Treating vision loss and lowering cholesterol could help reduce the risk of dementia, according to a new report.
Nick Blackmer is a librarian, fact-checker, and researcher with more than 20 years of experience in consumer-facing health and wellness content.These two conditions have been added to an existing list of 12 modifiable risk factors for dementia, which also includes smoking, obesity, and hypertension.
The study identified these two new risk factors by looking at meta-analyses, research, and recent studies on the topic. Their analysis revealed about 7% of all dementia cases can be tied to highIn 2020, this same commission identified 12 modifiable risk factors that could also put people at risk of developing dementia.These initial 12 risk factors were linked to 40% of dementia cases.
Cardiovascular disease, sedentary lifestyle, hearing loss, and other risk factors can cause a cascade of changes in the brain that increase dementia risk.Joel Salinas, MD“High cholesterol, on the other hand, can contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits in the brain’s blood vessels,” he said. “This can lead to blockages, reduced blood flow, and even brain cell damage, all of which increase the risk of dementia.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers identify new tools for anti-Acinetobacter drug development and AMR preparednessResearchers have engineered a library of strains that can be used to develop new antibacterial compounds to help address antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria.
Researchers identify new tools for anti-Acinetobacter drug development and AMR preparednessResearchers have engineered a library of strains that can be used to develop new antibacterial compounds to help address antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria.
Read more »
 Researchers identify new tools for anti-Acinetobacter drug development and AMR preparednessUniversity of Liverpool researchers have engineered a library of strains that can be used to develop new antibacterial compounds to help address antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria.
Researchers identify new tools for anti-Acinetobacter drug development and AMR preparednessUniversity of Liverpool researchers have engineered a library of strains that can be used to develop new antibacterial compounds to help address antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria.
Read more »
 Researchers Identify Potential New Strategy To Slow The Development Of Liver FibrosisA new study has shed light on the role inflammation plays in mitigating liver fibrosis, a condition often associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). The research brings researchers closer to understanding the pathology of MASH (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis), a consequence of MAFLD. The findings could lead to new strategies for slowing the progression of liver fibrosis.
Researchers Identify Potential New Strategy To Slow The Development Of Liver FibrosisA new study has shed light on the role inflammation plays in mitigating liver fibrosis, a condition often associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). The research brings researchers closer to understanding the pathology of MASH (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis), a consequence of MAFLD. The findings could lead to new strategies for slowing the progression of liver fibrosis.
Read more »
 Researchers develop analytical pipeline to identify unexploited genes that hold research valueA research team has developed an analysis pipeline to identify unexploited genes for a given disease against five databases that provide gene-disease associations. They used their pipeline to study oxidative stress and its related disease, Parkinson's disease, as a case study.
Researchers develop analytical pipeline to identify unexploited genes that hold research valueA research team has developed an analysis pipeline to identify unexploited genes for a given disease against five databases that provide gene-disease associations. They used their pipeline to study oxidative stress and its related disease, Parkinson's disease, as a case study.
Read more »
 Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genesResearchers have uncovered a key reason why a typically normal protein goes awry and fuels cancer. They found the protein NSD2 alters the function of the androgen receptor, an important regulator of normal prostate development. When androgen receptor binds with NSD2, it causes rapid cell division and growth leading to prostate cancer.
Researchers identify factor that drives prostate cancer-causing genesResearchers have uncovered a key reason why a typically normal protein goes awry and fuels cancer. They found the protein NSD2 alters the function of the androgen receptor, an important regulator of normal prostate development. When androgen receptor binds with NSD2, it causes rapid cell division and growth leading to prostate cancer.
Read more »
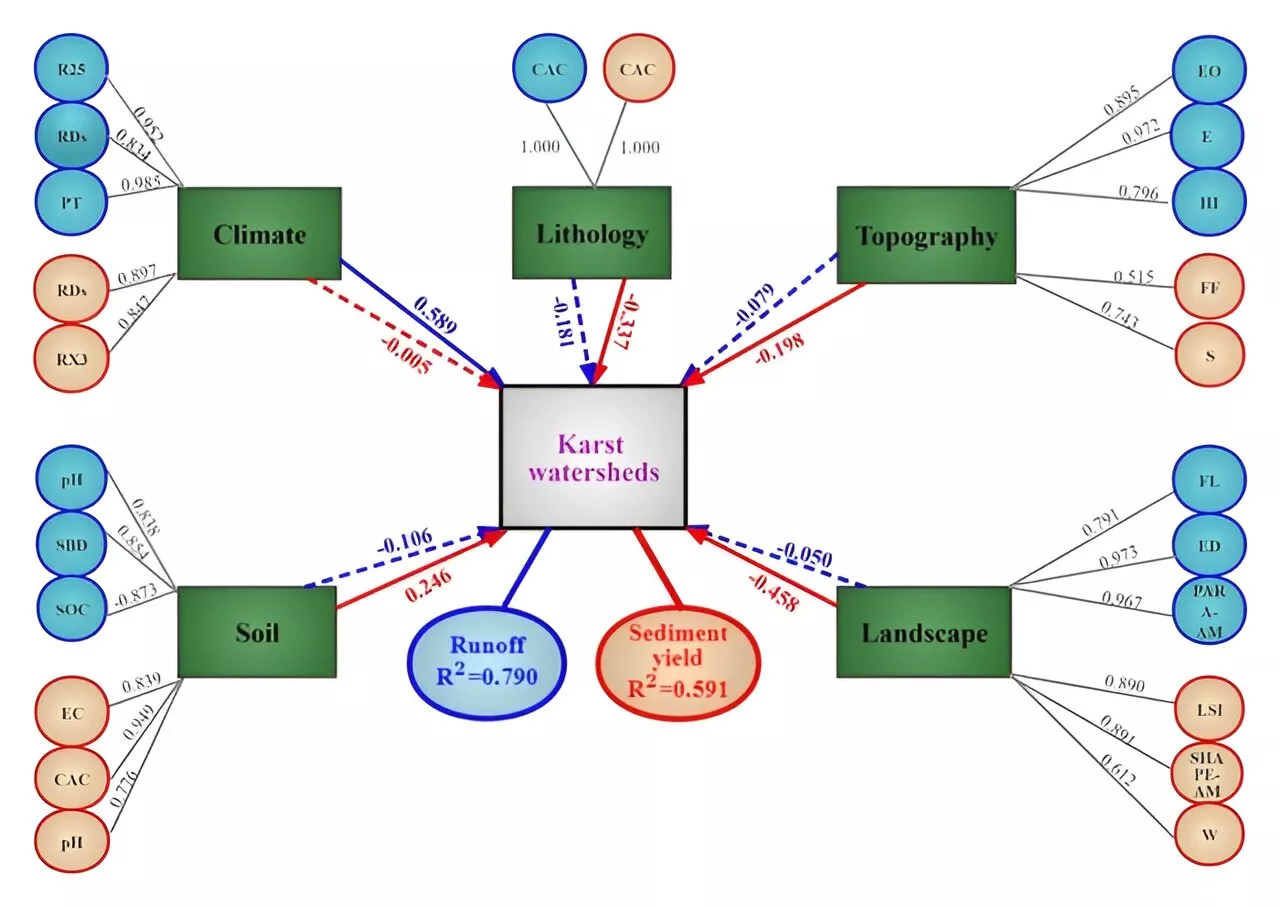 Researchers identify key factors influencing runoff and sediment yield changes in karst watershedsThe ecological environment in karst regions of southwest China is fragile and sensitive.
Researchers identify key factors influencing runoff and sediment yield changes in karst watershedsThe ecological environment in karst regions of southwest China is fragile and sensitive.
Read more »
