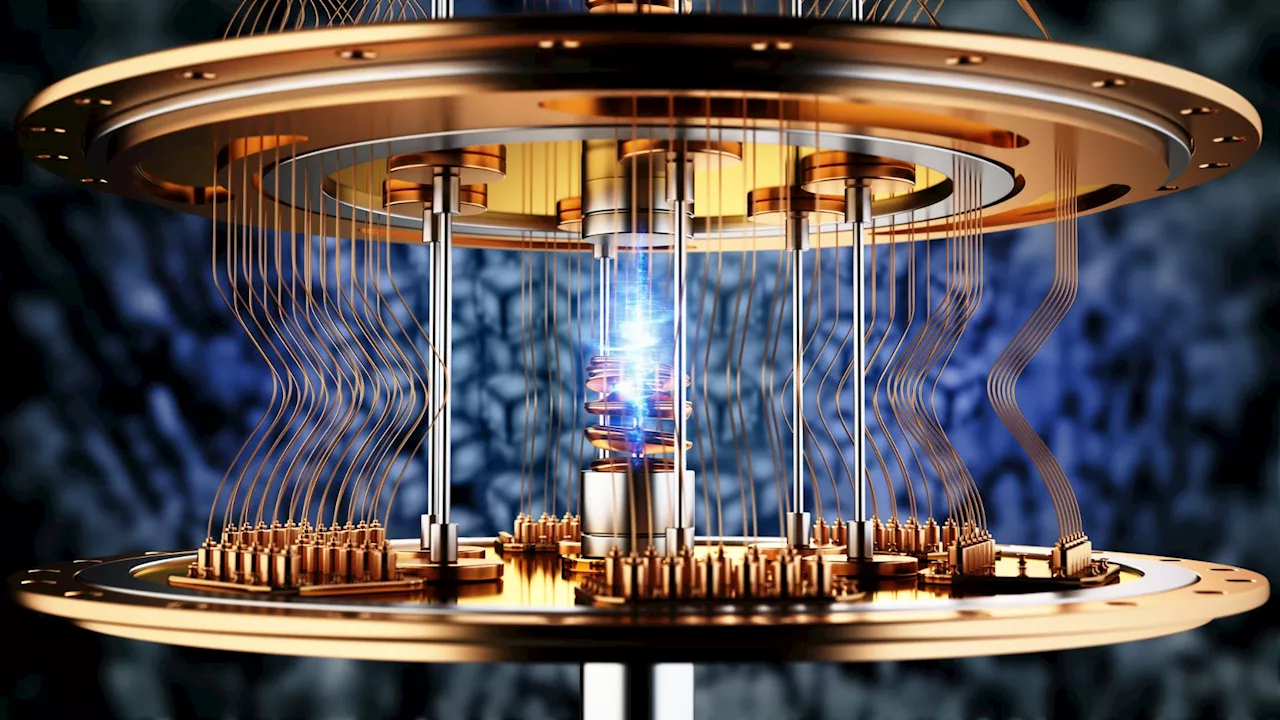
Researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) have made a breakthrough in quantum computing by successfully implementing a complete optical readout of superconducting qubits. This innovative approach promises to enable the development of more robust, scalable, room-temperature, and cost-effective quantum computers.
Researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology in Austria have achieved a major milestone in quantum computing after obtaining a complete optical readout of superconducting qubits.This will help in building scalable quantum computers that are robust, operate at room temperature, and at a much lower cost, a press release said. Quantum computers are the next frontier of computing, allowing calculations to occur at exponential rates compared to classical computers.
While this makes them ideal for qubit readouts, the challenge is communicating between these two and translating the optical signals to qubits and back. Representative image of a fiber optic network. Image credit: pingingz/iStockMicrowaves to the rescue“Ideally, one would try to get rid of all electrical signals, as the required wiring transports a lot of heat into the cooling chambers where the qubits are.
QUANTUM COMPUTING OPTICAL READOUT SUPERCONDUCTING QUBITS ROOM TEMPERATURE COMPUTING SCALABILITY
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Synchronization in neural nets: Mathematical insight into neuron readout drives significant improvements in prediction accuracyResearchers applied the mathematical theory of synchronization to clarify how recurrent neural networks (RNNs) generate predictions, revealing a certain map, based on the generalized synchronization, that yields correct target values.
Synchronization in neural nets: Mathematical insight into neuron readout drives significant improvements in prediction accuracyResearchers applied the mathematical theory of synchronization to clarify how recurrent neural networks (RNNs) generate predictions, revealing a certain map, based on the generalized synchronization, that yields correct target values.
Read more »
 Quantum internet breakthrough: Tin-vacancy qubits get signal boostA new study has figured out a way to measure the spin of tin-based qubits with 87 percent accuracy, enhancing the strength of signals from these qubits to a great extent.
Quantum internet breakthrough: Tin-vacancy qubits get signal boostA new study has figured out a way to measure the spin of tin-based qubits with 87 percent accuracy, enhancing the strength of signals from these qubits to a great extent.
