Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers at Sant Pau Research Institute, led by Dr. Ricard Rojas-García, have discovered a new mutation in the ARPP21 gene that may cause ALS, particularly noted in a high-incidence area in La Rioja, Spain. This finding, through whole-genome sequencing of familial and non-familial cases, suggests ARPP21 as a new ALS-linked gene.
The investigation was initiated after detecting an unusually high number of ALS cases in La Rioja, specifically in the southeast region of the autonomous community. The number of cases identified in the area, particularly familial, and the calculated minimum incidence considerably exceeded the number of cases expected during the study period given the usual incidence data, which are usually between two and three cases per 100,000 inhabitants annually.
The southeastern region of the community of La Rioja is an area of 1219.42 km². Between 2009 and 2022, it had an average population of 43,433, of which 31,324 were over 18 years of age. The population density was 35.62 inhabitants/km². This is an area with a high rate of emigration, so there may be cases in the rest of the State.Given an average incidence of ALS of 1.4–2.47 cases/100,000 people/year, we calculated an expected number of cases of 0.44–0.
Dr. Dols-Icardo believes that these findings could open new avenues for the diagnosis and treatment of ALS. The identification of ARPP21 as a causative gene underscores the importance of continued research in specific geographic areas to discover new genetic factors.Although this discovery has been made in a specific region of Spain, the researchers believe that it could have global implications.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
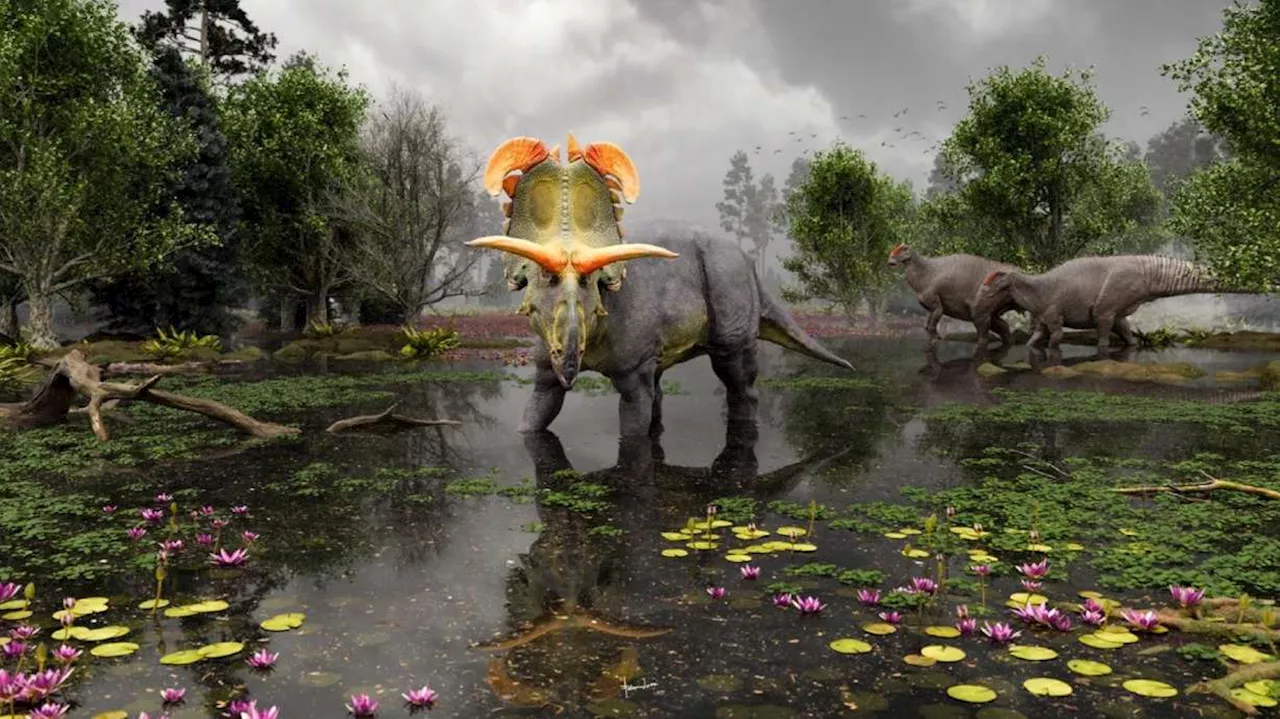 How Utah researchers helped discover a new 78 million-year-old dinosaur speciesUtah researchers helped lead a study outlining a previously unknown dinosaur species that once roamed the West.
How Utah researchers helped discover a new 78 million-year-old dinosaur speciesUtah researchers helped lead a study outlining a previously unknown dinosaur species that once roamed the West.
Read more »
 Using supercomputer researchers discover new clues to improving fusion confinementNuclear fusion—when two nuclei combine to form a new nucleus, thereby releasing energy—may be the clean, reliable, limitless power source of the future. But first, scientists must learn how to control its production.
