Regular Watermelon Consumption May Help Promote Cardio-Metabolic Health medicine science
, non-proteinaceous amino acids. Citrulline and arginine contents of watermelon vary according to variety and geographical region and in different parts of the watermelon.Dr. Britt Burton-Freeman“The current literature review provides evidence that watermelon intake and citrulline supplementation lower blood pressure in human trials.”
They explored studies related to the whole fruit as well as citrulline supplementation, focusing on key cardio-metabolic risk factors. “Our review provides evidence that watermelon intake and citrulline supplementation lower blood pressure in human trials,” the scientists said. “Emerging areas include brain and gut health indicated by nitric oxide bioavailability in all tissues and evidence showing improved gut barrier function and altered microbial composition after watermelon intake.”
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
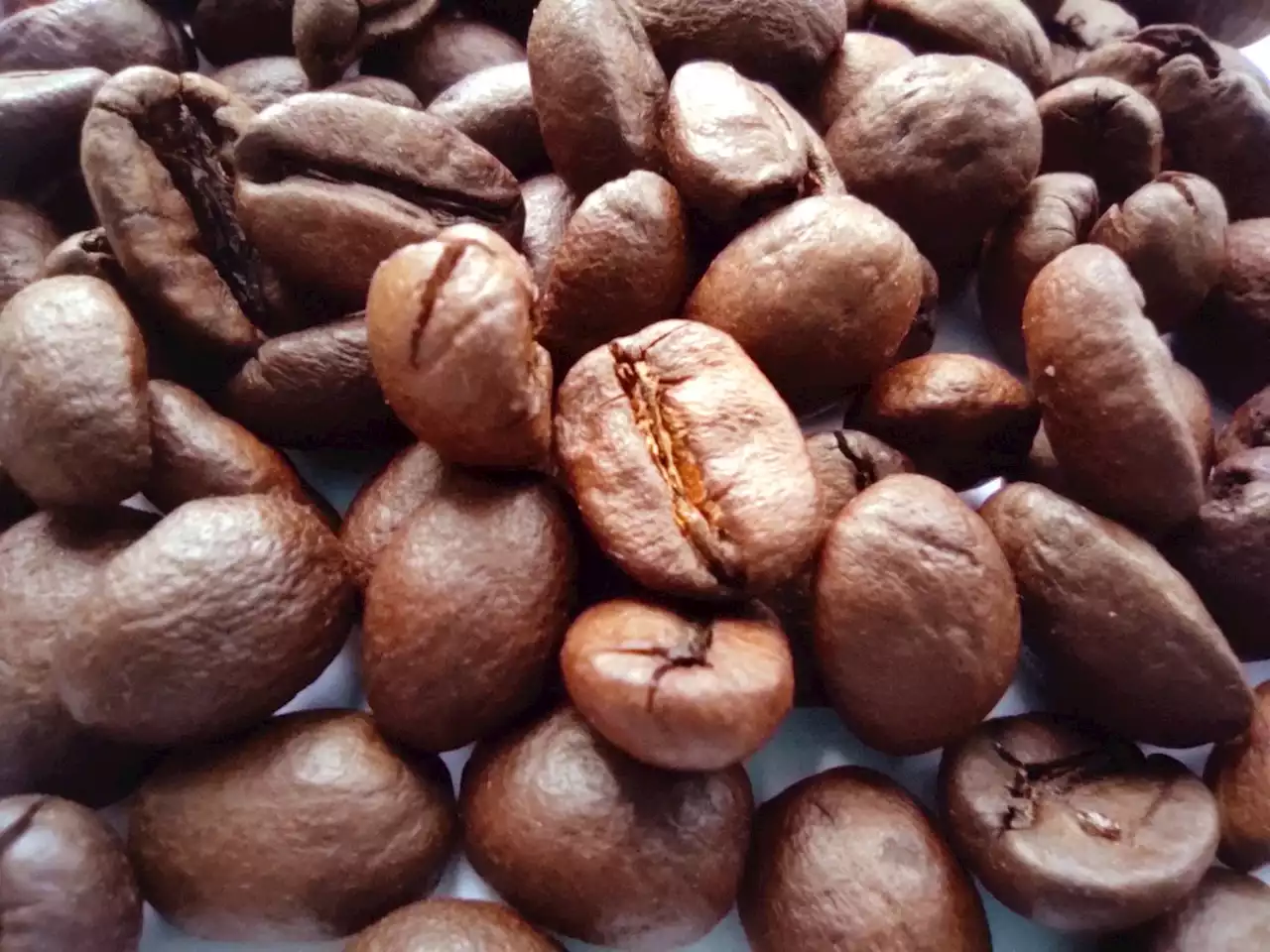 Coffee Consumption Has Stimulating Effect on Digestive Processes, New Review Says | Sci-News.comA new review of previous studies, published this week in the journal Nutrients, shows that coffee intake stimulates gastric, biliary, and pancreatic secretions, seeming to favor the first steps of the digestive process.
