The Healthy Eating Research (HER) initiative has released comprehensive recommendations for healthy beverage choices for children aged 5 and older. The guidelines, developed by a panel of experts, aim to help parents, healthcare providers, and policymakers make informed decisions about children's hydration and nutrition.
Beverages constitute a significant portion of most people's diets, with a wide variety readily available in supermarkets. The types of drinks children consume can have a profound impact on their overall health. However, deciphering which beverages are most nutritious for kids, particularly school-aged children and teenagers, can be challenging.
Parents often grapple with questions like: Is it permissible for children to have a small amount of caffeine in the morning? Are sugary sodas acceptable at occasional gatherings? Is 100% fruit juice a healthy choice? How can one ensure that a beverage lacks added sugars? The Healthy Eating Research (HER) initiative, dedicated to combating childhood obesity through mindful eating, recently unveiled new recommendations regarding the types of beverages children aged 5 and older should consume, limit, and avoid altogether. These recommendations, grounded in scientific research, were developed by a panel of experts from four prominent organizations specializing in children's nutrition: the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Heart Association.The HER and its collaborating health organizations aim to empower consumers to make healthier beverage choices, equip healthcare providers with the necessary tools to support families, and provide evidence-based guidance that can inform policies such as the upcoming 2025 Dietary Guidelines and the FDA's proposed front-of-pack label. While water plays a vital role in hydration, other drinks can offer children essential nutrients – vitamins, minerals, and fluoride – contributing to their daily nutrient requirements. Conversely, beverages containing added sugars, non-sugar sweeteners, and caffeine may introduce unnecessary calories to a child's diet and pose health risks. Over a period of five months, the expert panel meticulously analyzed scientific literature on beverages and their effects on children's health to formulate their final recommendations, outlining which beverages constitute a healthy part of a child's diet and which should be limited.The consensus statement offers practical hydration habits for children aged 5 to 18 years. Malkani emphasizes that these are the first comprehensive healthy drink recommendations specifically tailored to this age group. The guidelines suggest specific daily intake recommendations for water and milk based on age ranges: Children aged 5-8 should consume 2-5 cups of water and 2.5 cups of milk daily. Children aged 9-13 should aim for 2.75-7.6 cups of water and 3 cups of milk daily. For adolescents aged 14-18, the recommendation is 3.6-11 cups of water and 3 cups of milk daily. Plain drinking water is defined as potable water that is unsweetened, unflavored, and fluoridated. While not all plain water sources are naturally fluoridated, it's recommended to use fluoridated water when available. Examples include tap water, well water, or plain, unsweetened bottled