Using supercomputer researchers discover new clues to improving fusion confinementNuclear fusion—when two nuclei combine to form a new nucleus, thereby releasing energy—may be the clean, reliable, limitless power source of the future. But first, scientists must learn how to control its production.
Read more »
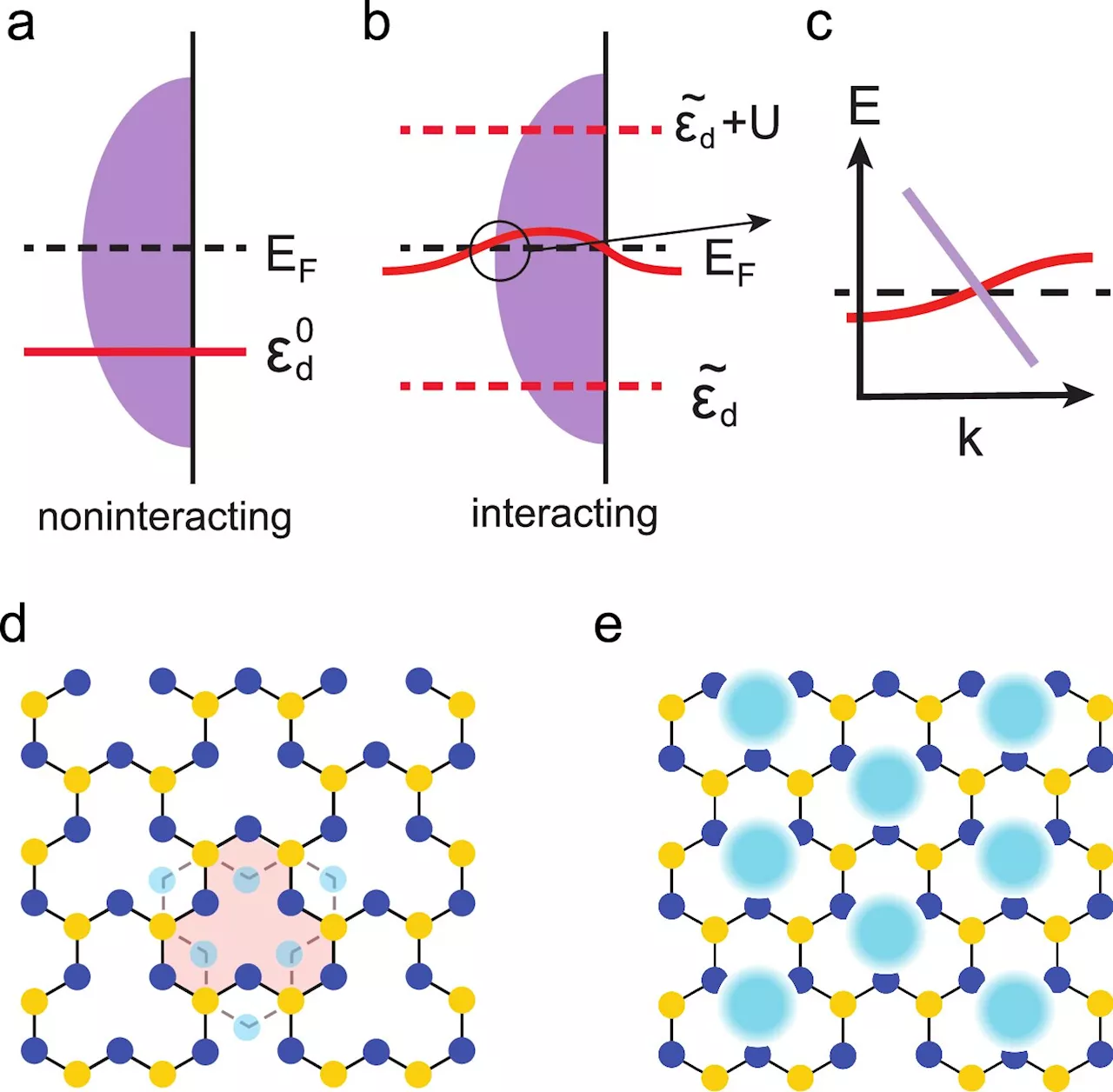 Researchers discover new flat electronic bands, paving way for advanced quantum materialsIn a study published in Nature Communications, a team of scientists led by Rice University's Qimiao Si predicts the existence of flat electronic bands at the Fermi level, a finding that could enable new forms of quantum computing and electronic devices.
Researchers discover new flat electronic bands, paving way for advanced quantum materialsIn a study published in Nature Communications, a team of scientists led by Rice University's Qimiao Si predicts the existence of flat electronic bands at the Fermi level, a finding that could enable new forms of quantum computing and electronic devices.
Read more »
 Researchers discover new flat electronic bands, paving way for advanced quantum materialsScientists predict the existence of flat electronic bands at the Fermi level, a finding that could enable new forms of quantum computing and electronic devices.
Researchers discover new flat electronic bands, paving way for advanced quantum materialsScientists predict the existence of flat electronic bands at the Fermi level, a finding that could enable new forms of quantum computing and electronic devices.
