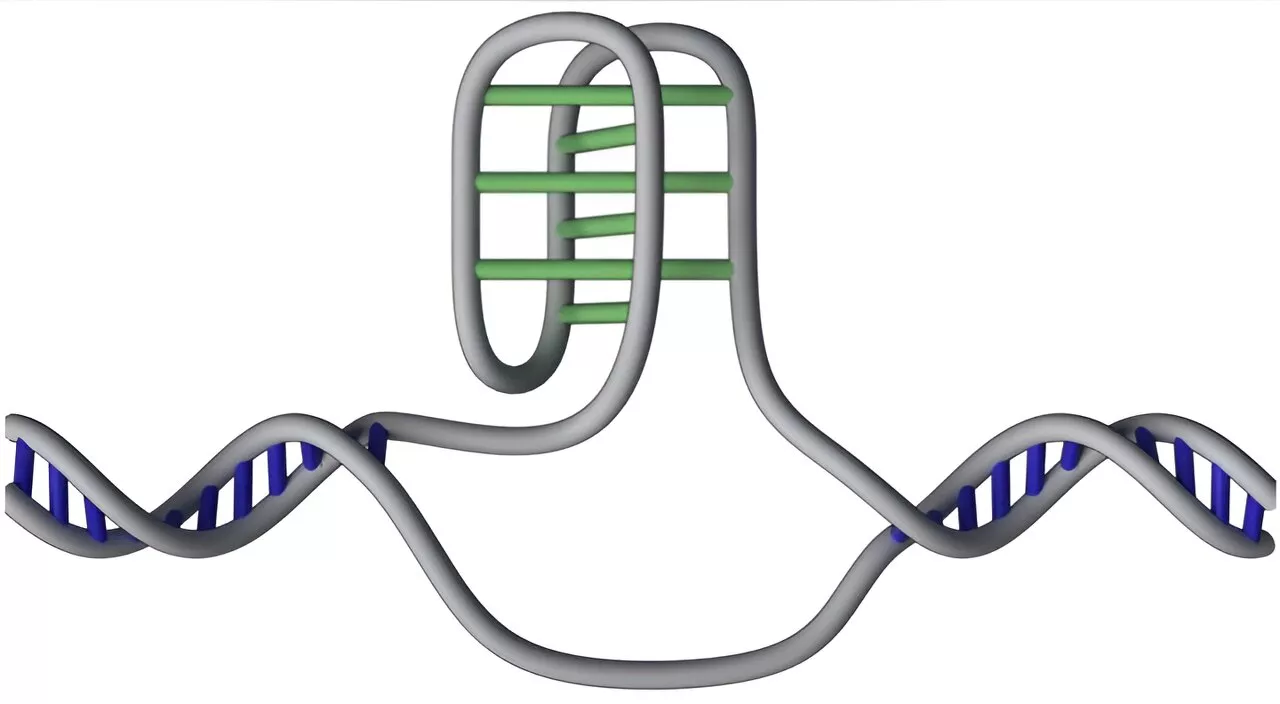
Researchers have mapped 50,000 of DNA's mysterious 'knots' in the human genome. The innovative study of DNA's hidden structures may open up new approaches for treatment and diagnosis of diseases, including cancer.
Researchers map 50,000 of DNA's mysterious 'knots' in the human genome retrieved 29 August 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-08-dna-mysterious-human-genome.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Ancient sea cow that was attacked by both a primeval crocodile and shark sheds new light on prehistoric food chainsSep 23, 2021
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors. Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers develop AI model that predicts the accuracy of protein–DNA bindingA new artificial intelligence model developed by USC researchers and published in Nature Methods can predict how different proteins may bind to DNA with accuracy across different types of protein, a technological advance that promises to reduce the time required to develop new drugs and other medical treatments.
Researchers develop AI model that predicts the accuracy of protein–DNA bindingA new artificial intelligence model developed by USC researchers and published in Nature Methods can predict how different proteins may bind to DNA with accuracy across different types of protein, a technological advance that promises to reduce the time required to develop new drugs and other medical treatments.
Read more »
 Researchers explore the interplay between high-affinity DNA and carbon nanotubesSingle-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) hold promise for biomedicine and nanoelectronics, yet the functionalization with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) remains a challenge. Researchers using high-affinity ssDNA sequences identified through high-throughput selection.
Researchers explore the interplay between high-affinity DNA and carbon nanotubesSingle-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) hold promise for biomedicine and nanoelectronics, yet the functionalization with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) remains a challenge. Researchers using high-affinity ssDNA sequences identified through high-throughput selection.