Coffee Consumption Has Stimulating Effect on Digestive Processes, New Review Says | Sci-News.comA new review of previous studies, published this week in the journal Nutrients, shows that coffee intake stimulates gastric, biliary, and pancreatic secretions, seeming to favor the first steps of the digestive process.
Read more »
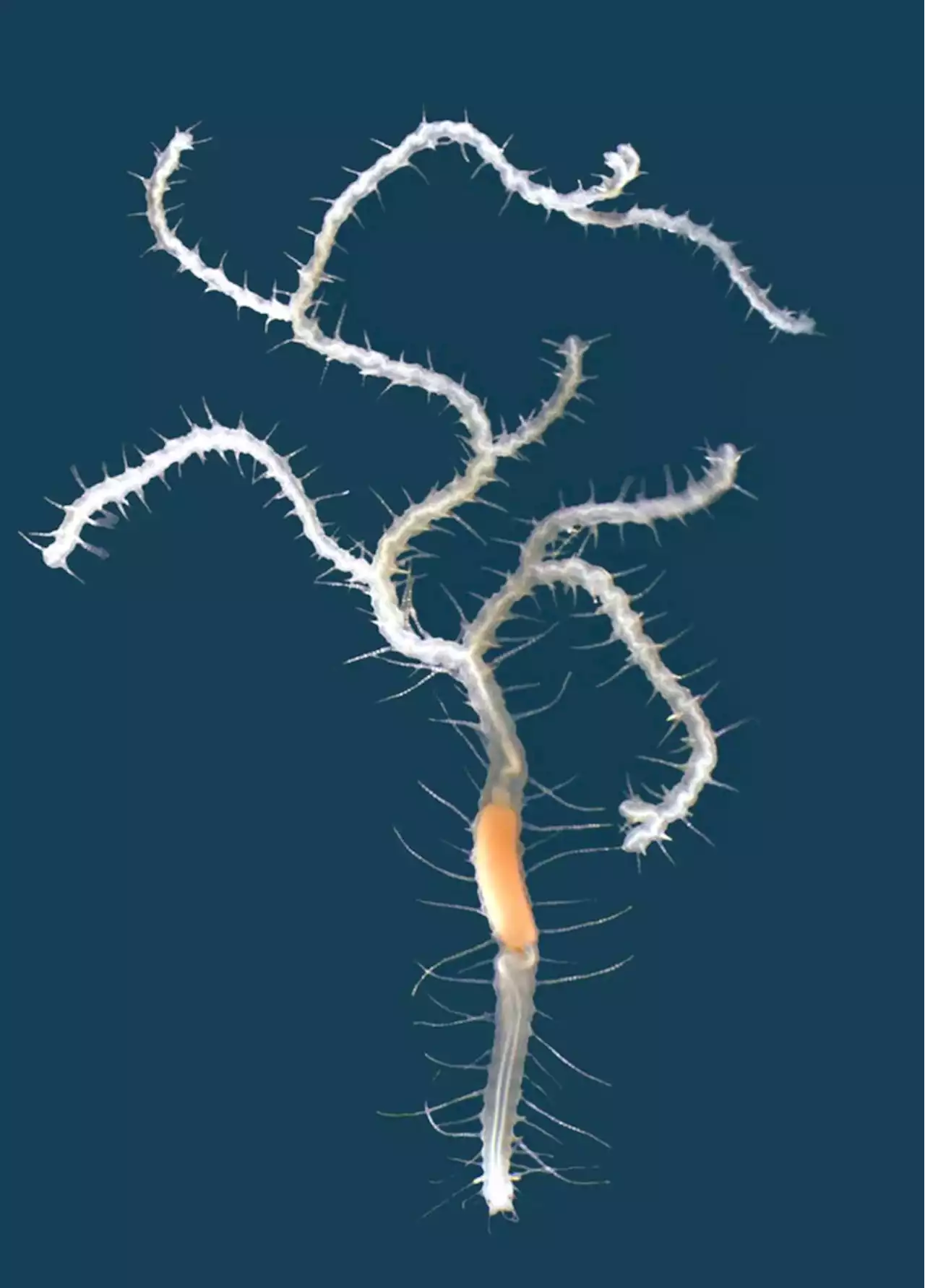 New Species of Branching Worm Discovered in Waters Off Japan | Sci-News.comMarine biologists have described a third species of branching syllid worm -- and the second within the genus Ramisyllis -- living inside an undescribed species of the sponge genus Petrosia found in shallow waters at Sado Island, Japan.