or carbonated water. Plain pasteurized milk is defined as cow's milk and other animal-based milk that has been heated to a specific temperature and duration to eliminate pathogens present in raw milk. This process ensures the milk is safe for consumption. Importantly, no caloric sweeteners, non-sugar sweeteners, or flavorings have been added to this milk. Common varieties include whole milk (also known as Vitamin D milk), reduced fat (2%), low-fat (1%), and skim (fat-free).According to the report, 100% fruit juice, while a source of vitamins, is lower in dietary fiber and more calorically dense than whole fruit and should be limited to three-quarters of a cup or 1 cup daily, depending on age. Plant-based milks are only recommended when medically indicated (e.g., milk protein allergy) or to adhere to specific dietary patterns (e.g., vegan). The guidelines advise choosing alternatives that are nutritionally comparable to milk, such as unsweetened, fortified soy milk. Parents should avoid plant-based milk alternatives containing added sugar or non-sugar sweeteners. 100% juice is defined as a beverage made from the extraction or pressing of the natural liquid found in fruits or vegetables. 100% juice signifies that everything in the container originates from a fruit or vegetable with no added sugars or artificial ingredients. Beverages made from 100% juice diluted with water (without any other added ingredients) are also included in this category.Plant-based milk alternatives are defined as non-dairy beverages derived from plant-based ingredients like grains (e.g., rice, oats), nuts/seeds, legumes, or blends of these ingredients. Many plant-based milk alternatives come in both sweetened and unsweetened varieties. Sweetened varieties generally contain added sugars and/or non-sugar sweeteners. Sweetened flavored milks are defined as pasteurized cow's milk to which sweeteners and/or flavorings have been added primarily to enhance palatability. Examples include chocolate or strawberry milk.Sugar-sweetened beverages, beverages with non-sugar sweeteners, and beverages with caffeine and other stimulants are discouraged. Sugar-sweetened beverages contain excessive sugar and calories and are not recommended as part of a healthy child or adolescent diet, according to the new guidelines. Sugar-sweetened beverages are defined as liquids to which any forms of sugar are added
CHILD HEALTH BEVERAGE GUIDELINES NUTRITION RECOMMENDATIONS WATER MILK JUICE PLANT-BASED MILK SUGAR-SWEETENED BEVERAGES CAFFEINE
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
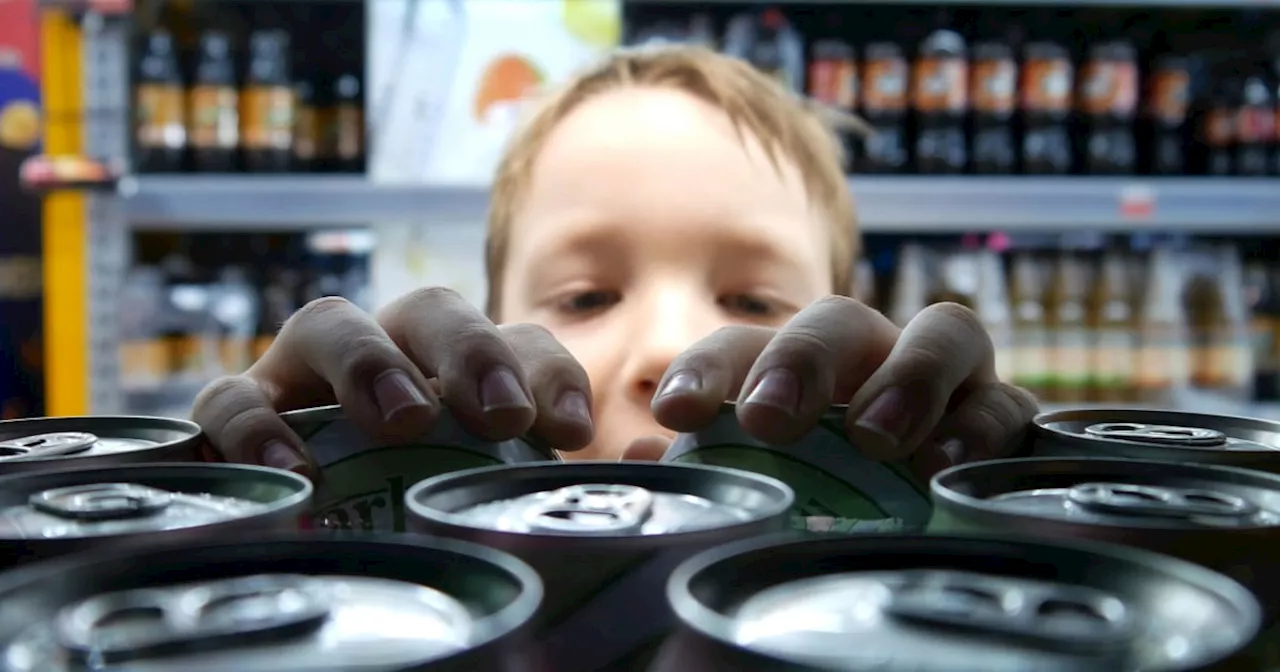 New Guidelines Recommend Healthy Beverage Choices for KidsThe Healthy Eating Research program has released new recommendations on beverages for children ages 5 and up. The guidelines, developed by a panel of experts, categorize drinks as recommended, limit, or avoid, emphasizing water, milk, and limiting sugary drinks.
New Guidelines Recommend Healthy Beverage Choices for KidsThe Healthy Eating Research program has released new recommendations on beverages for children ages 5 and up. The guidelines, developed by a panel of experts, categorize drinks as recommended, limit, or avoid, emphasizing water, milk, and limiting sugary drinks.
