Researchers at Karolinska Institutet may have found a new way to treat obesity and related disorders by targeting the cells' mitochondria. A study published in Nature Metabolism shows that a specific class of drugs that block mitochondrial function can reverse diet-induced obesity, fatty liver and diabetes in mice.
New drug candidate reverses obesity in mice retrieved 30 April 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-04-drug-candidate-reverses-obesity-mice.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Apr 25, 2024Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New state of mind: Rethinking how researchers understand brain activityUnderstanding the link between brain activity and behavior is among the core interests of neuroscience. Having a better grasp of this relationship will both help scientists understand how the brain works on a basic level and uncover what specifically goes awry in cases of neurological and psychological disease.
New state of mind: Rethinking how researchers understand brain activityUnderstanding the link between brain activity and behavior is among the core interests of neuroscience. Having a better grasp of this relationship will both help scientists understand how the brain works on a basic level and uncover what specifically goes awry in cases of neurological and psychological disease.
Read more »
 Researchers find new clues to understanding the progression of primary membranous nephropathyNo therapies currently exist that can halt the progression of chronic kidney disease in children or restore the ability of kidney cells to filter blood.
Researchers find new clues to understanding the progression of primary membranous nephropathyNo therapies currently exist that can halt the progression of chronic kidney disease in children or restore the ability of kidney cells to filter blood.
Read more »
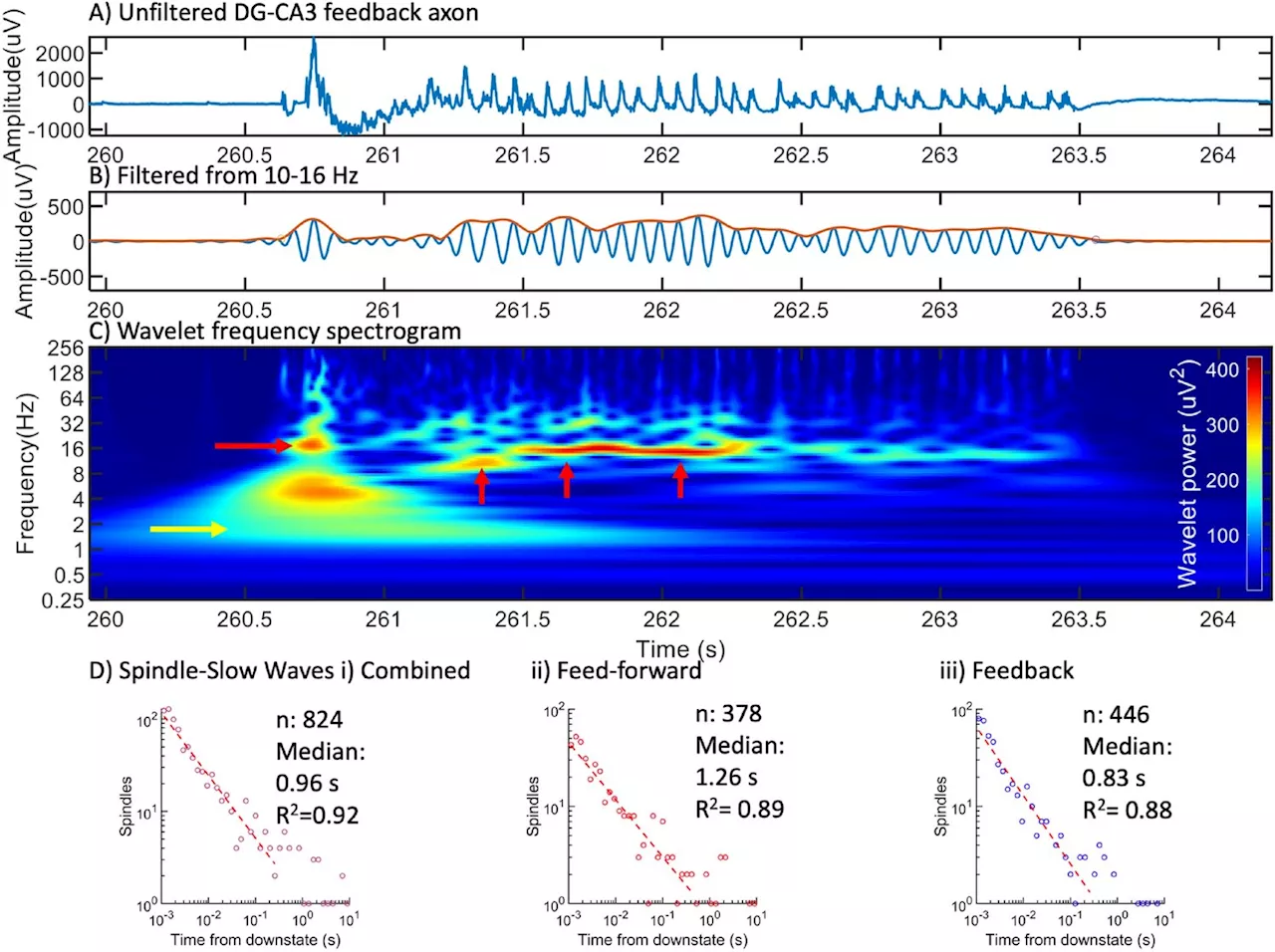 Researchers find new origin of deep brain wavesResearchers have discovered a new origin of deep brain waves, shedding light on the mechanisms behind brain activity. The findings have potential implications for understanding and treating neurological disorders.