New Species of Branching Worm Discovered in Waters Off Japan | Sci-News.comMarine biologists have described a third species of branching syllid worm -- and the second within the genus Ramisyllis -- living inside an undescribed species of the sponge genus Petrosia found in shallow waters at Sado Island, Japan.
Read more »
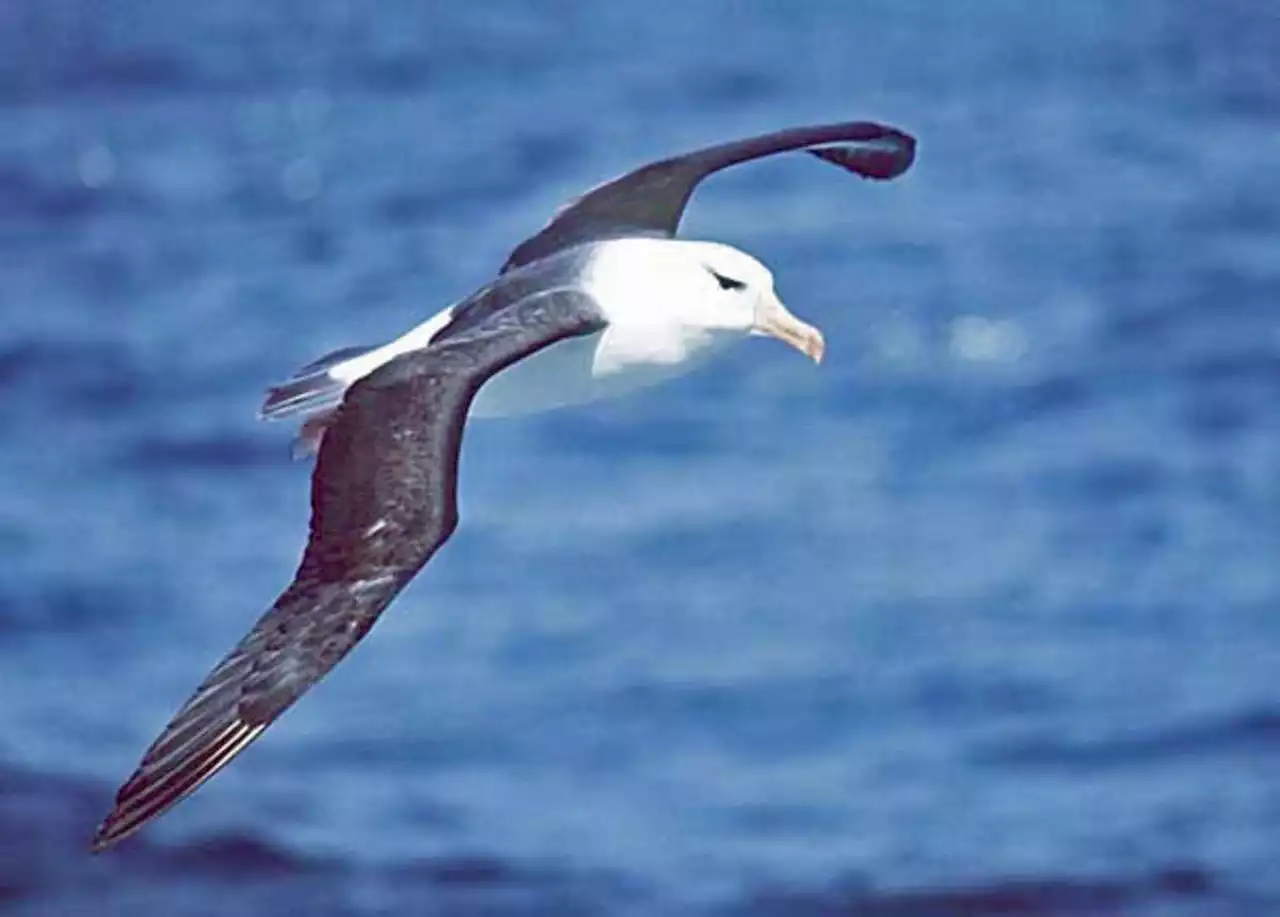 Albatrosses Can Dive to Much Greater Depths than Previously Thought | Sci-News.comNew research shows that the black-browed albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) can dive to much greater depths (19 m, or 62 feet) and for much longer (52 seconds) than previously thought.