Read more »
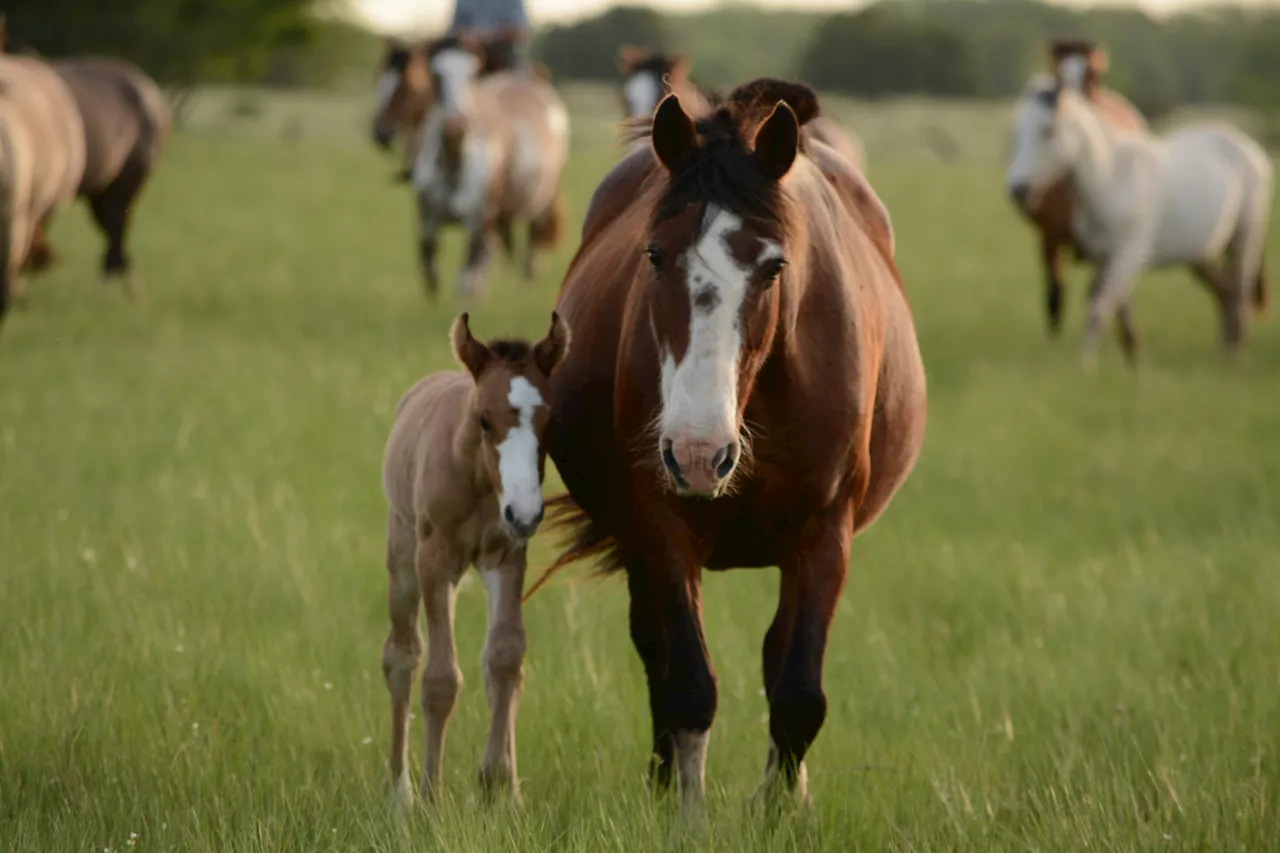 Researchers investigate cell-free DNA as early sepsis marker in foalsIt's hard to be a horse. It's especially hard to be a newborn foal, dropped into a world of microbes and bacteria with your sole initial defense against devastating infections being the antibodies you get from your mother's milk, or colostrum.
Researchers investigate cell-free DNA as early sepsis marker in foalsIt's hard to be a horse. It's especially hard to be a newborn foal, dropped into a world of microbes and bacteria with your sole initial defense against devastating infections being the antibodies you get from your mother's milk, or colostrum.
Read more »
 Technology to predict the deformation of DNA origami structures induced by DNA-binding moleculesA research team has developed a technology that can quickly predict the mechanochemical shape changes of DNA origami nanostructures. The team includes Professor Do-Nyun Kim's research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at The College of Engineering of Seoul National University.
Technology to predict the deformation of DNA origami structures induced by DNA-binding moleculesA research team has developed a technology that can quickly predict the mechanochemical shape changes of DNA origami nanostructures. The team includes Professor Do-Nyun Kim's research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at The College of Engineering of Seoul National University.
Read more »
 Cracking the code of life: new AI model learns DNA's hidden languageWith GROVER, a new large language model trained on human DNA, researchers could now attempt to decode the complex information hidden in our genome. GROVER treats human DNA as a text, learning its rules and context to draw functional information about the DNA sequences.
