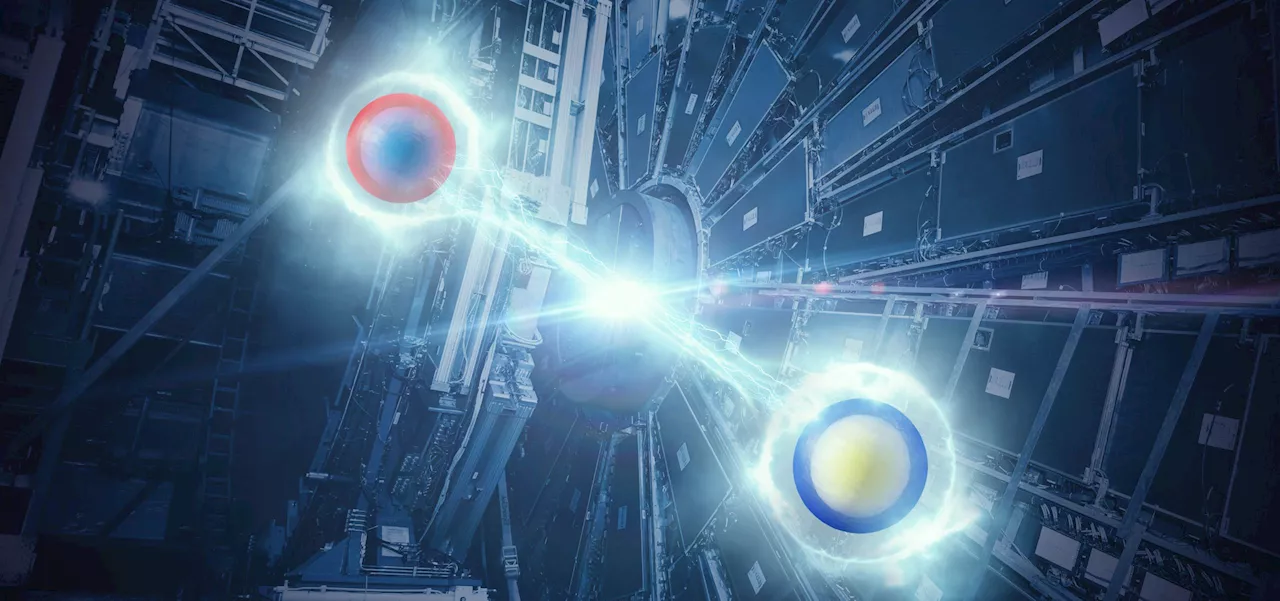
Explores the phenomenon of quantum entanglement, where two particles become linked and share the same fate regardless of distance. Despite seeming to violate the speed of light, it doesn't involve information transfer.
Illustration depicting quantum entanglement between particles. Credit: ATLAS Experiment Entanglement is perhaps one of the most confusing aspects of quantum mechanics. On its surface, entanglement allows particles to communicate over vast distances instantly, apparently violating the speed of light. But while entangled particles are connected, they don’t necessarily share information between them. In quantum mechanics, a particle isn’t really a particle.
Instead of being a hard, solid, precise point, a particle is really a cloud of fuzzy probabilities, with those probabilities describing where we might find the particle when we go to actually look for it. But until we actually perform a measurement, we can’t exactly know everything we’d like to know about the particle. These fuzzy probabilities are known as quantum states. In certain circumstances, we can connect two particles in a quantum way, so that a single mathematical equation describes both sets of probabilities simultaneously. When this happens, we say thatWhen particles share a quantum state, then measuring the properties of one can grant us automatic knowledge of the state of the other. For example, let’s look at the case of quantum spin, a property of subatomic particles. For particles like electrons, the spin can be in one of two states, either up or down. Once we entangle two electrons, their spins are correlated. We canIf we measure the first particle, we might randomly find the spin pointing up. What does this tell us about the second particle? Since we carefully arranged our entangled quantum state, we now know with 100% absolute certainty that the second particle must be pointing down. Its quantum state was entangled with the first particle, and as soon as one revelation is made, both revelations are mad
QUANTUM MECHANICS ENTANGLEMENT PARTICLES SPIN QUANTUM STATES
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 'Spooky action' at a very short distance: Scientists map out quantum entanglement in protonsScientists have a new way to use data from high-energy particle smashups to peer inside protons. Their approach uses quantum information science to map out how particle tracks streaming from electron-proton collisions are influenced by quantum entanglement inside the proton.
'Spooky action' at a very short distance: Scientists map out quantum entanglement in protonsScientists have a new way to use data from high-energy particle smashups to peer inside protons. Their approach uses quantum information science to map out how particle tracks streaming from electron-proton collisions are influenced by quantum entanglement inside the proton.
Read more »
 Scientists created the world’s first engine powered by quantum entanglement instead of gas or oilResearchers have finally created a quantum engine that runs off entanglement and it could revolutionize quantum mechanics.
Scientists created the world’s first engine powered by quantum entanglement instead of gas or oilResearchers have finally created a quantum engine that runs off entanglement and it could revolutionize quantum mechanics.
Read more »
 New quantum computing milestone smashes entanglement world recordOwen Hughes is a freelance writer and editor specializing in data and digital technologies. Previously a senior editor at ZDNET, Owen has been writing about tech for more than a decade, during which time he has covered everything from AI, cybersecurity and supercomputers to programming languages and public sector IT.
