Researchers have traced the family tree of Coffea arabica, the world's most popular type of coffee, back to its origins in Ethiopia and Yemen. The study aims to better understand the plants and protect them from pests and climate change.
around the world, researchers built a family tree for the world's most popular type of coffee, known to scientists as Coffea arabica and to coffee lovers simply as “arabica.”
These wild coffee plants originated in Ethiopia but are thought to have been first roasted and brewed primarily in Yemen starting in the 1400s. In the 1600s, Indian monk Baba Budan is fabled to have smuggled seven raw coffee beans back to his homeland from Yemen, laying the foundation for coffee’s global takeover.
The arabica plant’s population fluctuated over thousands of years before humans began cultivating it, flourishing during warm, wet periods and suffering through dry ones. These lean times created so-called population bottlenecks, when only a small number of genetically similar plants survived.
Researchers Family Tree Arabica Coffee Origins Ethiopia Yemen Pests Climate Change
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers Uncover Family Tree of Arabica CoffeeResearchers have traced the origins of arabica coffee back to natural crossbreeding of two other coffee species around 600,000 years ago. The study aims to protect the plants from pests and climate change.
Researchers Uncover Family Tree of Arabica CoffeeResearchers have traced the origins of arabica coffee back to natural crossbreeding of two other coffee species around 600,000 years ago. The study aims to protect the plants from pests and climate change.
Read more »
 Researchers find unusual heat resilience in tree swallowsA study reveals that tree swallows have a unique heat resilience, enabling them to withstand high temperatures and cope with heat stress. This adaptation is crucial in the context of climate change and offers insights for conservation efforts.
Researchers find unusual heat resilience in tree swallowsA study reveals that tree swallows have a unique heat resilience, enabling them to withstand high temperatures and cope with heat stress. This adaptation is crucial in the context of climate change and offers insights for conservation efforts.
Read more »
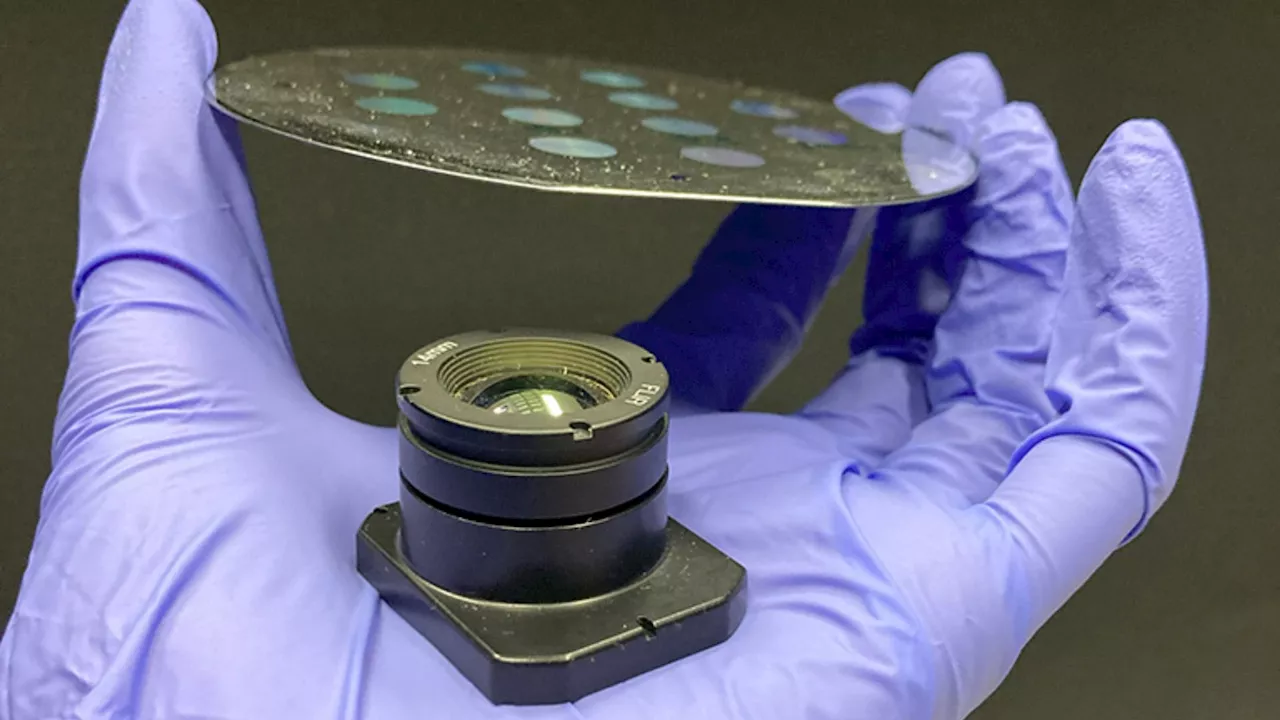 Researchers reveal ultra-thin meta-optics for next-gen thermal imagingResearchers pioneer MTF-engineering framework, leveraging meta-optics and AI for thinner, lighter, and higher-quality infrared imaging.
Researchers reveal ultra-thin meta-optics for next-gen thermal imagingResearchers pioneer MTF-engineering framework, leveraging meta-optics and AI for thinner, lighter, and higher-quality infrared imaging.
