An international team has found a new RNA virus that they believe is hitching a ride with a common human parasite. The virus is associated with severe inflammation in humans infected with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii, leading the team to hypothesize that it exacerbates toxoplasmosis disease.
An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has found a new RNA virus that they believe is hitching a ride with a common human parasite., along with 18 others that are closely related to it, was discovered through a computational screen of human neuron data -- an effort aimed at elucidating the connection between RNA viruses and neuroinflammatory disease.
Symptoms of toxoplasmosis can be aggravated by a hyperactivated human immune response. The virus-carrying parasite triggers this type of response when the immune system senses the foreign RNA of the virus. Zoonotic viruses that infect other living things in our environment in order to reach us are expected to cause the majority of emerging infectious diseases in humans, Babaian noted."This study underscores the importance of looking beyond the viruses that infect humans directly into the extended virome," he said.Purav Gupta, Aiden Hiller, Jawad Chowdhury, Declan Lim, Dillon Yee Lim, Jeroen P J Saeij, Artem Babaian, Felipe Rodriguez, Luke Pereira, Alejandro Morales-Tapia.
HIV And AIDS Infectious Diseases Human Biology Virology Pests And Parasites Microbiology Microbes And More
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
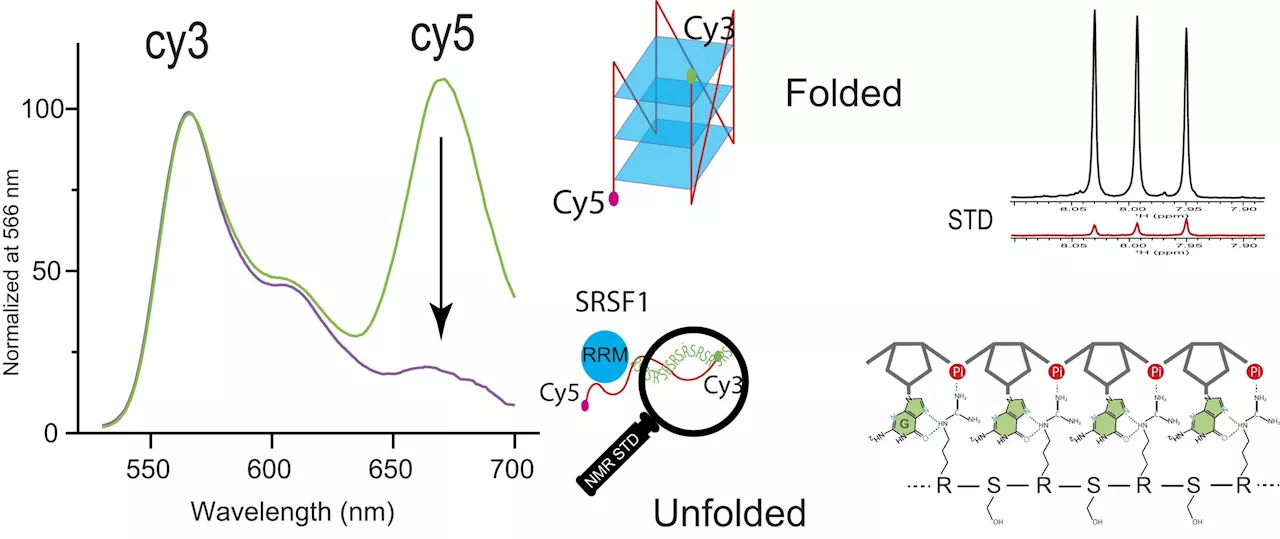 Researchers uncover protein SRSF1's uncommon ability to bind and unfold RNA G-quadruplexesRNA transcription is the genomic process in which a cell produces a duplicate of a gene's DNA sequence. In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research, University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Chemistry Professor Jun Zhang, Ph.D.
Researchers uncover protein SRSF1's uncommon ability to bind and unfold RNA G-quadruplexesRNA transcription is the genomic process in which a cell produces a duplicate of a gene's DNA sequence. In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research, University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Chemistry Professor Jun Zhang, Ph.D.