Albatrosses Can Dive to Much Greater Depths than Previously Thought | Sci-News.comNew research shows that the black-browed albatross (Thalassarche melanophris) can dive to much greater depths (19 m, or 62 feet) and for much longer (52 seconds) than previously thought.
Read more »
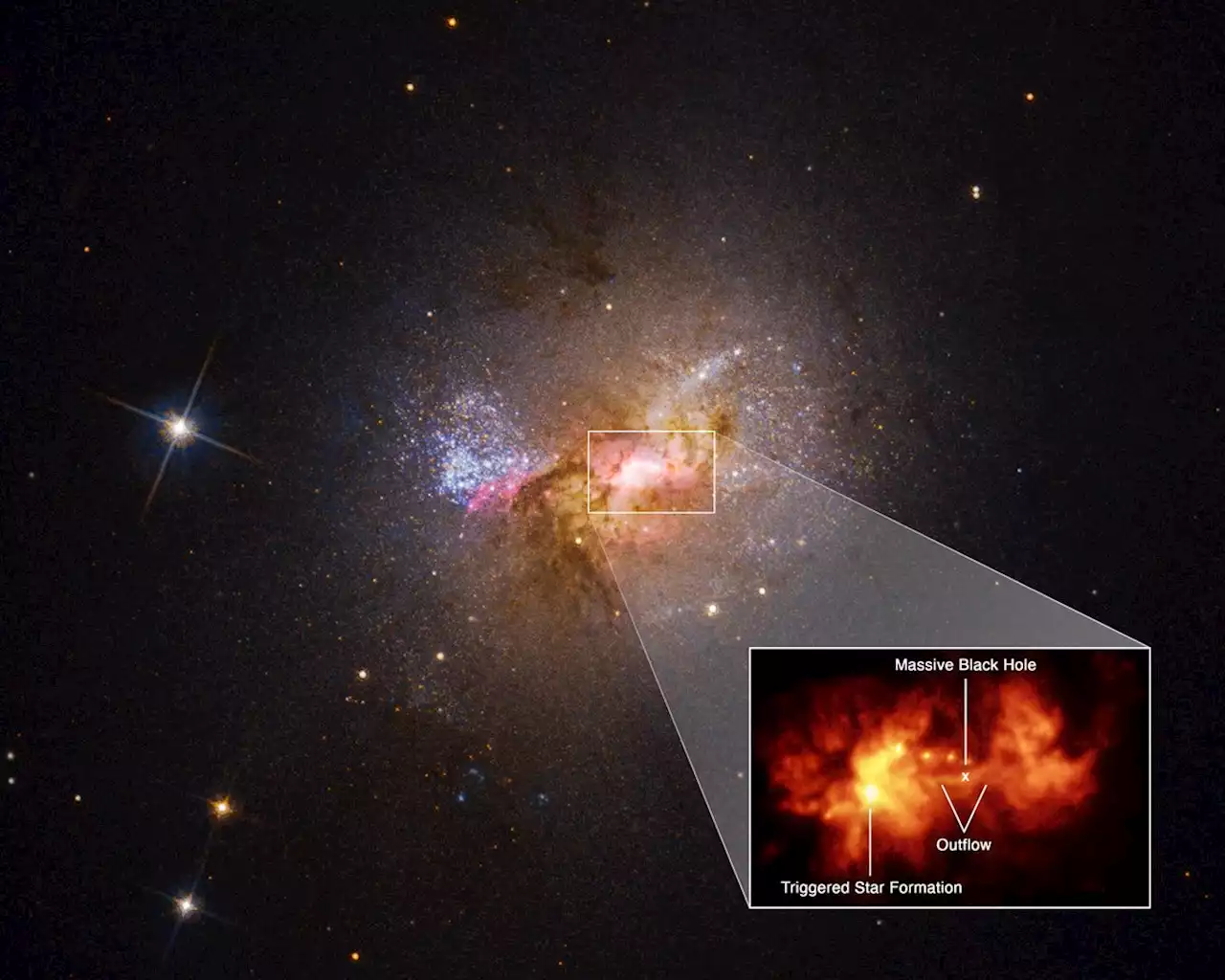 Supermassive Black Hole Triggered Star Formation in Dwarf Galaxy | Sci-News.comAstronomers have observed the central regions of Henize 2-10, a dwarf starburst galaxy previously reported to have a central massive black hole, at optical wavelengths using the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) on the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
Supermassive Black Hole Triggered Star Formation in Dwarf Galaxy | Sci-News.comAstronomers have observed the central regions of Henize 2-10, a dwarf starburst galaxy previously reported to have a central massive black hole, at optical wavelengths using the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) on the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
Read more »
