Researchers have developed a new technology called tARC-seq that revealed a genetic mechanism affecting SARS-CoV-2 divergence and enabled the team to calculate SARS-CoV-2's mutation rate.
Researchers have developed a new technology called tARC-seq that revealed a genetic mechanism affecting SARS-CoV-2 divergence and enabled the team to calculate SARS-CoV-2's mutation rate. Using tARC-seq, the researchers also captured new mutations in SARS-CoV-2 in infected cells in the lab that recapitulated observations revealed by worldwide pandemic viral sequencing data. The findings can be useful for monitoring viral evolution in the human population.
"The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses RNA, instead of DNA, to store its genetic information. Our lab has long been interested in studying RNA biology, and when SARS-CoV-2 emerged we decided to investigate its process of RNA replication, which is typically error prone in RNA viruses," said corresponding author Dr. Christophe Herman, professor of molecular and human genetics and of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor.
"This idea contrasted with the fact that during the pandemic new COVID variants emerged often around the world," Herman said."Since the pandemic began, we've seen a number of prominent variants, including Alpha, Beta, Delta and Omicron, as well as variants within these groups." The tARC-seq method also revealed that the generation of new variants involved template switching."We determined that, as RdRp is copying one RNA template or sequence, it jumps to another template on a nearby virus and then continues copying the RNA, so the resulting new RNA copy is a mixture of both RNA templates," Herman said."This template switching will result in sequence insertions or deletions that bring about viral variability. We also observed complex mutations.
The study was supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01GM088653, 3R01AG061105-03S1, 1R21CA259780 and 1R21HG011229, and by National Science Foundation grant DBI-2032904.Catherine C. Bradley, Chen Wang, Alasdair J. E. Gordon, Alice X. Wen, Pamela N. Luna, Matthew B. Cooke, Brendan F. Kohrn, Scott R. Kennedy, Vasanthi Avadhanula, Pedro A. Piedra, Olivier Lichtarge, Chad A. Shaw, Shannon E. Ronca, Christophe Herman.
