonUniversity of South Alabama researchers are helping to pave the way for artificial mitochondria creation.Dr. Mikhail Alexeyev, a professor at the Frederick P. W
University of South Alabama researchers studying mitochondrial DNA phenomenonUniversity of South Alabama researchers are helping to pave the way for artificial mitochondria creation.Dr. Mikhail Alexeyev, a professor at the Frederick P. W
Read more »
 University Of Limerick Researchers Design Molecules To Revolutionize ComputingA research team at University of Limerick has made a major breakthrough by designing molecules that could revolutionize computing. The researchers at UL's Bernal Institute have discovered new ways to probe, control and tailor materials at the molecular scale. These findings have been used in an international project to create a novel hardware platform for artificial intelligence that offers unprecedented improvements in computational speed and energy efficiency.
University Of Limerick Researchers Design Molecules To Revolutionize ComputingA research team at University of Limerick has made a major breakthrough by designing molecules that could revolutionize computing. The researchers at UL's Bernal Institute have discovered new ways to probe, control and tailor materials at the molecular scale. These findings have been used in an international project to create a novel hardware platform for artificial intelligence that offers unprecedented improvements in computational speed and energy efficiency.
Read more »
 University of Michigan Researchers Develop Artificial Photosynthesis System to Turn CO2 into EthyleneResearchers at the University of Michigan have created a novel artificial photosynthesis system that can successfully bind two carbon atoms together to form ethylene, a vital step towards producing solar fuels. This method surpasses existing artificial photosynthesis systems in efficiency, abundance, and consistency.
University of Michigan Researchers Develop Artificial Photosynthesis System to Turn CO2 into EthyleneResearchers at the University of Michigan have created a novel artificial photosynthesis system that can successfully bind two carbon atoms together to form ethylene, a vital step towards producing solar fuels. This method surpasses existing artificial photosynthesis systems in efficiency, abundance, and consistency.
Read more »
 University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh job with University of Pittsburgh | DCSBFaculty.Professor.Associate - Full-Time Med-Computational and Systems Biology - Pennsylvania-Pittsburgh - (24006988) Full-time, Tenure Stream, Associate Professor position at the University of Pittsburgh in the School of Medicine in the Department of Computational & Systems Biology.
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh job with University of Pittsburgh | DCSBFaculty.Professor.Associate - Full-Time Med-Computational and Systems Biology - Pennsylvania-Pittsburgh - (24006988) Full-time, Tenure Stream, Associate Professor position at the University of Pittsburgh in the School of Medicine in the Department of Computational & Systems Biology.
Read more »
 University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh job with University of Pittsburgh | DCSBFaculty.Professor.Assistant - Full-Time Med-Computational and Systems Biology - Pennsylvania-Pittsburgh - (24006607) Full-time, Tenure Stream, Assistant Professor position at the University of Pittsburgh in the School of Medicine in the Department of Computational & Systems Biology.
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh job with University of Pittsburgh | DCSBFaculty.Professor.Assistant - Full-Time Med-Computational and Systems Biology - Pennsylvania-Pittsburgh - (24006607) Full-time, Tenure Stream, Assistant Professor position at the University of Pittsburgh in the School of Medicine in the Department of Computational & Systems Biology.
Read more »