Cracking the code of life: new AI model learns DNA's hidden languageWith GROVER, a new large language model trained on human DNA, researchers could now attempt to decode the complex information hidden in our genome. GROVER treats human DNA as a text, learning its rules and context to draw functional information about the DNA sequences.
Read more »
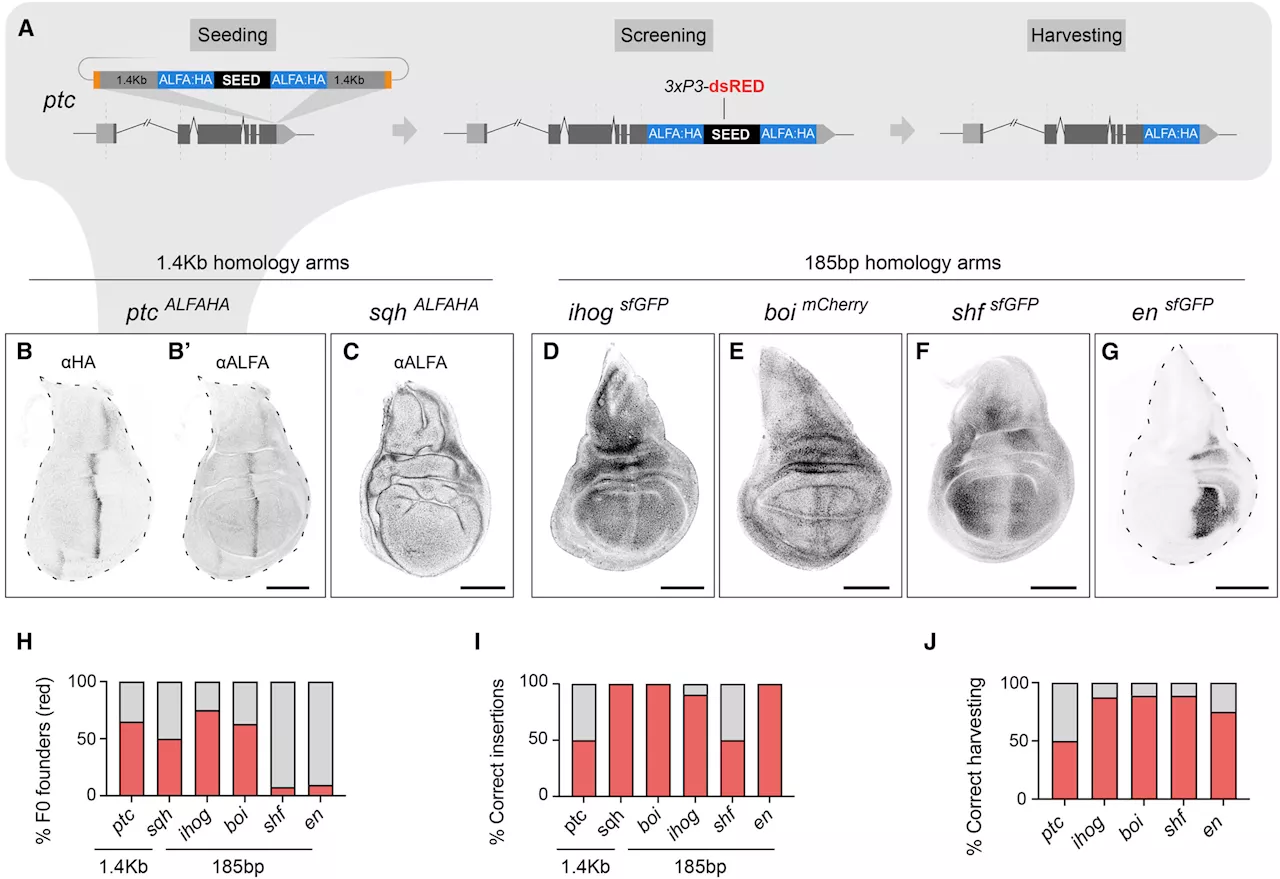 Precise genetics: New CRISPR method enables efficient DNA modificationWith the revolutionary CRISPR/Cas technology, the DNA of living organisms can be precisely altered. Using a guide RNA that recognizes a specific DNA sequence, Cas9 protein is recruited to that sequence and cuts the DNA. This targeted cut allows the DNA to be repaired or altered at this specific location.
Precise genetics: New CRISPR method enables efficient DNA modificationWith the revolutionary CRISPR/Cas technology, the DNA of living organisms can be precisely altered. Using a guide RNA that recognizes a specific DNA sequence, Cas9 protein is recruited to that sequence and cuts the DNA. This targeted cut allows the DNA to be repaired or altered at this specific location.
Read more »