Read more »
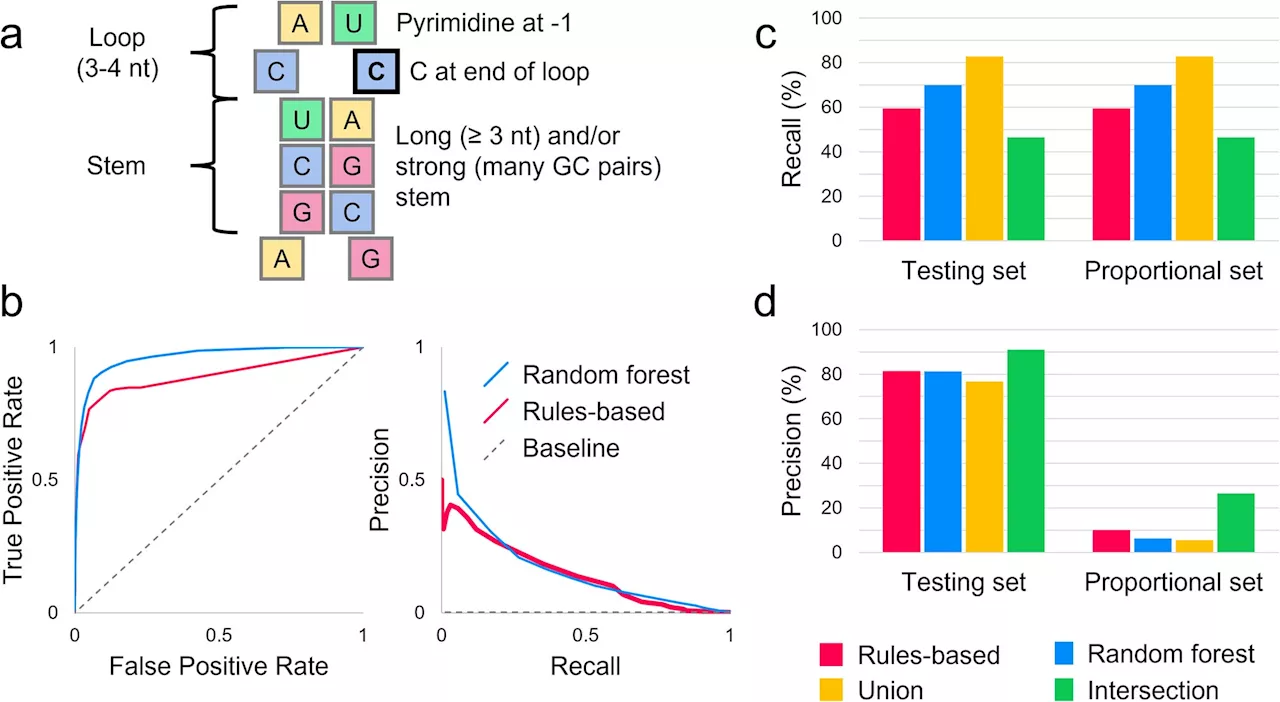 Researchers find RNA editing sites likely play a more significant role in genetic diseaseNew findings by University at Buffalo researchers reveal that RNA editing may play a larger role in human biology and in the development of human disease than has generally been understood.
Researchers find RNA editing sites likely play a more significant role in genetic diseaseNew findings by University at Buffalo researchers reveal that RNA editing may play a larger role in human biology and in the development of human disease than has generally been understood.
Read more »
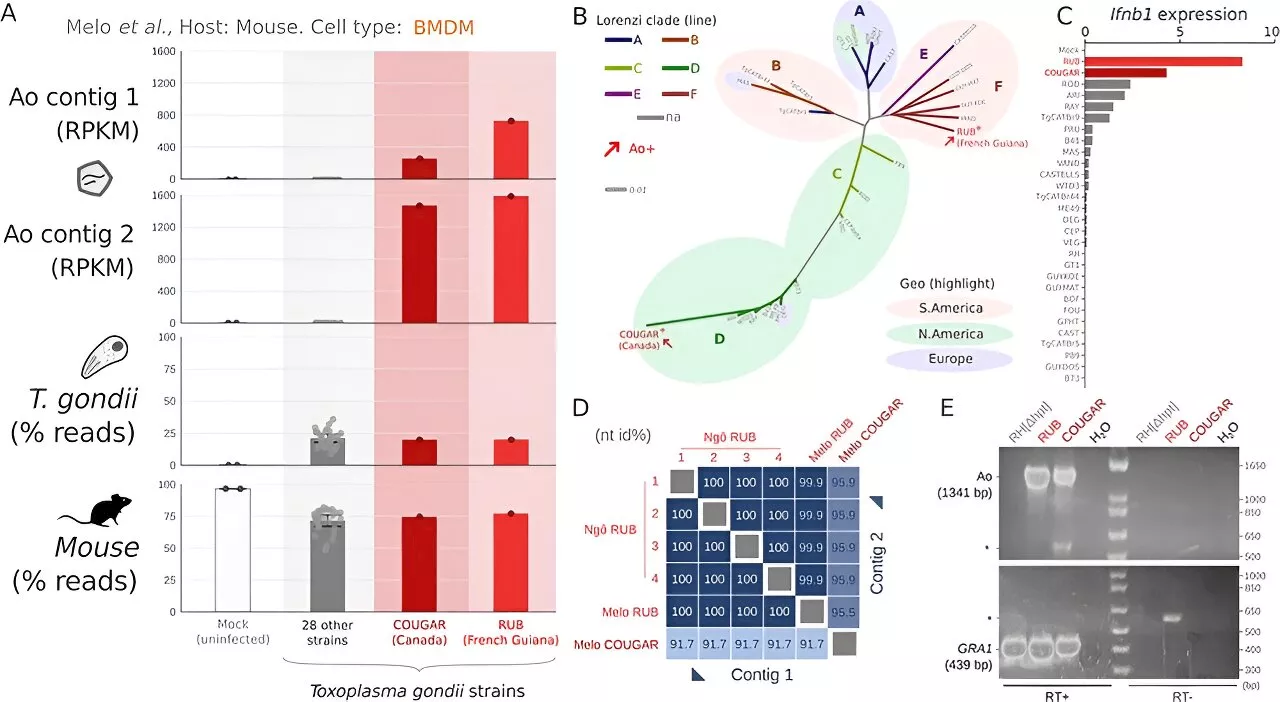 Researchers discover 'Trojan Horse' virus hiding in human parasiteAn international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has found a new RNA virus that they believe is hitching a ride with a common human parasite.