Read more »
 New IRS Tax Deadlines and Guidelines for 2025Americans face new tax deadlines and guidelines for 2025, with potential changes to tax amounts due to IRS budget cuts and updated tax brackets.
New IRS Tax Deadlines and Guidelines for 2025Americans face new tax deadlines and guidelines for 2025, with potential changes to tax amounts due to IRS budget cuts and updated tax brackets.
Read more »
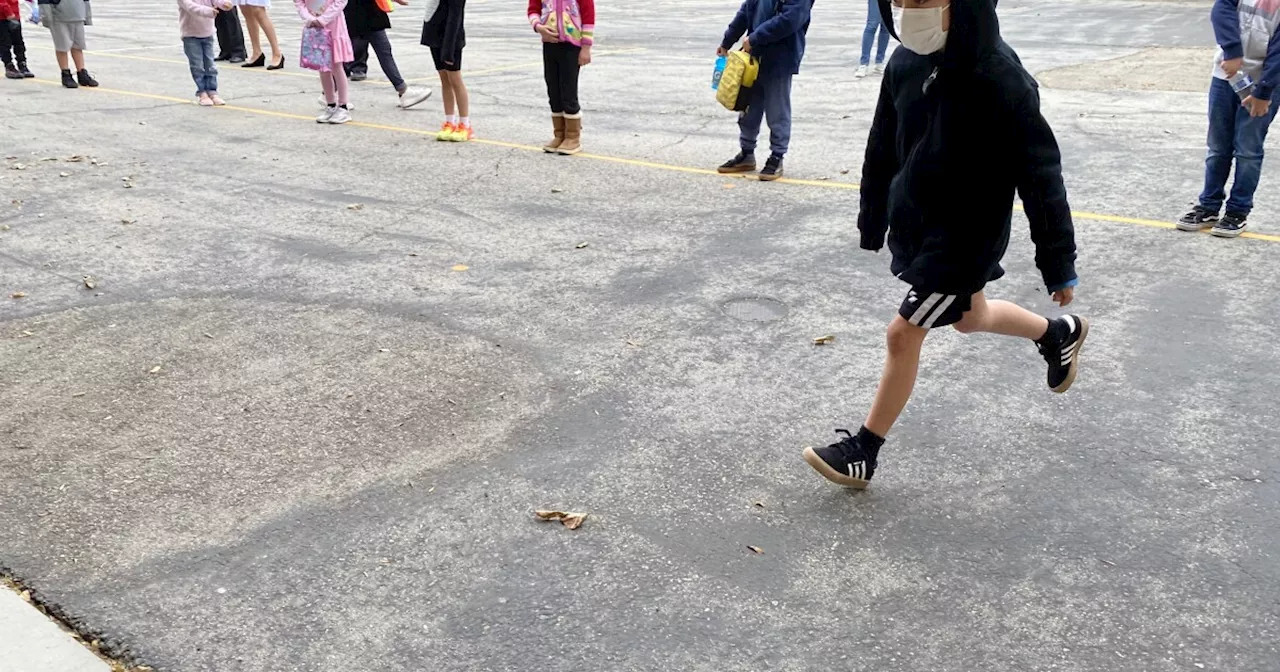 California Schools Issue New Guidelines on Protecting Immigrant Students Amidst Deportation FearsIn light of President-elect Donald Trump's pledge to increase deportations, California schools are implementing updated policies to safeguard immigrant students and families. The guidelines cover data privacy, interactions with immigration enforcement, responses to family detentions, and addressing bullying based on immigration status.
California Schools Issue New Guidelines on Protecting Immigrant Students Amidst Deportation FearsIn light of President-elect Donald Trump's pledge to increase deportations, California schools are implementing updated policies to safeguard immigrant students and families. The guidelines cover data privacy, interactions with immigration enforcement, responses to family detentions, and addressing bullying based on immigration status.
