Researchers have demonstrated a technique that allows people who manufacture metal machine parts with 3D printing technologies to conduct automated quality control of manufactured parts during the finishing process.
The technique allows users to identify potential flaws without having to remove the parts from the manufacturing equipment, making production time more efficient.
After a metal machine part is printed, it requires additional finishing and has to be measured to ensure the part meets critical tolerances. In other words, every aspect of the part must be the right size. Currently, that involves taking a part out of the relevant manufacturing equipment, measuring it, and then putting it back into the manufacturing equipment to make modest adjustments.
To test the performance of the new approach, researchers manufactured a machine part using conventional 3D printing and finishing techniques, and then manufactured the same part using their new process. "All of the hardware we used in this technique is commercially available, and we outline the necessary software clearly in the paper -- so we feel that this new approach could be adopted and put into use almost immediately," McConnell says."And we are certainly open to working with partners who are interested in making use of this technique in their operations."Chicago
3-D Printing Materials Science Electronics Nanotechnology Thermodynamics Engineering And Construction Engineering
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers discover new clues to how tardigrades can survive intense radiationUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel Hill researchers have discovered that tardigrades—microscopic animals famed for surviving harsh extremes—have an unusual response to radiation.
Researchers discover new clues to how tardigrades can survive intense radiationUniversity of North Carolina at Chapel Hill researchers have discovered that tardigrades—microscopic animals famed for surviving harsh extremes—have an unusual response to radiation.
Read more »
 Researchers need ‘open’ bibliographic databases, new declaration saysMajor platforms such as the Web of Science, widely used to generate metrics and evaluate researchers, are proprietary
Researchers need ‘open’ bibliographic databases, new declaration saysMajor platforms such as the Web of Science, widely used to generate metrics and evaluate researchers, are proprietary
Read more »
 Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactionsUnderstanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for developing new treatments and understanding diseases. Thanks to computational advances, a team of researchers led by Assistant Professor of Chemistry Alberto Perez have developed an algorithm to identify these molecular interactions.
Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactionsUnderstanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for developing new treatments and understanding diseases. Thanks to computational advances, a team of researchers led by Assistant Professor of Chemistry Alberto Perez have developed an algorithm to identify these molecular interactions.
Read more »
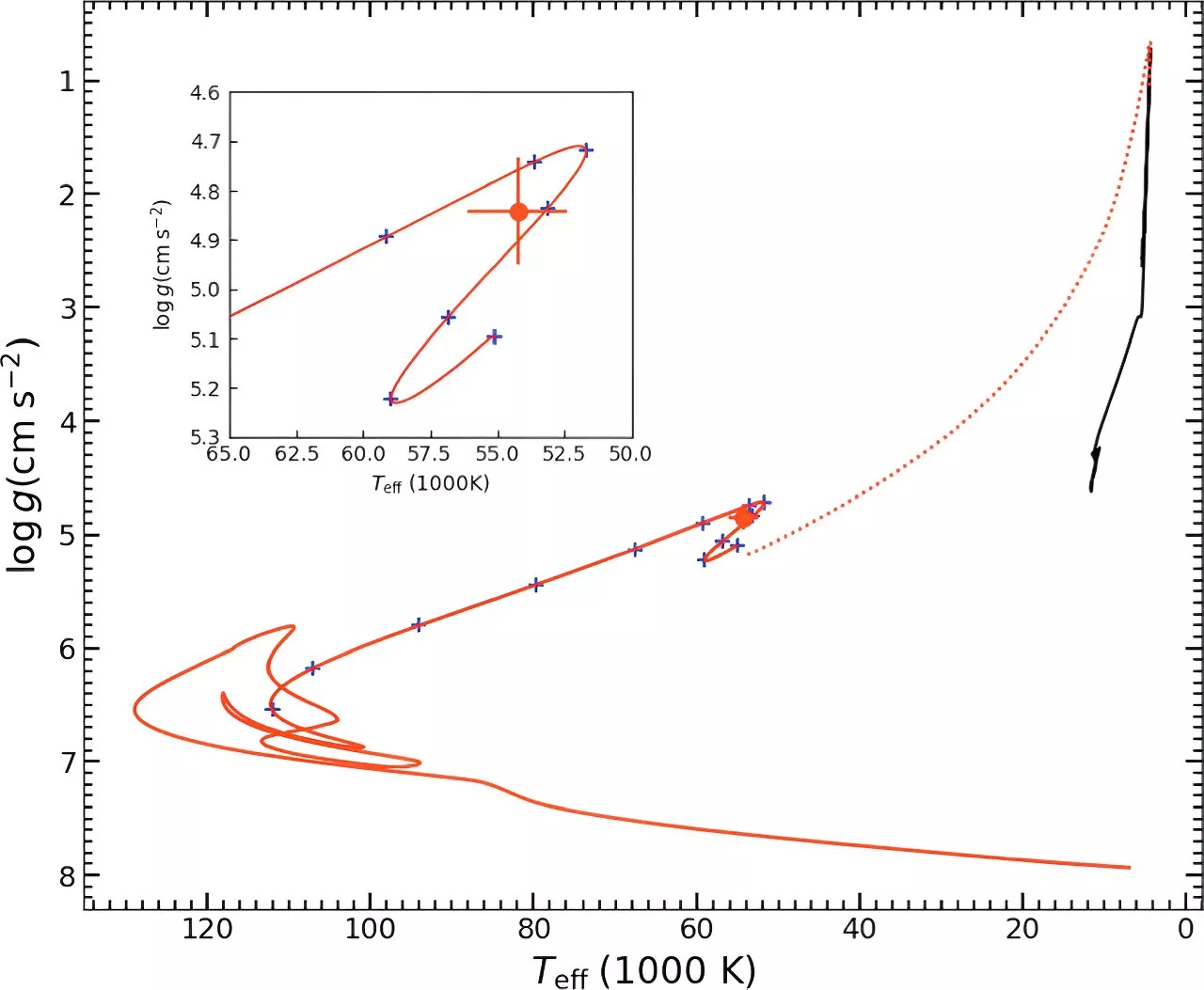 Researchers propose new formation model for massive hot subdwarfsIn a new study published in the The Astrophysical Journal, Dr. Li Zhenwei and his collaborators from Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and Dr.
Researchers propose new formation model for massive hot subdwarfsIn a new study published in the The Astrophysical Journal, Dr. Li Zhenwei and his collaborators from Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and Dr.
Read more »
 Researchers Develop “Goldene” – A New Form of Ultra-Thin Gold With Semiconductor PropertiesScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Researchers Develop “Goldene” – A New Form of Ultra-Thin Gold With Semiconductor PropertiesScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactionsAI developments in chemical biology could unlock new types of disease treatments.
Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactionsAI developments in chemical biology could unlock new types of disease treatments.
Read more »
