Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers from Singapore and China have experimentally observed negative entanglement entropy using classical electrical circuits, providing new insights into quantum phenomena without the complexities of true quantum systems. Their work suggests that electrical circuits could serve as a low-cost platform for exploring exotic quantum behaviors, with implications for future quantum technologies. Credit: SciTechDaily.
While usual gapless points that are not geometrically defective i.e. Dirac points possess only eigenvalues within , defective exceptional points also exhibit special isolated EB eigenvalues far outside of . It can be realized by an electric circuit . Credit: Science China Press High Entanglement: If the colors of the two socks are almost perfectly correlated, then knowing the color of one sock gives you almost perfect information about the other. In particular, if one sock suddenly becomes inaccessible, one would also lose knowledge of the color of the other sock.
While the theoretical recipe for achieving negative entanglement entropy in a non-Hermitian quantum system has been thought of since a few years ago, actually observing negative entanglement in quantum experiments cannot be easily done. This is due to significant challenges in manipulating intricate quantum states in a way that they gain or lose energy, while at the same time also measuring how entangled they are.
“EB states are special states that provide the key fingerprints for negative entanglement,” said Professor Haiyu Meng from Xiangtan University, co-author of this work. Whenever the host system becomes very sensitive due to the non-Hermiticity, EB states may emerge as a direct consequence of negative entanglement.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Solving Quantum Mysteries: Physicists Confirm Entropy Rule for EntanglementScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Solving Quantum Mysteries: Physicists Confirm Entropy Rule for EntanglementScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Physicists Rewrite Quantum Rules – New Theories Could Revolutionize Materials ScienceScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Physicists Rewrite Quantum Rules – New Theories Could Revolutionize Materials ScienceScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
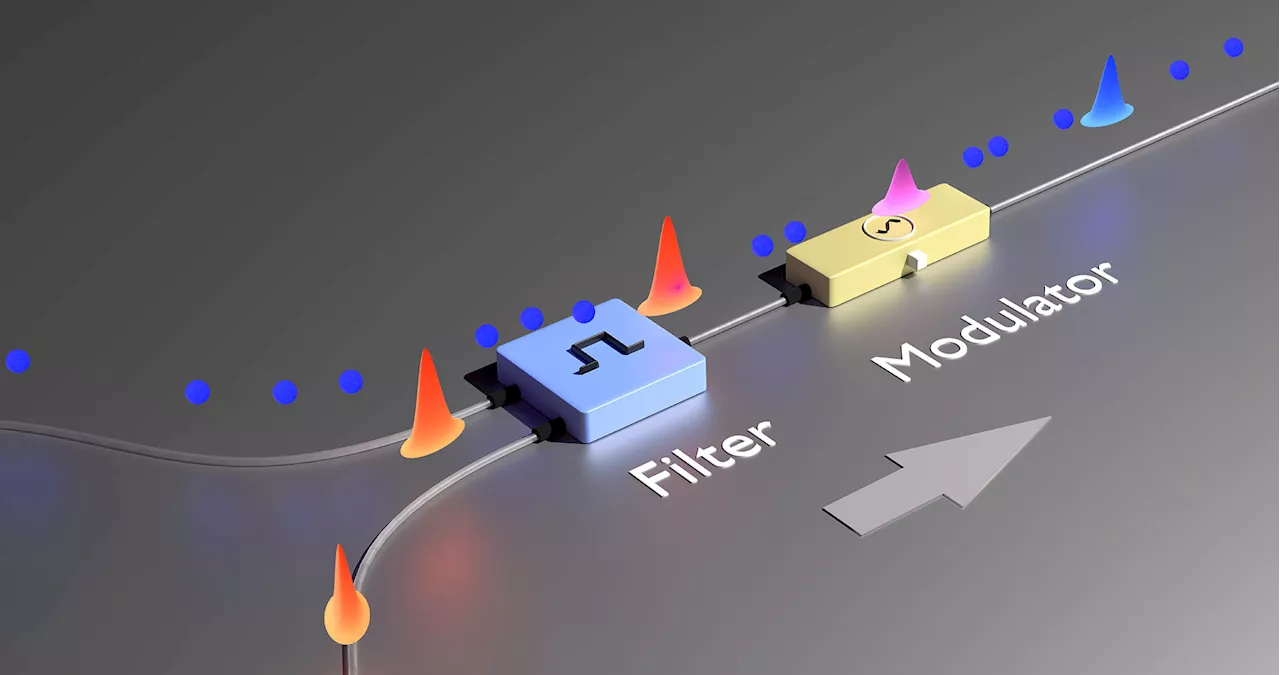 Physicists develop new method to combine conventional internet with the quantum internetFour researchers from the Institute of Photonics at Leibniz University Hannover have developed a new transmitter-receiver concept for transmitting entangled photons over an optical fiber. This breakthrough could enable the next generation of telecommunications technology, the quantum internet, to be routed via optical fibers.
Physicists develop new method to combine conventional internet with the quantum internetFour researchers from the Institute of Photonics at Leibniz University Hannover have developed a new transmitter-receiver concept for transmitting entangled photons over an optical fiber. This breakthrough could enable the next generation of telecommunications technology, the quantum internet, to be routed via optical fibers.