Read more »
 New Facebook guidelines, censorship draw mixed reaction from AmericansAmericans had mixed reactions to Meta's decision to end fact-checking programs on Facebook and Instagram, with some telling Fox News Digital the move was concerning.
New Facebook guidelines, censorship draw mixed reaction from AmericansAmericans had mixed reactions to Meta's decision to end fact-checking programs on Facebook and Instagram, with some telling Fox News Digital the move was concerning.
Read more »
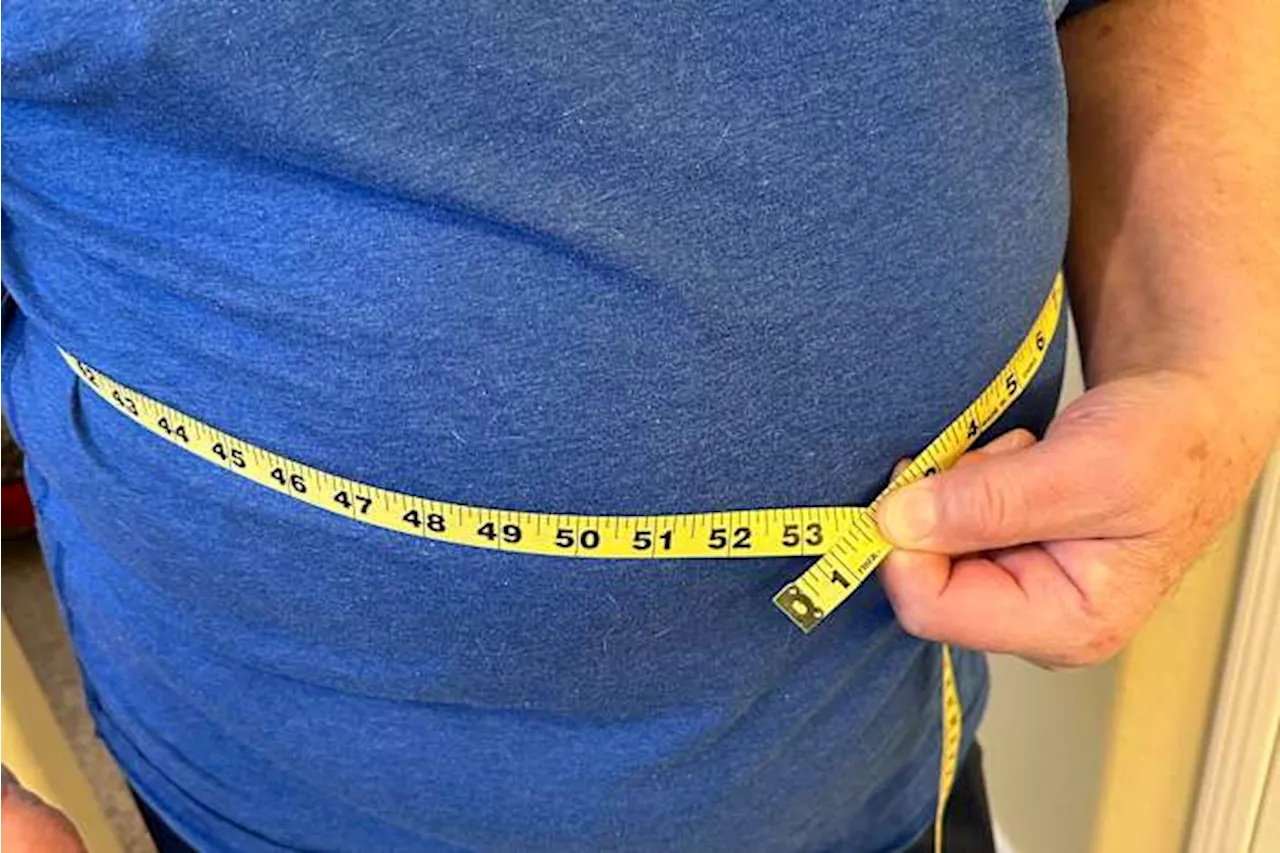 New Obesity Guidelines Move Beyond BMIRevised recommendations shift focus from solely BMI to a more comprehensive assessment incorporating waist circumference and health indicators linked to excess weight.