New quantum computing milestone smashes entanglement world recordOwen Hughes is a freelance writer and editor specializing in data and digital technologies. Previously a senior editor at ZDNET, Owen has been writing about tech for more than a decade, during which time he has covered everything from AI, cybersecurity and supercomputers to programming languages and public sector IT.
Read more »
 Riding the light highway: Quantum entanglement on live internet cables achievedFor quantum computing to take off, quantum networks need to be developed as well. This research shows how existing infrastructure can help.
Riding the light highway: Quantum entanglement on live internet cables achievedFor quantum computing to take off, quantum networks need to be developed as well. This research shows how existing infrastructure can help.
Read more »
 Advancing a trustworthy quantum era: A novel approach to quantum protocol verificationThe future of data security depends on the reliable application of quantum technology, but its widespread adoption requires rigorous verification. Researchers have developed a novel approach to verify quantum protocols, ensuring their reliability in safety- and security-critical applications.
Advancing a trustworthy quantum era: A novel approach to quantum protocol verificationThe future of data security depends on the reliable application of quantum technology, but its widespread adoption requires rigorous verification. Researchers have developed a novel approach to verify quantum protocols, ensuring their reliability in safety- and security-critical applications.
Read more »
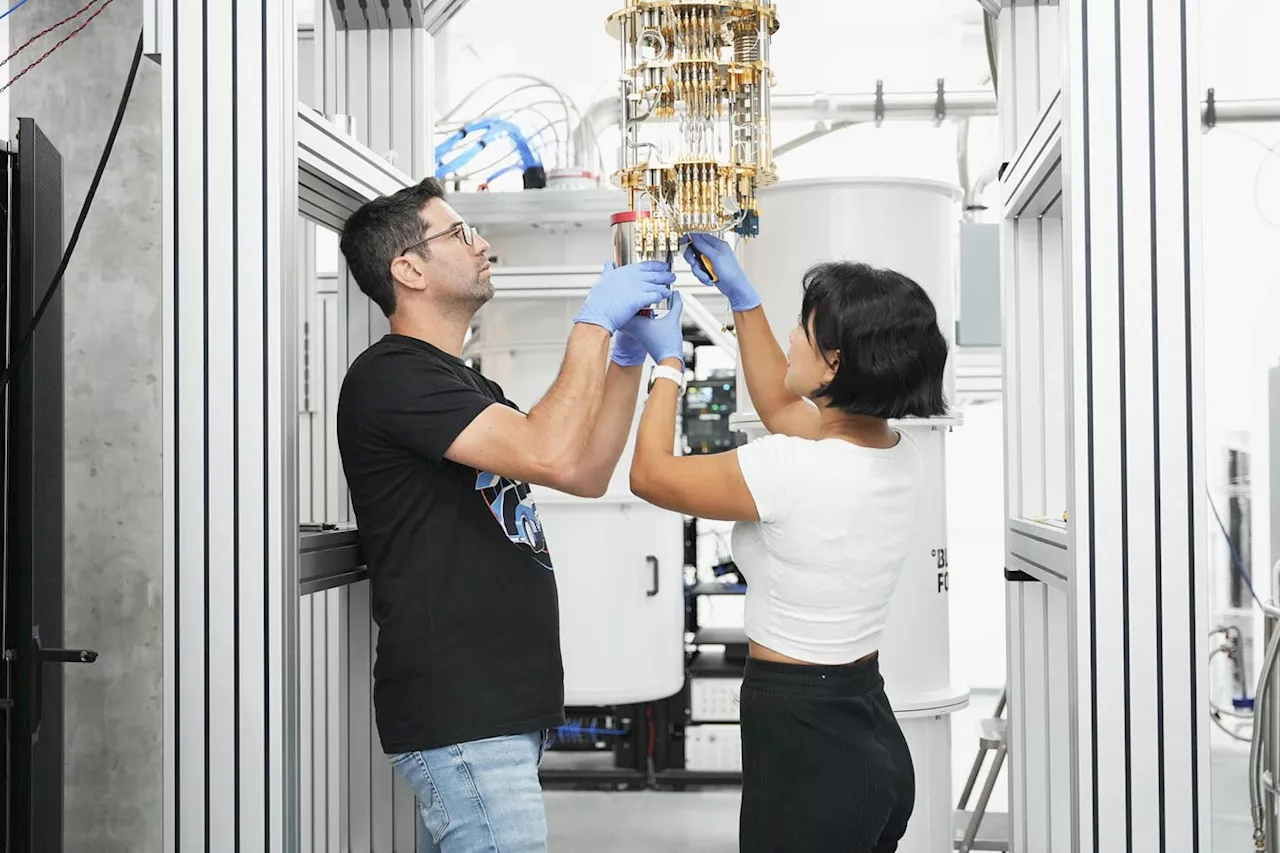 Nvidia, Rigetti, Quantum Machines Deliver AI-Powered Quantum ComputingQuantum Machines, Rigetti Computing, and Nvidia announced the successful application of AI to automate the calibration of a quantum computer.
Nvidia, Rigetti, Quantum Machines Deliver AI-Powered Quantum ComputingQuantum Machines, Rigetti Computing, and Nvidia announced the successful application of AI to automate the calibration of a quantum computer.
Read more »