Genes Human Biology Viruses Vaccines Infectious Diseases HIV And AIDS Influenza
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
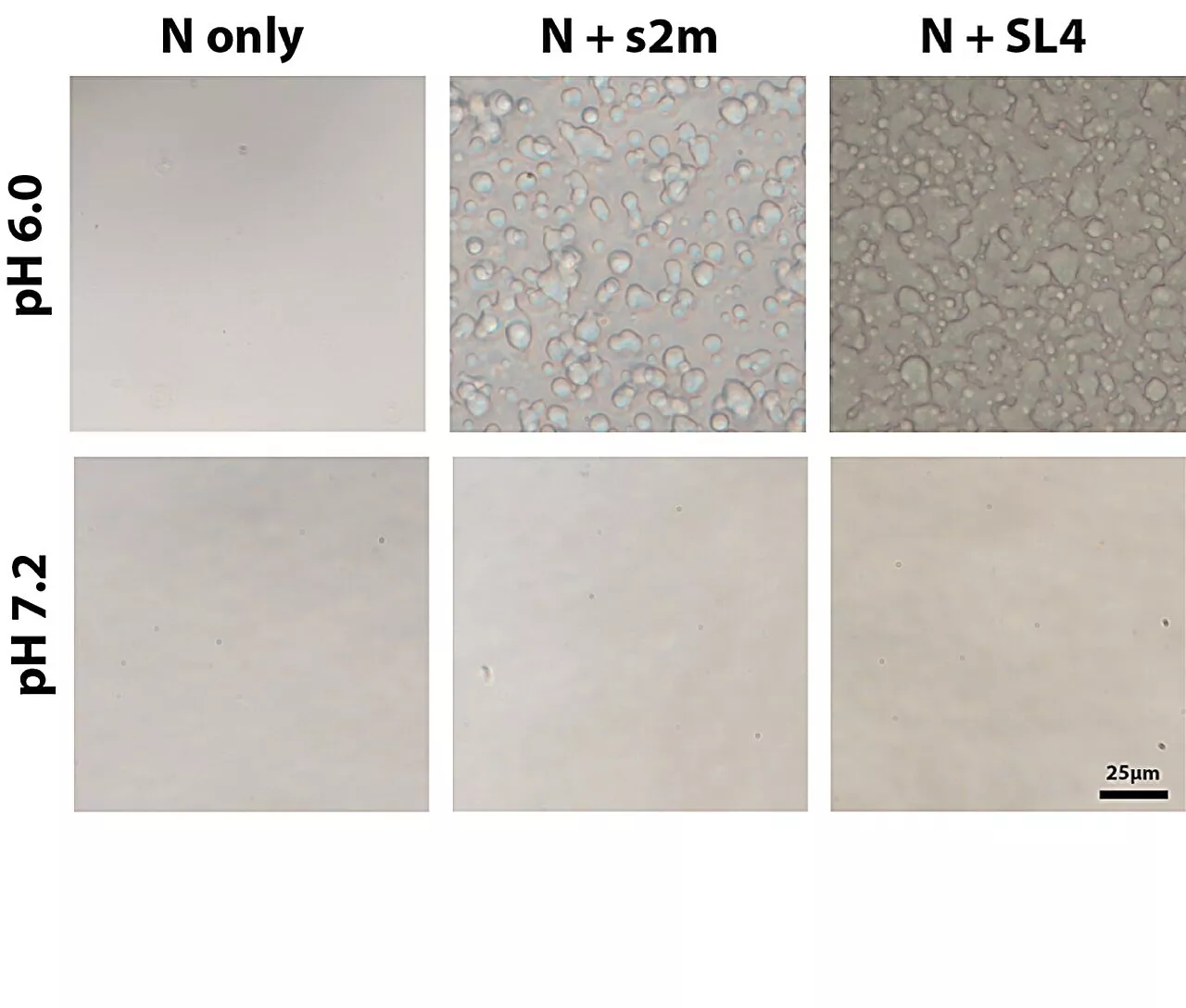 Scientists report the effect of buffer and pH on SARS-CoV-2 N protein phase separationScientists have discovered that buffer and pH levels have a strong impact on the phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 N protein.
Scientists report the effect of buffer and pH on SARS-CoV-2 N protein phase separationScientists have discovered that buffer and pH levels have a strong impact on the phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 N protein.
Read more »
 The pandemic cost 7 million lives, but talks to prevent a repeat stallAn unknown future pathogen could have far more devastating consequences than SARS-CoV-2.
The pandemic cost 7 million lives, but talks to prevent a repeat stallAn unknown future pathogen could have far more devastating consequences than SARS-CoV-2.
Read more »
 The pandemic cost 7 million lives, but talks to prevent a repeat stallAn unknown future pathogen could have far more devastating consequences than SARS-CoV-2.
The pandemic cost 7 million lives, but talks to prevent a repeat stallAn unknown future pathogen could have far more devastating consequences than SARS-CoV-2.
Read more »
 Mama's Day tasting event returns with new leader, new location and new dateNow in its 33rd year, the annual food event raises money for Mama's Kitchen charity, which provides home-delivered meals to critically ill San Diegans
Mama's Day tasting event returns with new leader, new location and new dateNow in its 33rd year, the annual food event raises money for Mama's Kitchen charity, which provides home-delivered meals to critically ill San Diegans
Read more »
 ‘New energy, new era’: Texans unveiling new uniforms ahead of NFL DraftTexans to unveil four new uniforms April 23 at reveal party
‘New energy, new era’: Texans unveiling new uniforms ahead of NFL DraftTexans to unveil four new uniforms April 23 at reveal party
Read more »
 Texans unveil new uniforms, helmets: ‘New energy, new era’Texans roll out new uniforms
Texans unveil new uniforms, helmets: ‘New energy, new era’Texans roll out new uniforms
Read more »