New Obesity Guidelines Move Beyond BMIRevised recommendations shift focus from solely BMI to a more comprehensive assessment incorporating waist circumference and health indicators linked to excess weight.
Read more »
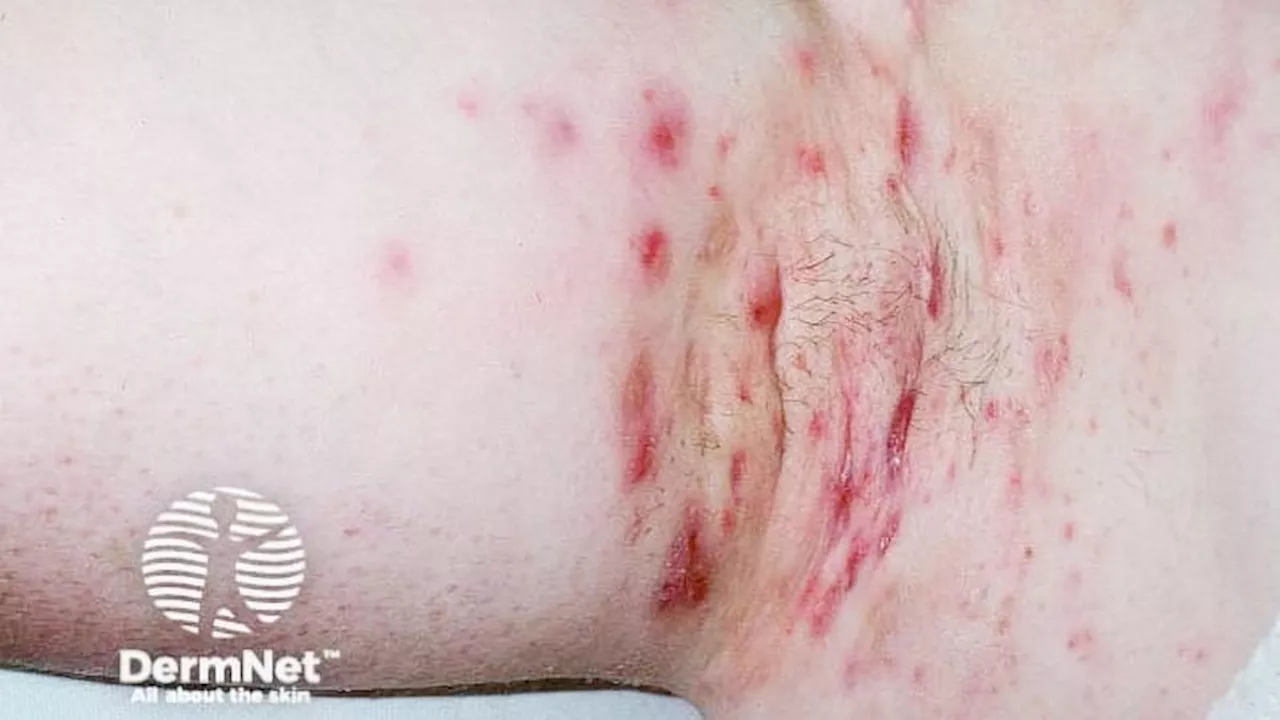 New Guidelines Offer First-Ever Recommendations for Managing Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Special Patient PopulationsThe North American Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Medical Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Special Patient Populations provide crucial recommendations for treating HS in pregnant, breastfeeding, pediatric, and immunocompromised individuals. These guidelines address the gap in clinical trials that often exclude these patient groups, offering clinicians evidence-based guidance on safely and effectively managing HS in diverse populations.
New Guidelines Offer First-Ever Recommendations for Managing Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Special Patient PopulationsThe North American Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Medical Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Special Patient Populations provide crucial recommendations for treating HS in pregnant, breastfeeding, pediatric, and immunocompromised individuals. These guidelines address the gap in clinical trials that often exclude these patient groups, offering clinicians evidence-based guidance on safely and effectively managing HS in diverse populations.
Read more »
