Researchers have developed a miniature battery that could be used to power tiny devices integrated into human tissues. The design uses an ionic gradient across a chain of droplets -- inspired by how electric eels generate electricity. The device was able to regulate the biological activity of human neurons. This could open the way to the development of tiny bio-integrated devices, with a range of applications in biology and medicine.
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature bio-integrated devices, capable of directly stimulating cells. The work has been published today in the journalSmall bio-integrated devices that can interact with and stimulate cells could have important therapeutic applications, including the delivery of targeted drug therapies and the acceleration of wound healing. However, such devices all need a power source to operate.
The miniaturized soft power source is produced by depositing a chain of five nanolitre-sized droplets of a conductive hydrogel . Each droplet has a different composition so that a salt concentration gradient is created across the chain. The droplets are separated from their neighbours by lipid bilayers, which provide mechanical support while preventing ions from flowing between the droplets.
In the study, the activated droplet power source produced a current which persisted for over 30 minutes. The maximum output power of a unit made of 50 nanolitre droplets was around 65 nanowatts . The devices produced a similar amount of current after being stored for 36 hours. According to the researchers, the device's modular design would allow multiple units to be combined in order to increase the voltage and/or current generated. This could open the door to powering next-generation wearable devices, bio-hybrid interfaces, implants, synthetic tissues, and microrobots. By combining 20 five-droplet units in series, they were able to illuminate a light-emitting diode, which requires about 2 Volts.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Yale Researchers Discover Potential New Way To Treat CancerA recent study from Yale indicates that additional chromosomes in cancer cells are essential for the growth of tumors. Removing these extra chromosomes inhibits tumor formation. The findings, said the researchers, indicate that selectively targeting extra chromosomes may offer a new route for treati
Yale Researchers Discover Potential New Way To Treat CancerA recent study from Yale indicates that additional chromosomes in cancer cells are essential for the growth of tumors. Removing these extra chromosomes inhibits tumor formation. The findings, said the researchers, indicate that selectively targeting extra chromosomes may offer a new route for treati
Read more »
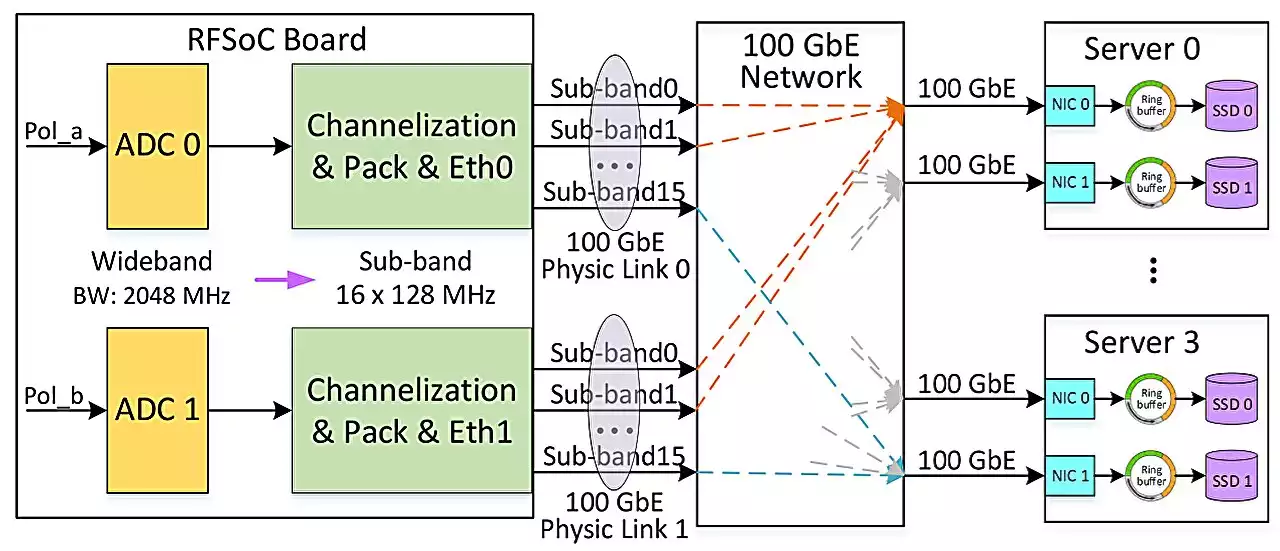 Researchers propose new technology to improve observation sensitivity of QiTai radio telescopeThe world's most powerful steerable 110-meter radio telescope, also known as the QiTai radio Telescope (QTT), will be built by Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) over a period of six years. Its ceremony kicked off on Sept. 21, 2022.