Read more »
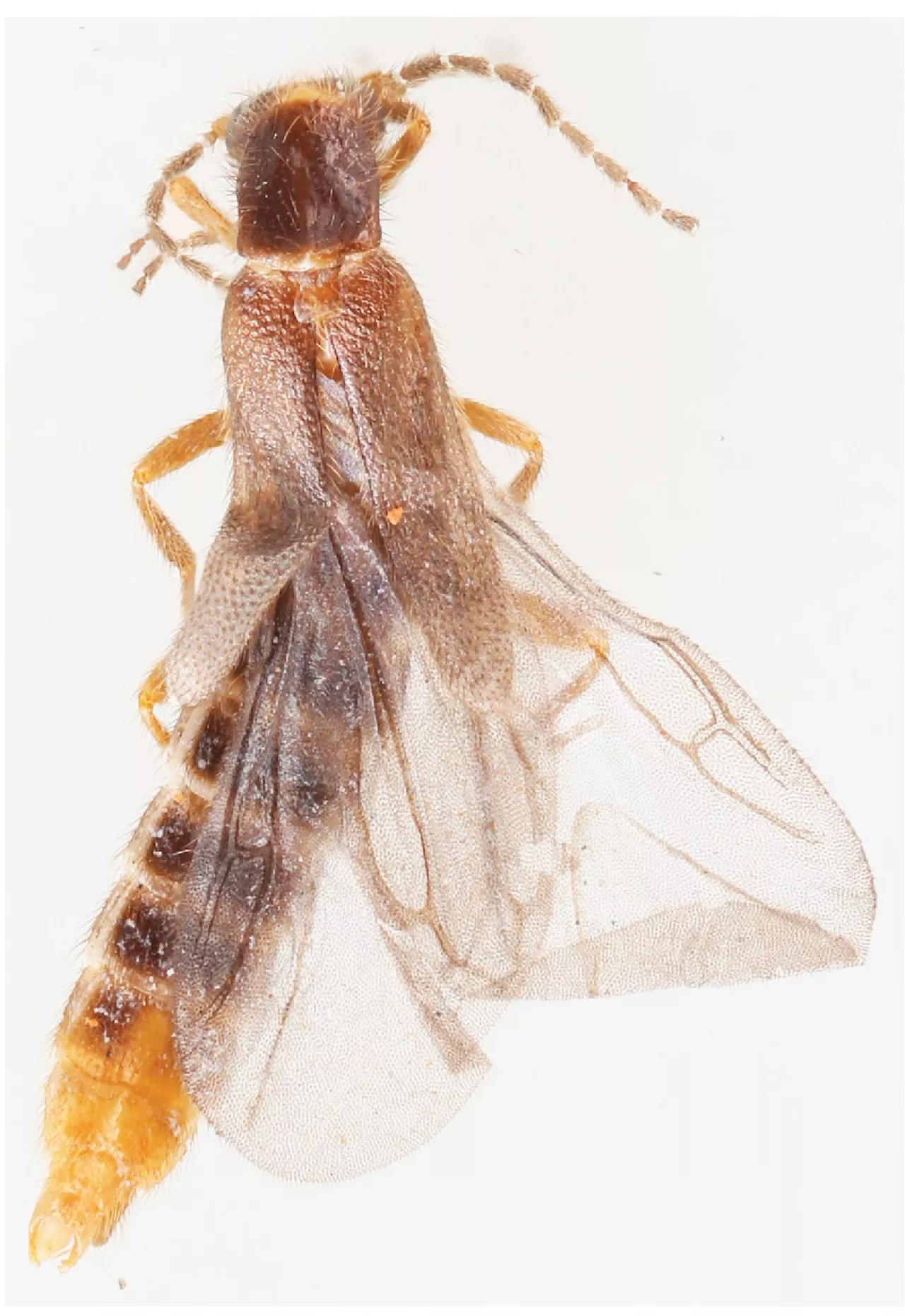 Researchers discover mysterious new beetle species in GuatemalaTogether with a Brazilian–German team, Senckenberg researcher Vinicius S. Ferreira has described a new species from the glowworm beetle genus Adendrocera. This group of insects is rare and only documented by very few specimens in scientific collections.
Researchers discover mysterious new beetle species in GuatemalaTogether with a Brazilian–German team, Senckenberg researcher Vinicius S. Ferreira has described a new species from the glowworm beetle genus Adendrocera. This group of insects is rare and only documented by very few specimens in scientific collections.
Read more »
 Researchers discover a new form of scientific fraud: Uncovering 'sneaked references'A researcher working alone—apart from the world and the rest of the wider scientific community—is a classic yet misguided image. Research is, in reality, built on continuous exchange within the scientific community: First you understand the work of others, and then you share your findings.
Researchers discover a new form of scientific fraud: Uncovering 'sneaked references'A researcher working alone—apart from the world and the rest of the wider scientific community—is a classic yet misguided image. Research is, in reality, built on continuous exchange within the scientific community: First you understand the work of others, and then you share your findings.
Read more »