Researchers find new origin of deep brain wavesResearchers have discovered a new origin of deep brain waves, shedding light on the mechanisms behind brain activity. The findings have potential implications for understanding and treating neurological disorders.
Read more »
 Researchers Find New Method to Bypass Spectre Protections and Steal DataResearchers have developed a tool called InSpectre Gadget that can bypass Spectre protections and steal sensitive data from kernel memory and other areas of RAM. The tool was used to successfully perform a Native Branch History Injection (Native BHI) attack on Intel microprocessors.
Researchers Find New Method to Bypass Spectre Protections and Steal DataResearchers have developed a tool called InSpectre Gadget that can bypass Spectre protections and steal sensitive data from kernel memory and other areas of RAM. The tool was used to successfully perform a Native Branch History Injection (Native BHI) attack on Intel microprocessors.
Read more »
 University of Manchester Researchers Develop New Catalyst with Wide Range of UsesResearchers at The University of Manchester have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in catalyst technology by developing a new catalyst which has been shown to have a wide variety of uses and the potential to streamline catalyzed optimization processes in industry and support new scientific discoveries.
University of Manchester Researchers Develop New Catalyst with Wide Range of UsesResearchers at The University of Manchester have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in catalyst technology by developing a new catalyst which has been shown to have a wide variety of uses and the potential to streamline catalyzed optimization processes in industry and support new scientific discoveries.
Read more »
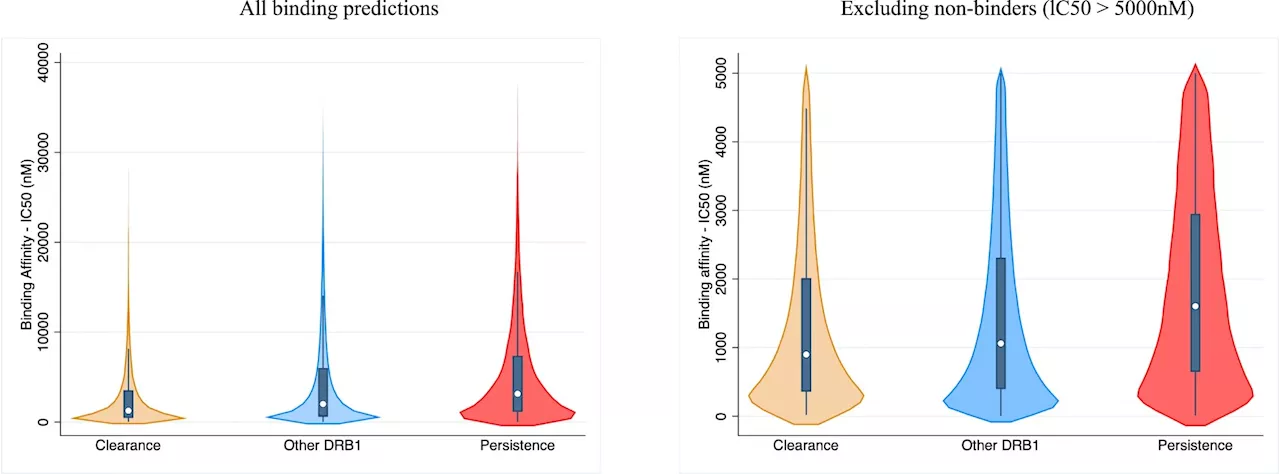 Researchers identify new genetic risk factors for persistent HPV infectionsHuman papillomavirus (HPV) is the second most common cancer-causing virus, accounting for 690,000 cervical and other cancers each year worldwide.
Researchers identify new genetic risk factors for persistent HPV infectionsHuman papillomavirus (HPV) is the second most common cancer-causing virus, accounting for 690,000 cervical and other cancers each year worldwide.
Read more »
