Researchers have discovered a new bacterium that weakens the immune system in the gut, potentially contributing to certain inflammatory and infectious gut diseases. The team identified the bacterium, Tomasiella immunophila (T.
Researchers have discovered a new bacterium that weakens the immune system in the gut, potentially contributing to certain inflammatory and infectious gut diseases. The team identified the bacterium, Tomasiella immunophila , which plays a key role in breaking down a crucial immune component of the gut's multi-faceted protective immune barrier.
Identifying this bacterium is the first step to developing new treatments for a variety of inflammatory and infectious gut diseases. These conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's and ulcerative colitis, are associated with decreased levels of secretory immunoglobulin A , an antibody that protects mucosal surfaces.was led by Thaddeus Stappenbeck, M.D., Ph.D., chair of Cleveland Clinic's Department of Inflammation and Immunity, and Qiuhe Lu, Ph.D.
"Drs. Stappenbeck and Lu's rigorous and elegant study provides a key insight and an exciting potential mechanism for why some people have low or absent levels of SIgA in their gut, yet retain normal levels of SIgA in their bloodstream," says Michael Silverman, M.D., Ph.D., a physician with the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Gastrointestinal Problems Immune System Crohn's Disease Veterinary Medicine Bacteria Microbes And More New Species
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
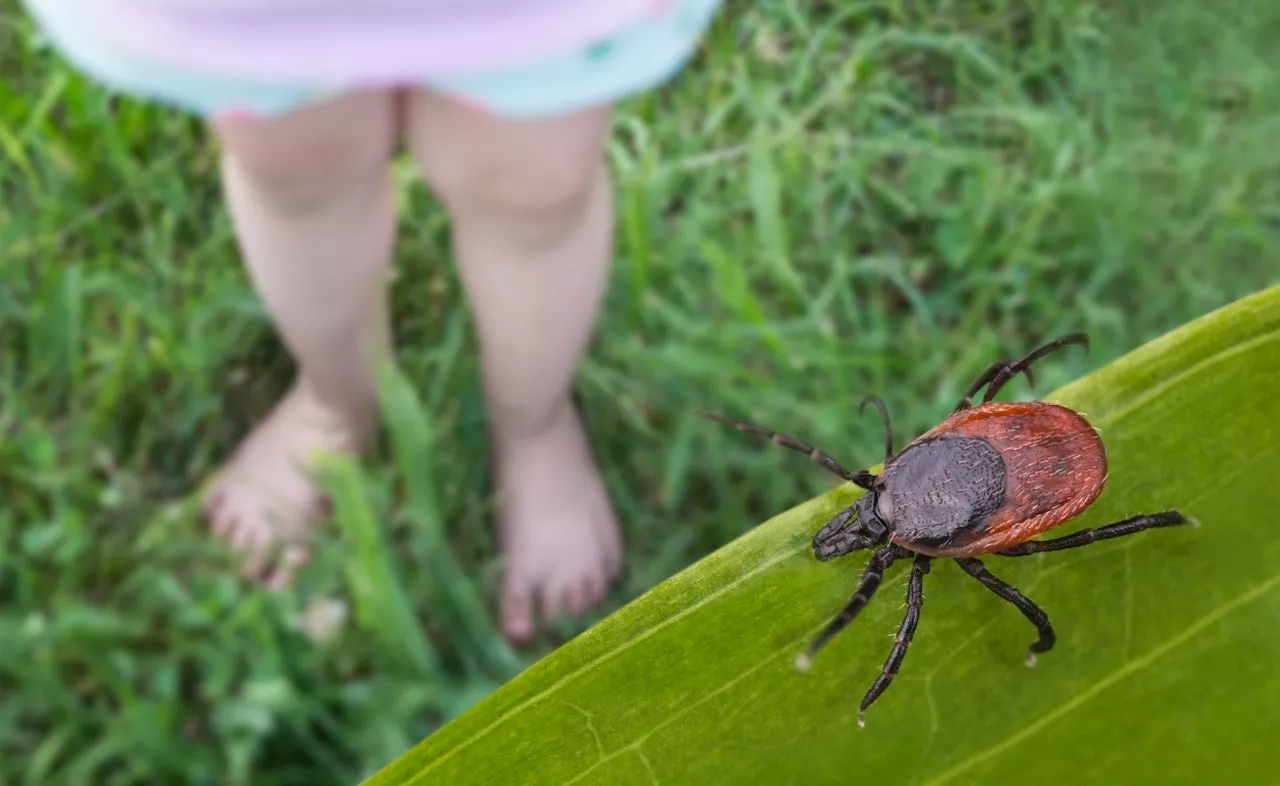 Tick-borne ‘Wetland virus,’ newly discovered in China, could cause damage to brain, researchers sayScientists are warning of a new tick-borne disease — which they are calling the Wetland virus (WELV) — that was recently discovered in China. Here's what to know about the symptoms and risks.
