A team led by researchers has discovered that a group of cells located in the skin and other areas of the body, called neural crest stem cells, are the source of reprogrammed neurons found by other researchers.
Their findings refute the popular theory in cellular reprogramming that any developed cell can be induced to switch its identity to a completely unrelated cell type through the infusion of transcription factors.
"We believed that most cases of cell reprogramming could be attributed to a rare, multi-potential stem cell that is found throughout the body and lays dormant within populations of mature cells," said Justin Belair-Hickey, first author on the study and graduate student of U of T's Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research."It was not fully understood why reprogramming tends to be an inefficient process.
Neural crest stem cells are found throughout the body, including in skin, bone and connective tissue. Their distribution throughout the body, ability to be reprogrammed into many types of cells and accessibility within the skin for collection makes them a high-potential candidate for stem cell transplantation to treat disease.
Skin Cancer Lymphoma Nervous System Developmental Biology Biotechnology Biotechnology And Bioengineering Molecular Biology
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers restore the performance of quantum dot solar cells as if 'flattening crumpled paper'Researchers adopt a new ligand to enhance the efficiency and stability of perovskite quantum dot solar cells. Solar cell efficiency increases to 15.3% by correcting distortions on the surface of quantum dots.
Researchers restore the performance of quantum dot solar cells as if 'flattening crumpled paper'Researchers adopt a new ligand to enhance the efficiency and stability of perovskite quantum dot solar cells. Solar cell efficiency increases to 15.3% by correcting distortions on the surface of quantum dots.
Read more »
 Researchers identify key enzyme in aging cells to promote healthy agingA team has made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of aging and inflammation. Japan's aging population is growing at an unprecedented rate, making it crucial to extend healthy lifespans rather than just lifespans.
Researchers identify key enzyme in aging cells to promote healthy agingA team has made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of aging and inflammation. Japan's aging population is growing at an unprecedented rate, making it crucial to extend healthy lifespans rather than just lifespans.
Read more »
 Researchers targeting childhood heart disease with stem cells, AIResearchers in the U.S. and Australia are ushering in a new era of pediatric medicine by using stem cells and AI to solve childhood heart disease.
Researchers targeting childhood heart disease with stem cells, AIResearchers in the U.S. and Australia are ushering in a new era of pediatric medicine by using stem cells and AI to solve childhood heart disease.
Read more »
 San Francisco, Australian researchers targeting childhood heart disease with stem cells, AIThe global research program involves the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne and the Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco, with researchers working to identify the genetic causes of infant heart disease and develop new treatments for it through the use of stem cells and AI technology.
San Francisco, Australian researchers targeting childhood heart disease with stem cells, AIThe global research program involves the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute in Melbourne and the Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco, with researchers working to identify the genetic causes of infant heart disease and develop new treatments for it through the use of stem cells and AI technology.
Read more »
 Soil's secret language: Researchers decode plant-to-fungi communicationResearchers have cracked the code of plant-to-fungi communication in a new study. Using baker's yeast, the researchers discovered that the plant hormone strigolactone (SL) activates fungal genes and proteins associated with phosphate metabolism, a system that is key to growth.
Soil's secret language: Researchers decode plant-to-fungi communicationResearchers have cracked the code of plant-to-fungi communication in a new study. Using baker's yeast, the researchers discovered that the plant hormone strigolactone (SL) activates fungal genes and proteins associated with phosphate metabolism, a system that is key to growth.
Read more »
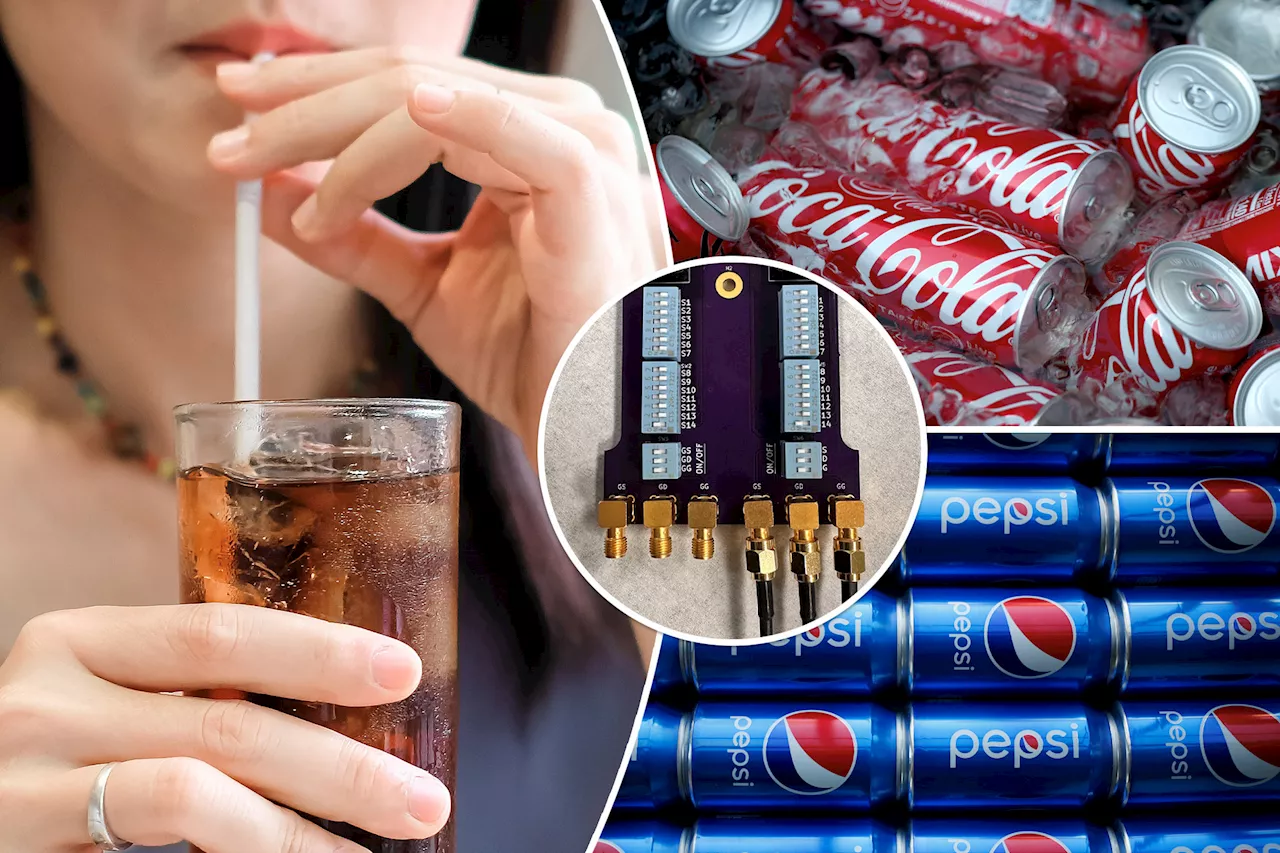 AI 'tongue' can 'taste' the difference between Coke and Pepsi, Penn State researchers revealCould this be the ultimate taste-tester?
AI 'tongue' can 'taste' the difference between Coke and Pepsi, Penn State researchers revealCould this be the ultimate taste-tester?
Read more »