Researchers propose new technology to improve observation sensitivity of QiTai radio telescopeThe world's most powerful steerable 110-meter radio telescope, also known as the QiTai radio Telescope (QTT), will be built by Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) over a period of six years. Its ceremony kicked off on Sept. 21, 2022.
Read more »
 New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
Read more »
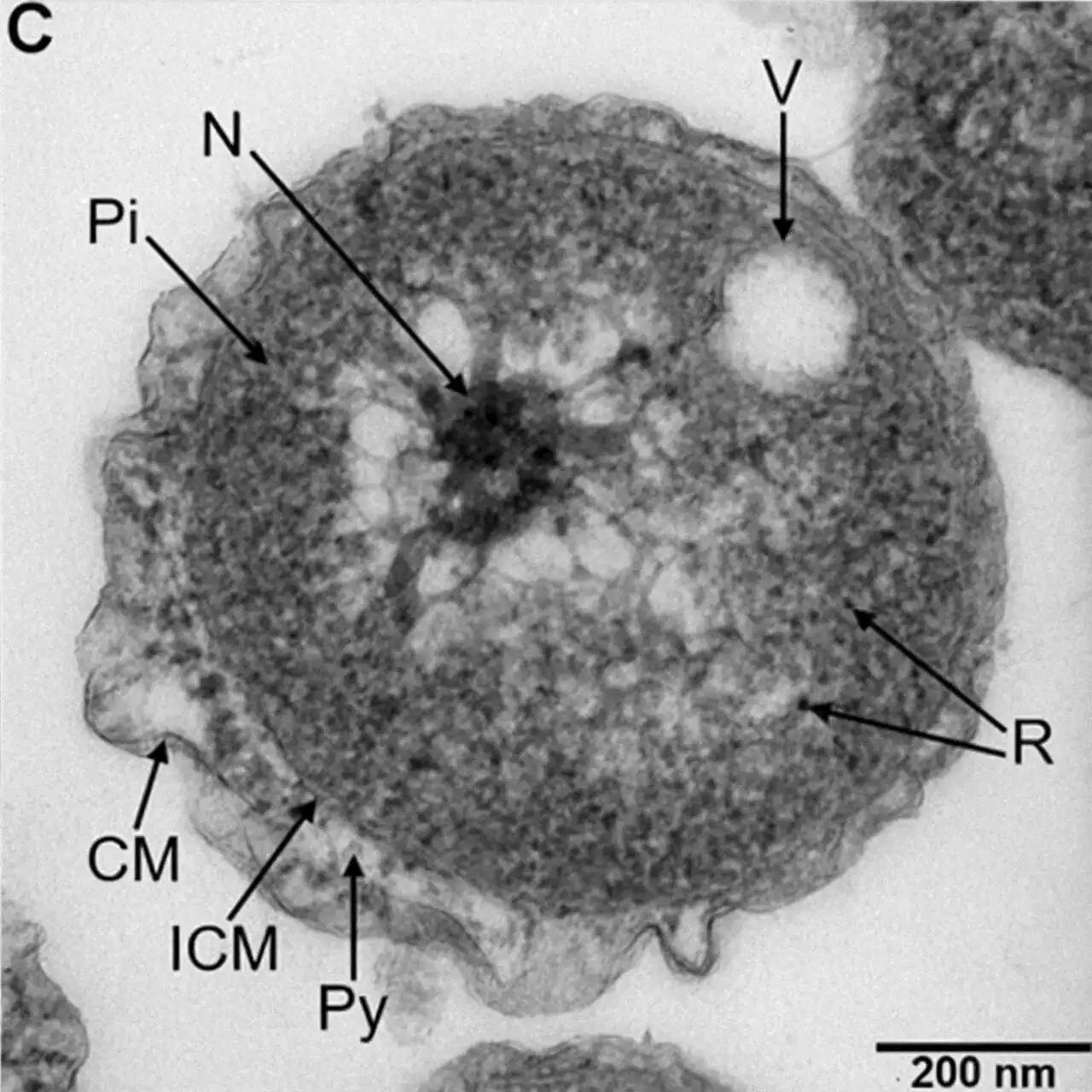 New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
New species of marine bacteria isolated from a deep-sea cold seepResearchers have isolated a new strain of marine bacteria with unique characteristics from the ocean seabed.