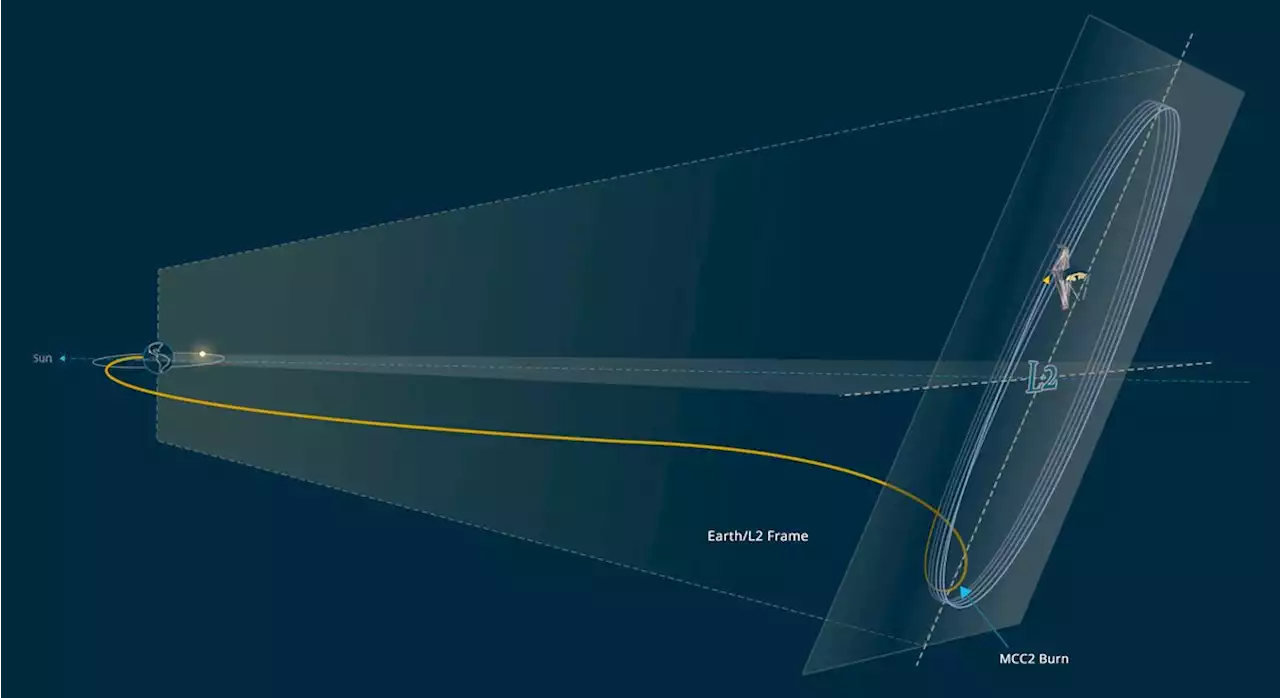 Webb Arrives at Second Lagrange Point of Sun-Earth System | Sci-News.comOn January 24, 2021, the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope fired its thrusters for 297 seconds to complete the final post launch course correction to its trajectory.
Webb Arrives at Second Lagrange Point of Sun-Earth System | Sci-News.comOn January 24, 2021, the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope fired its thrusters for 297 seconds to complete the final post launch course correction to its trajectory.
Read more »
 Physicists Detect Exotic Particles in Quark-Gluon Plasma | Sci-News.comPhysicists from the CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) Collaboration at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider have detected about 100 particles of a type known as X(3872) in quark-gluon plasma, an environment that they hope will illuminate the particles’ as-yet unknown structure.
Physicists Detect Exotic Particles in Quark-Gluon Plasma | Sci-News.comPhysicists from the CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) Collaboration at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider have detected about 100 particles of a type known as X(3872) in quark-gluon plasma, an environment that they hope will illuminate the particles’ as-yet unknown structure.
Read more »