Tick-borne ‘Wetland virus,’ newly discovered in China, could cause damage to brain, researchers sayScientists are warning of a new tick-borne disease — which they are calling the Wetland virus (WELV) — that was recently discovered in China. Here's what to know about the symptoms and risks.
Read more »
 Tick-borne Wetland virus, newly discovered in China, could cause damage to brain, researchers sayScientists are warning of a new tick-borne disease, which they are calling the Wetland virus, recently discovered in China. Here's what to know about the symptoms and risks.
Tick-borne Wetland virus, newly discovered in China, could cause damage to brain, researchers sayScientists are warning of a new tick-borne disease, which they are calling the Wetland virus, recently discovered in China. Here's what to know about the symptoms and risks.
Read more »
 Quantum researchers cause controlled 'wobble' in the nucleus of a single atomResearchers have been able to initiate a controlled movement in the very heart of an atom. They caused the atomic nucleus to interact with one of the electrons in the outermost shells of the atom. This electron could be manipulated and read out through the needle of a scanning tunneling microscope.
Quantum researchers cause controlled 'wobble' in the nucleus of a single atomResearchers have been able to initiate a controlled movement in the very heart of an atom. They caused the atomic nucleus to interact with one of the electrons in the outermost shells of the atom. This electron could be manipulated and read out through the needle of a scanning tunneling microscope.
Read more »
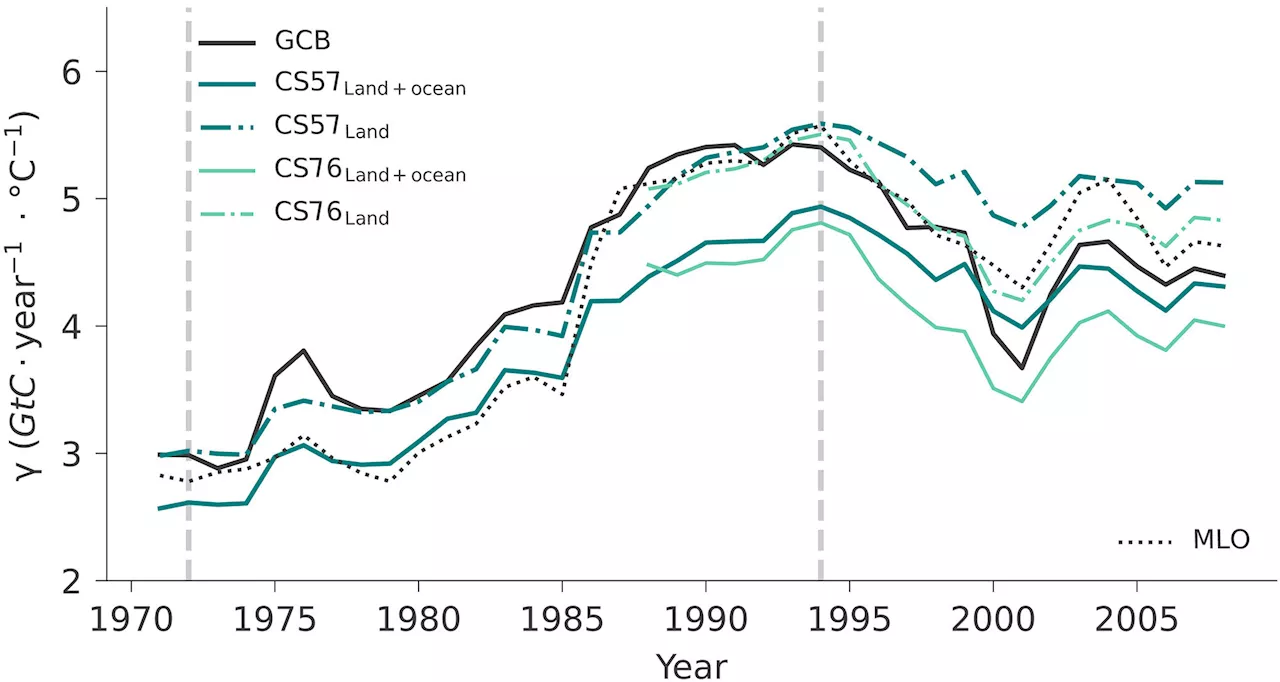 Extreme El Niño events cause short-term CO₂ fluctuations, researchers findA recent study challenges previous assumptions about the connection between CO₂ in the atmosphere and temperatures in the tropics. Between 1959 and 2011, the CO₂ content in the atmosphere responded twice as strongly to temperatures in the tropics than before.