Read more »
 Physicists develop new method to combine conventional internet with the quantum internetResearchers send entangled photons and laser pulses of the same color over a single optical fiber for the first time.
Physicists develop new method to combine conventional internet with the quantum internetResearchers send entangled photons and laser pulses of the same color over a single optical fiber for the first time.
Read more »
 Physicists Develop Next-Gen Optical Fibers for Future Quantum Data TransferScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Physicists Develop Next-Gen Optical Fibers for Future Quantum Data TransferScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
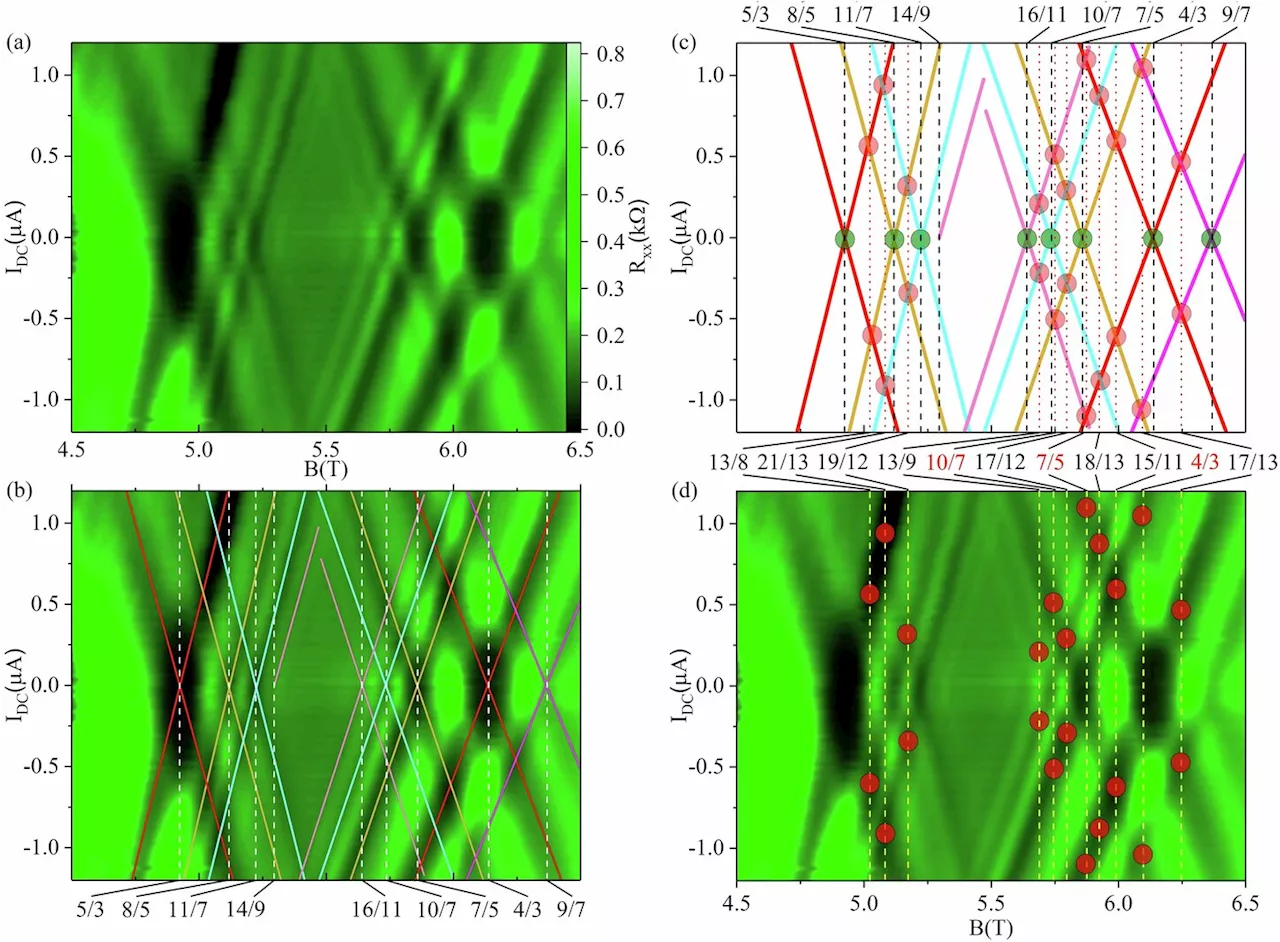 Physicists uncover new phenomena in fractional quantum Hall effectsImagine a two-dimensional flatland, instead of our three-dimensional world, where the rules of physics are turned on their head and particles like electrons defy expectations to reveal new secrets. That's exactly what a team of researchers, including Georgia State University Professor of Physics Ramesh G. Mani and recent Ph.D. graduate U.
Physicists uncover new phenomena in fractional quantum Hall effectsImagine a two-dimensional flatland, instead of our three-dimensional world, where the rules of physics are turned on their head and particles like electrons defy expectations to reveal new secrets. That's exactly what a team of researchers, including Georgia State University Professor of Physics Ramesh G. Mani and recent Ph.D. graduate U.
Read more »
