An estimated one in six people suffer from a brain disorder worldwide, according to the American Brain Foundation.
Mar 20 2024Virginia Tech Current research has provided some insight into cell-communication inside the brain, but there are still a lot of unknowns surrounding how this crucial organ functions. What if there was a comprehensive map that took into consideration not just the biology of the brain, but the specific location where the biology occurs?
Their goal? Mapping and visualization of the brain biology at genome scale in the most cost-effective way possible to improve healthy functioning. Epigenomic tomography involves the creation of a detailed map of the epigenome, or the genome-scale profile of the epigenetic change, across a large area and volume of the brain. Lu believes this is an important method for scientists to use to understand the genetic and environmental factors that affect the ways genes behave outside of DNA sequences.
Related StoriesOnce the digital tomography of the brain is reassembled, the researchers have a map that is characteristic of the brain's epigenome across a significant area. When the map changes, this reflects a significant change in terms of how the brain is performing at the epigenomic level, which Jia says is groundbreaking for understanding brain disorders.
Funding for their research came from a variety of sources who are interested in future drug development for neurological disorders, including: "Our findings wouldn't have been possible without the close collaboration across multiple disciplines," Jia said. "It's really exciting to see that epigenomic tomography facilitates the understanding of spatially dynamic processes across a large brain area underlying seizure, and I expect it can enable applications in a wide range of brain diseases in the future."
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
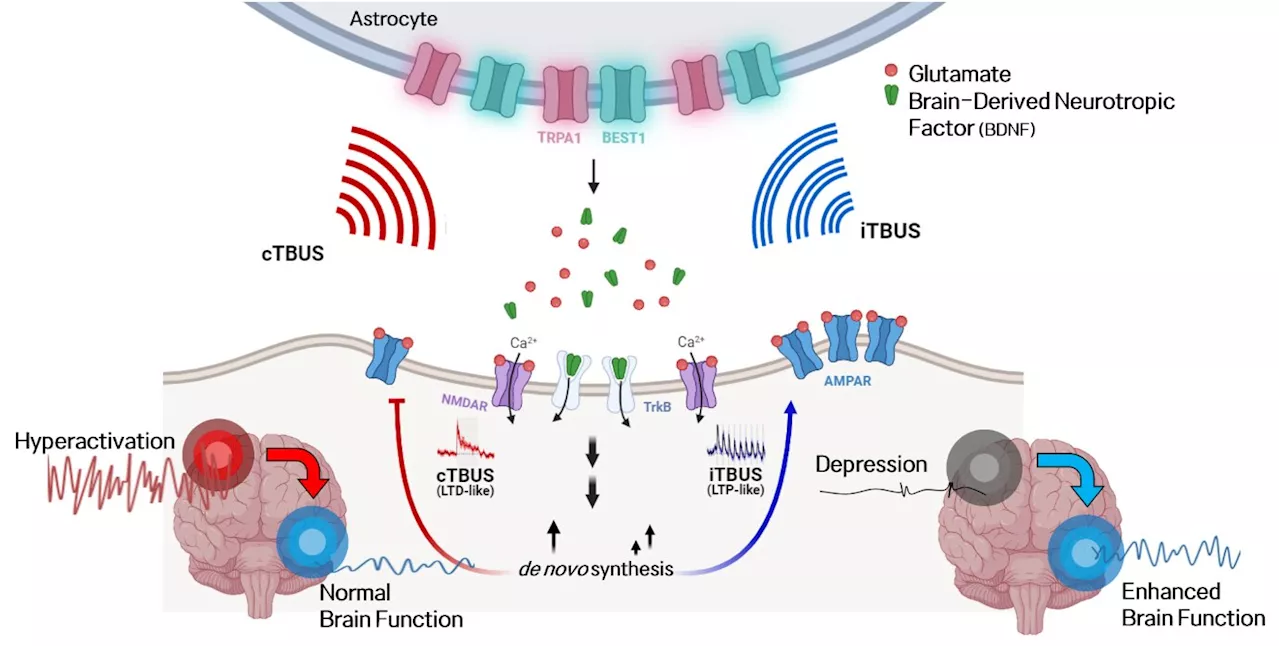 New brain stimulation technique shows promise for treating brain disordersThe human brain's adaptability to internal and external changes, known as neural plasticity, forms the foundation for understanding cognitive functions like memory and learning, as well as various neurological disorders.
New brain stimulation technique shows promise for treating brain disordersThe human brain's adaptability to internal and external changes, known as neural plasticity, forms the foundation for understanding cognitive functions like memory and learning, as well as various neurological disorders.
Read more »
 Study reveals novel brain recovery mechanism after traumatic brain injuryA team of Medical University of South Carolina researchers, led by Onder Albayram, Ph.D., reports in PNAS Nexus that they have discovered a novel protective response by which the brain naturally repairs itself after traumatic brain injury.