Researchers discover 'Trojan Horse' virus hiding in human parasiteAn international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has found a new RNA virus that they believe is hitching a ride with a common human parasite.
Read more »
 Tiny target discovered on RNA to short-circuit inflammationResearchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus.
Tiny target discovered on RNA to short-circuit inflammationResearchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus.
Read more »
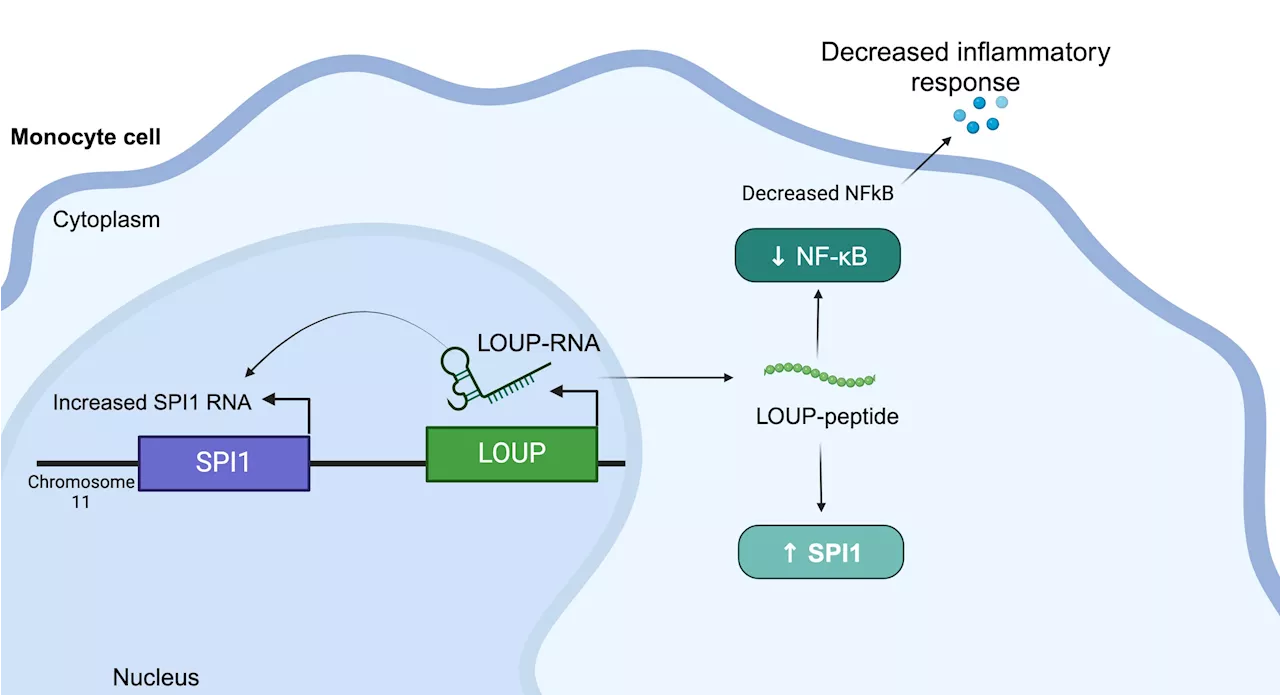 New study discovers tiny target on RNA to short-circuit inflammationUC Santa Cruz researchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus.