Read more »
 Researchers reveal highly efficient bit-switch using skyrmionsResearchers develop skyrmion-based microelectronic device for sustainable, high-performance AI computing with energy-efficient technology.
Researchers reveal highly efficient bit-switch using skyrmionsResearchers develop skyrmion-based microelectronic device for sustainable, high-performance AI computing with energy-efficient technology.
Read more »
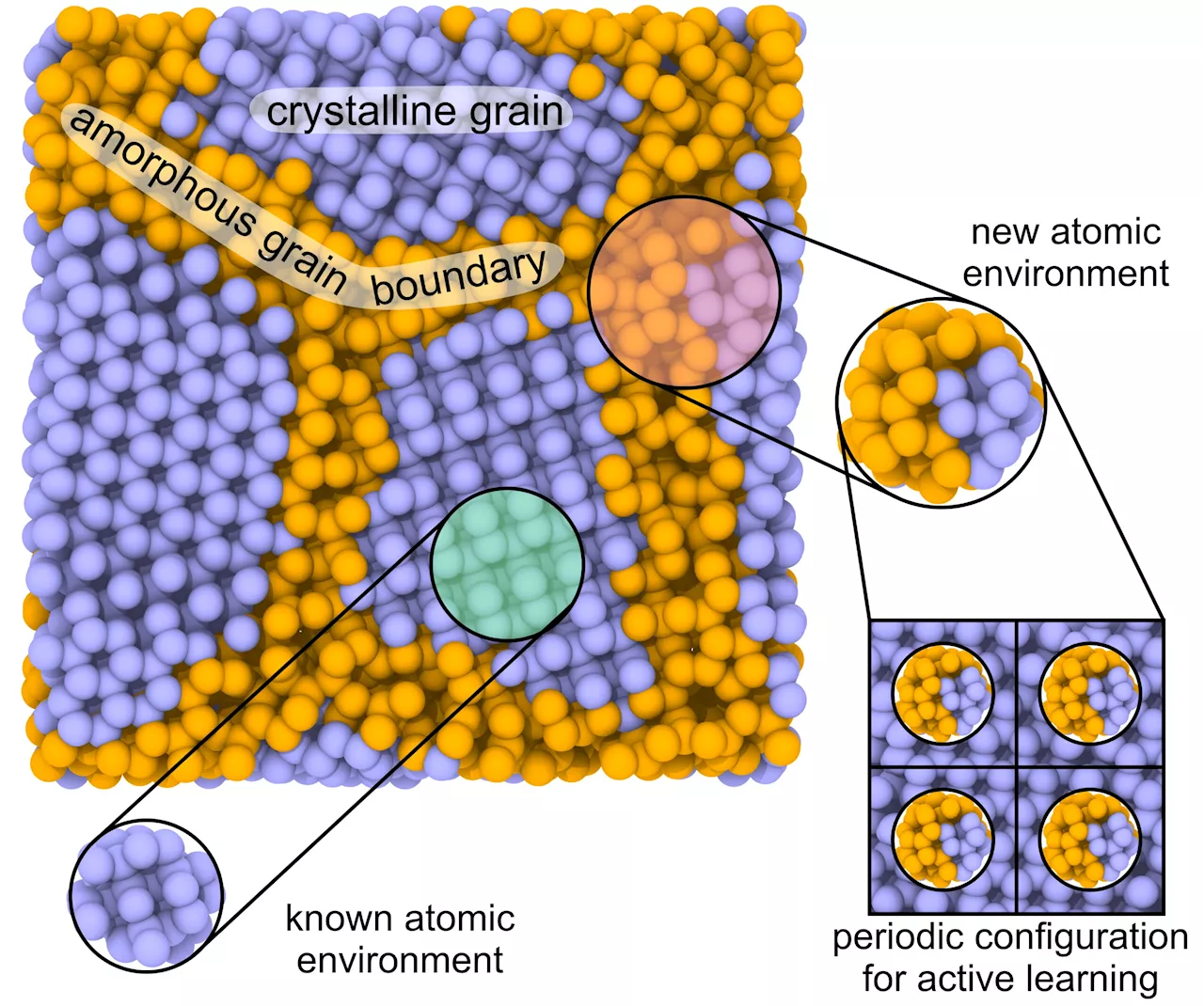 Researchers reveal new method for calculating mechanical properties of solids using machine learningA research team from Skoltech introduced a new method that takes advantage of machine learning for studying the properties of polycrystals, composites, and multiphase systems. It attained high accuracy, nearly as good as that of quantum-mechanical methods, which are only applicable to materials with less than a few hundred atoms.
Researchers reveal new method for calculating mechanical properties of solids using machine learningA research team from Skoltech introduced a new method that takes advantage of machine learning for studying the properties of polycrystals, composites, and multiphase systems. It attained high accuracy, nearly as good as that of quantum-mechanical methods, which are only applicable to materials with less than a few hundred atoms.
Read more »
 A tiny spot leads to a large advancement in nano-processing, researchers revealFocusing a tailored laser beam through transparent glass can create a tiny spot inside the material. Researchers have reported on a way to use this small spot to improve laser material processing, boosting processing resolution.
A tiny spot leads to a large advancement in nano-processing, researchers revealFocusing a tailored laser beam through transparent glass can create a tiny spot inside the material. Researchers have reported on a way to use this small spot to improve laser material processing, boosting processing resolution.
Read more »