Read more »
 ‘Magic-angle’: Graphene’s superconductivity secret can fuel quantum computingMIT scientists have unlocked why magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene behaves like superconducting material.
‘Magic-angle’: Graphene’s superconductivity secret can fuel quantum computingMIT scientists have unlocked why magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene behaves like superconducting material.
Read more »
 Sony to End Production of Recordable Optical MediaSony will halt production of recordable Blu-ray discs, MiniDiscs, MD Data, and MiniDV cassettes next month due to declining sales. The company says there will be no successor models. While Sony is discontinuing these formats, they will still be available from other manufacturers like Verbatim.
Sony to End Production of Recordable Optical MediaSony will halt production of recordable Blu-ray discs, MiniDiscs, MD Data, and MiniDV cassettes next month due to declining sales. The company says there will be no successor models. While Sony is discontinuing these formats, they will still be available from other manufacturers like Verbatim.
Read more »
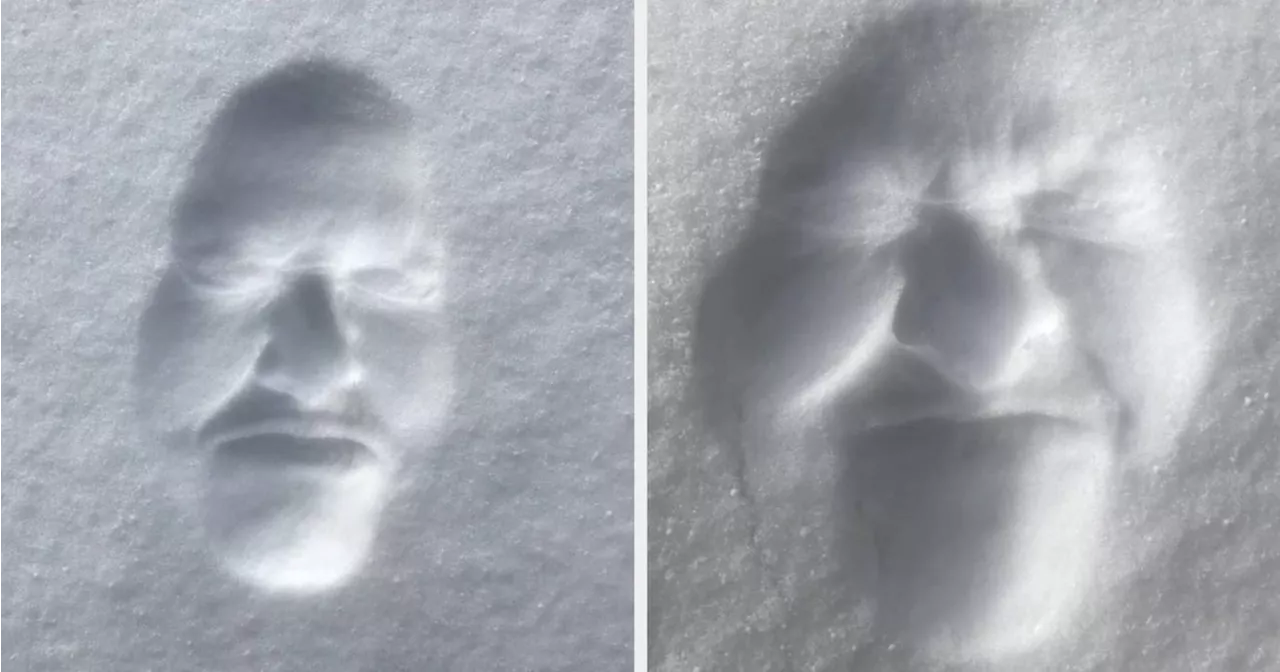 Confusing Perspective: Optical Illusions That Will Make You See DoubleGet ready to have your mind blown! This week's collection of optical illusions and mind-bending images will leave you questioning what you see. From disappearing heads and impossible perspectives to cleverly disguised animals, these tricks will challenge your perception and make you look twice.
Confusing Perspective: Optical Illusions That Will Make You See DoubleGet ready to have your mind blown! This week's collection of optical illusions and mind-bending images will leave you questioning what you see. From disappearing heads and impossible perspectives to cleverly disguised animals, these tricks will challenge your perception and make you look twice.
Read more »
 Programmable Photonic Latch: A Breakthrough in Optical MemoryResearchers at Nokia Bell Labs have developed a new type of optical memory called a programmable photonic latch, offering a high-speed and scalable solution for volatile memory using silicon photonics. This innovative technology, inspired by electronic set-reset latches, enables temporary data storage in optical processing systems, paving the way for faster and more energy-efficient computing.
Programmable Photonic Latch: A Breakthrough in Optical MemoryResearchers at Nokia Bell Labs have developed a new type of optical memory called a programmable photonic latch, offering a high-speed and scalable solution for volatile memory using silicon photonics. This innovative technology, inspired by electronic set-reset latches, enables temporary data storage in optical processing systems, paving the way for faster and more energy-efficient computing.
Read more »