New study discovers tiny target on RNA to short-circuit inflammationUC Santa Cruz researchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus.
Read more »
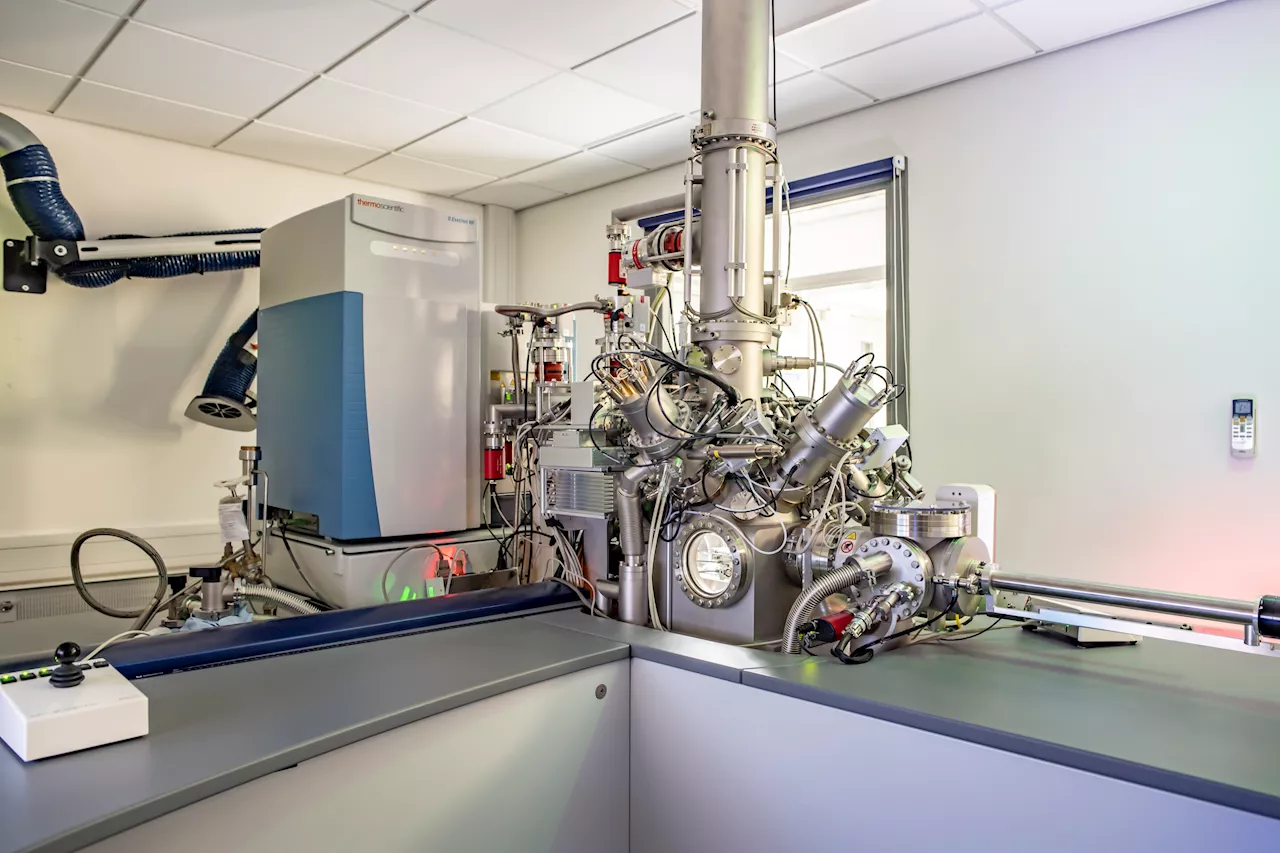 Scientists develop technique to analyze RNA structures in ultra-high definitionScientists at the University of Nottingham have developed a technique to analyze the atomic-level structure of RNA molecules with exceptional precision and speed, and are the first in the world to use the method to examine structural changes in RNA when a cell gets infected with HIV.
Scientists develop technique to analyze RNA structures in ultra-high definitionScientists at the University of Nottingham have developed a technique to analyze the atomic-level structure of RNA molecules with exceptional precision and speed, and are the first in the world to use the method to examine structural changes in RNA when a cell gets infected with HIV.
Read more »