Extreme El Niño events cause short-term CO₂ fluctuations, researchers findA recent study challenges previous assumptions about the connection between CO₂ in the atmosphere and temperatures in the tropics. Between 1959 and 2011, the CO₂ content in the atmosphere responded twice as strongly to temperatures in the tropics than before.
Read more »
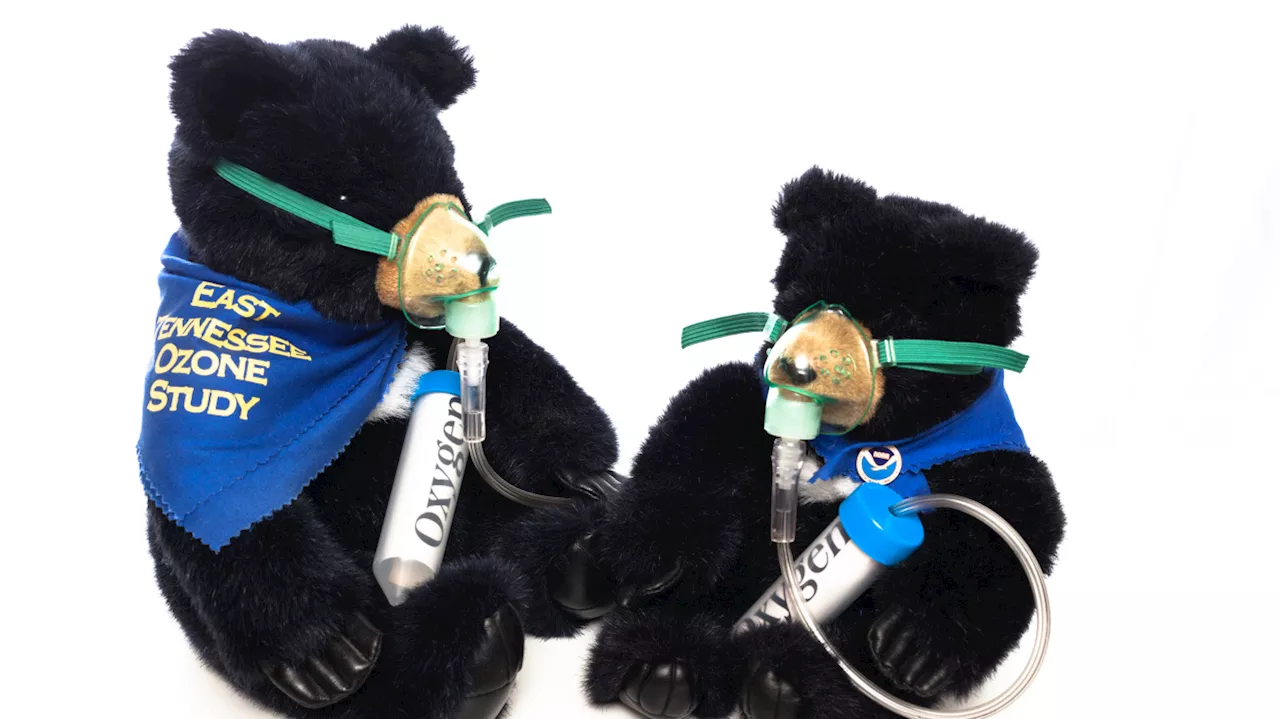 Friday Find: How NOAA researchers tackled a 'bear' of an air pollution problemVisitors to NOAA’s Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Division in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, may notice a toy bear perched high on a shelf in the hallway. That small, stuffed bear wearing a gas mask and kerchief tells a story about one of NOAA’s research achievements in air quality.
Friday Find: How NOAA researchers tackled a 'bear' of an air pollution problemVisitors to NOAA’s Atmospheric Turbulence and Diffusion Division in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, may notice a toy bear perched high on a shelf in the hallway. That small, stuffed bear wearing a gas mask and kerchief tells a story about one of NOAA’s research achievements in air quality.