Read more »
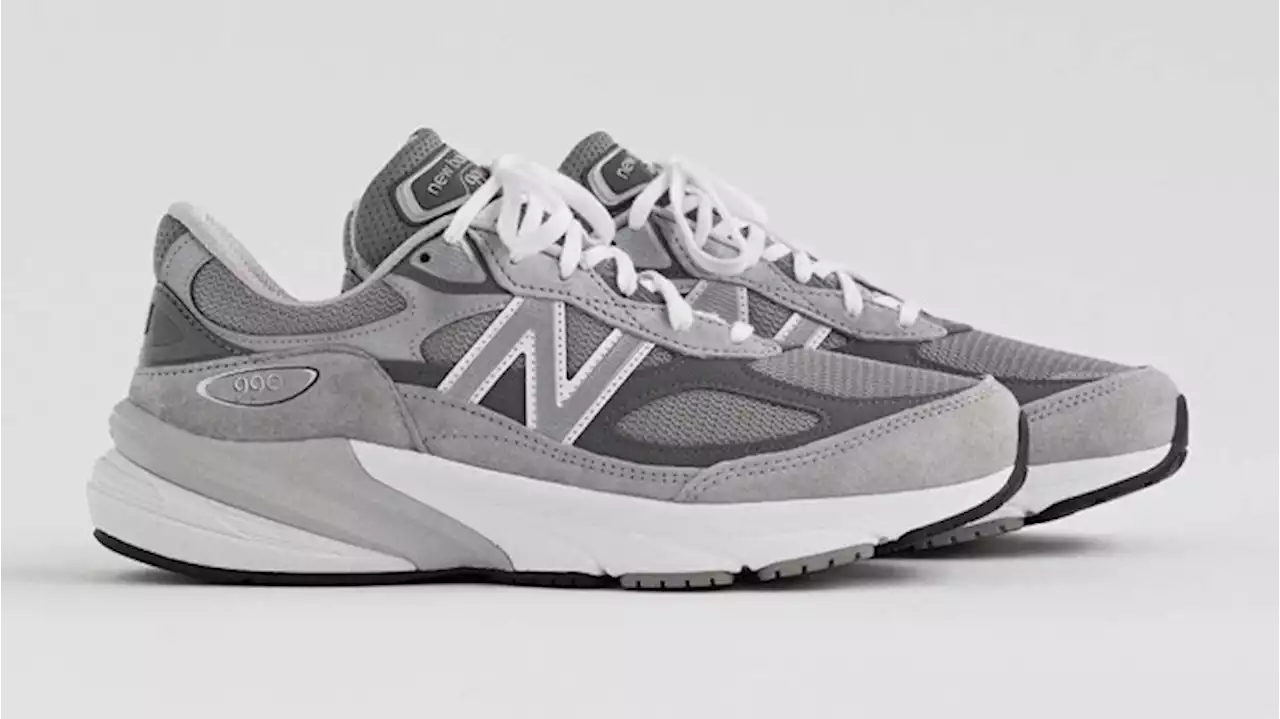 New Balance Claims Golden Goose Copied Its 990 Sneaker in a New LawsuitThe brand claims Golden Goose’s “Dad-Star” sneaker is a “confusingly similar design” to its classic release.
New Balance Claims Golden Goose Copied Its 990 Sneaker in a New LawsuitThe brand claims Golden Goose’s “Dad-Star” sneaker is a “confusingly similar design” to its classic release.
Read more »