Study reveals novel brain recovery mechanism after traumatic brain injuryA team of Medical University of South Carolina researchers, led by Onder Albayram, Ph.D., reports in PNAS Nexus that they have discovered a novel protective response by which the brain naturally repairs itself after traumatic brain injury.
Read more »
 Non-invasive brain stimulation can change specific brain mechanism linked to human behaviorFor the first time, researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities showed that non-invasive brain stimulation can change a specific brain mechanism that is directly related to human behavior.
Non-invasive brain stimulation can change specific brain mechanism linked to human behaviorFor the first time, researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities showed that non-invasive brain stimulation can change a specific brain mechanism that is directly related to human behavior.
Read more »
 Breast Cancer Now funds researchers to investigate targeted radiotherapy for metastatic breast cancer in the brainResearchers are trialing a new type of targeted radiotherapy to treat secondary breast cancer tumors in the brain, thanks to new funding from Breast Cancer Now.
Breast Cancer Now funds researchers to investigate targeted radiotherapy for metastatic breast cancer in the brainResearchers are trialing a new type of targeted radiotherapy to treat secondary breast cancer tumors in the brain, thanks to new funding from Breast Cancer Now.
Read more »
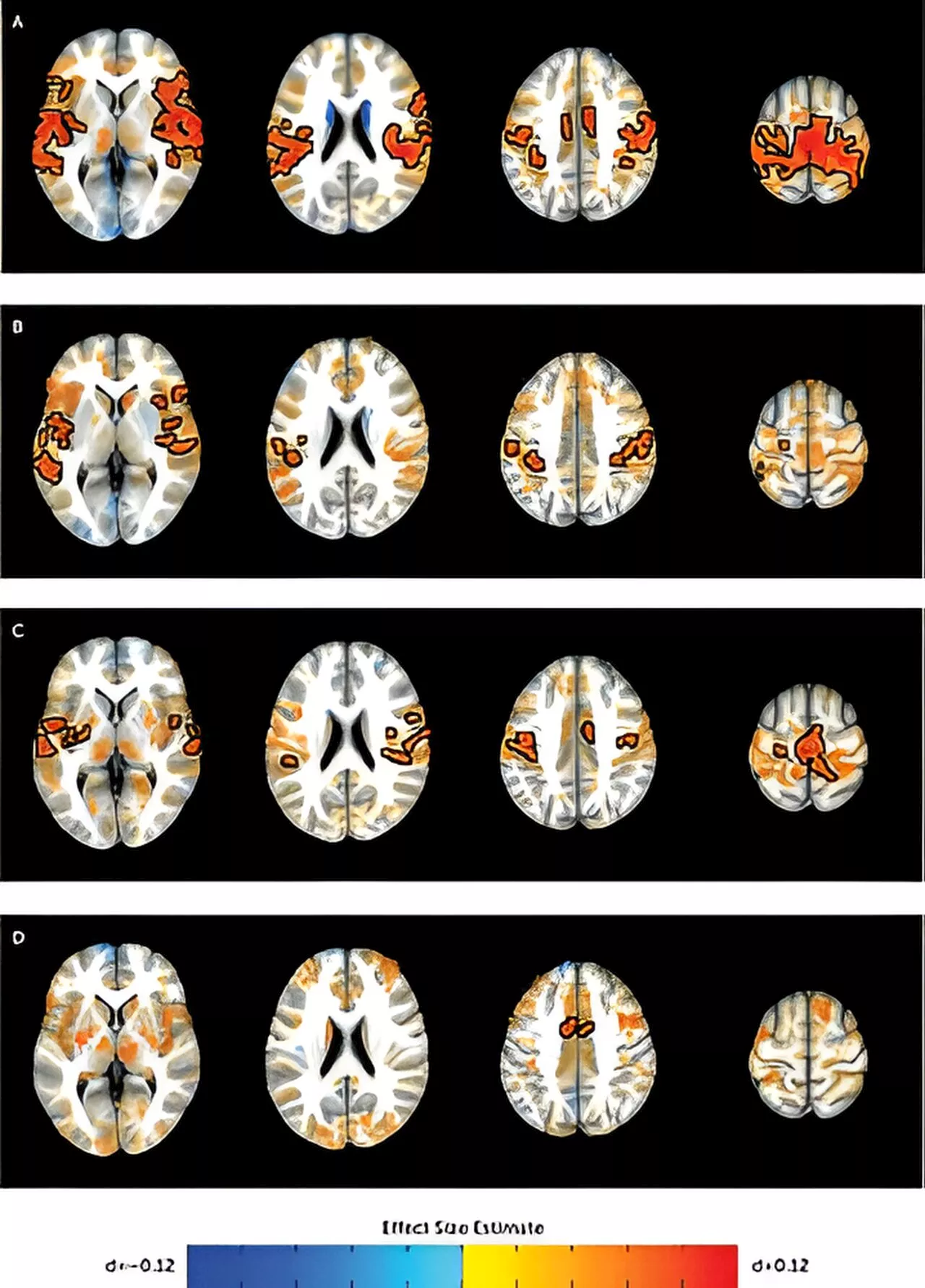 Researchers identify brain connections associated with ADHD in youthResearchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered that symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are tied to atypical interactions between the brain's frontal cortex and information processing centers deep in the brain.