Read more »
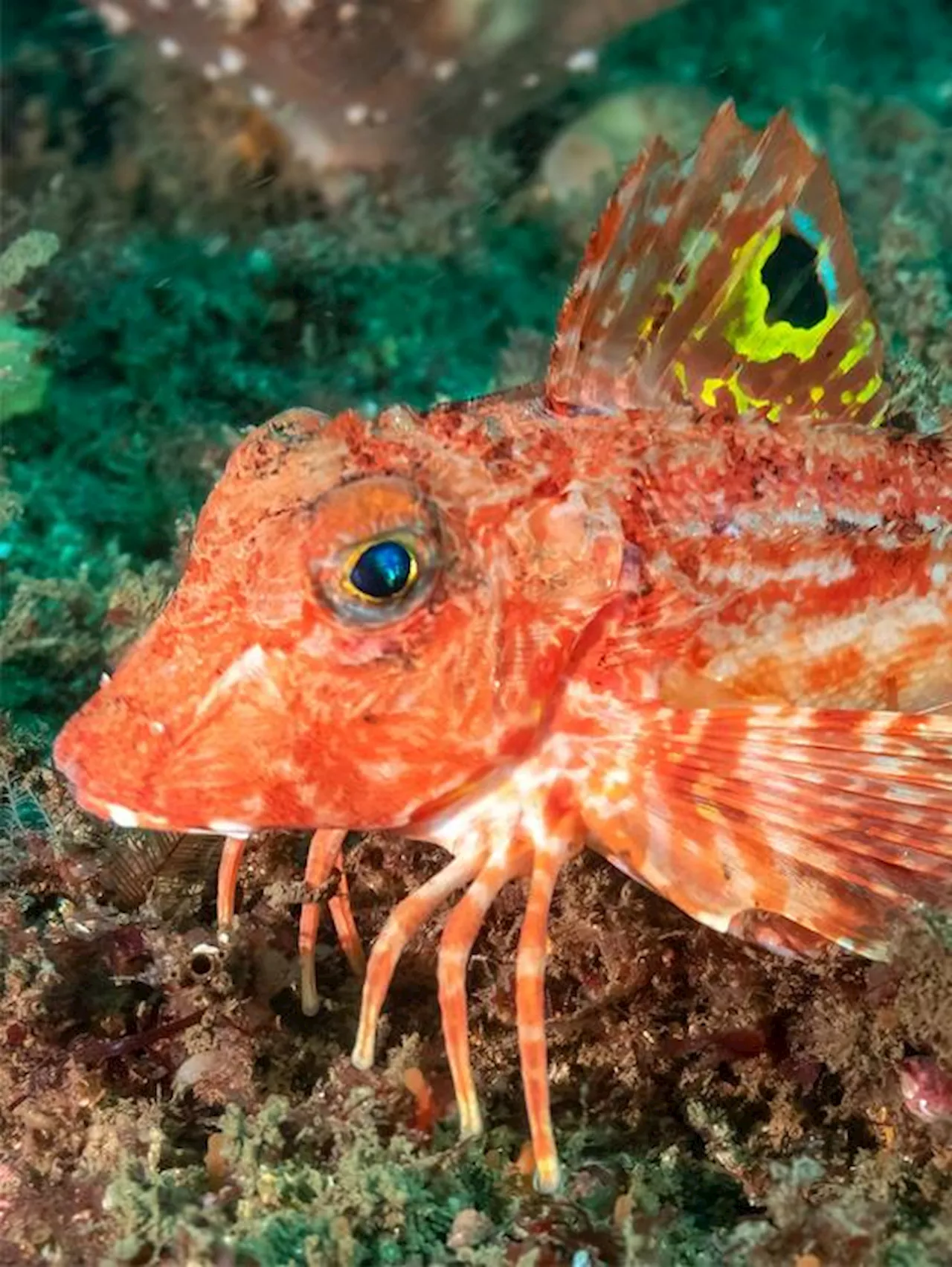 Researchers Discover How a Fish With Legs Uses Them To Find FoodCuriosity and serendipity helped two teams of scientists learn that one species of sea robin employs legs that have both the sense of touch and taste.
Researchers Discover How a Fish With Legs Uses Them To Find FoodCuriosity and serendipity helped two teams of scientists learn that one species of sea robin employs legs that have both the sense of touch and taste.
Read more »