Researchers identify brain connections associated with ADHD in youthResearchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered that symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are tied to atypical interactions between the brain's frontal cortex and information processing centers deep in the brain.
Read more »
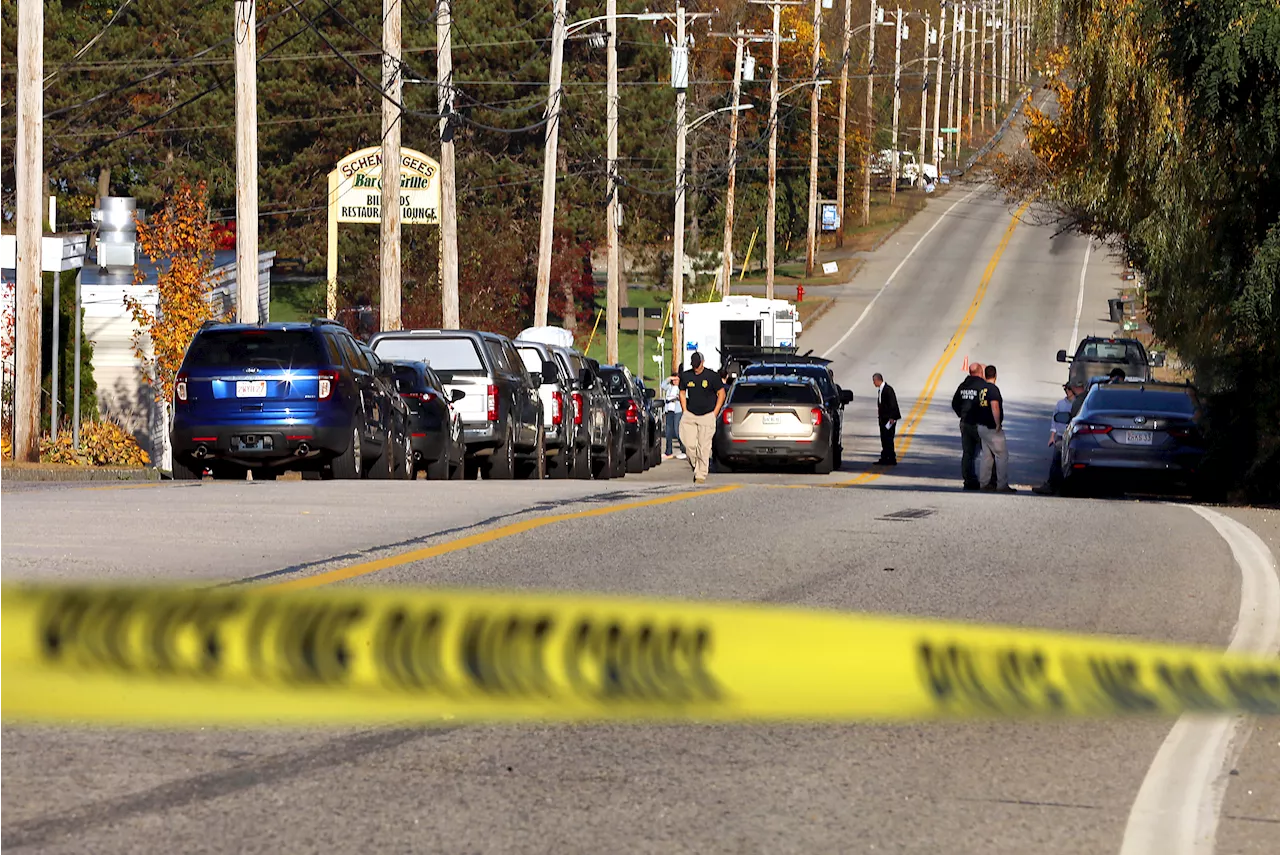 Brain of Lewiston gunman showed signs of traumatic injury, researchers sayThe brain of a gunman who killed 18 people and injured 13 others in Lewiston, Maine, showed signs of significant traumatic injury at the time of the mass…
Brain of Lewiston gunman showed signs of traumatic injury, researchers sayThe brain of a gunman who killed 18 people and injured 13 others in Lewiston, Maine, showed signs of significant traumatic injury at the time of the mass…
Read more »
