Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have developed a new computational method for linking molecular marks on our DNA to gene activity.
Jun 4 2024La Jolla Institute for Immunology Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology have developed a new computational method for linking molecular marks on our DNA to gene activity. Their work may help researchers connect genes to the molecular "switches" that turn them on or off.
Ay and Rao are working to pinpoint regions of the genome that contain molecular enhancers, or "switches," which fine tune the levels of gene expression and determine when and where genes will be on or off. This work requires researchers to develop computational tools that can harness complex genomic data and find which enhancers are connected to which genes.
The neural network goes to work The researchers trained new neural networks that learn how the presence of an important DNA modification called 5hmC, either near the gene or far away from it, is related to gene expression activity. This attachment of a hydroxymethyl group to cytosine has been associated with enhancer activity.
This 5hmC distribution controlled the expression of different gene sets in these different types of cells. The researchers had found that 5hmC attaches to regions of the genomes that work as enhancers-;the same regions that help switch gene expression on and off-;as well as to the genes themselves. These differences in active genes and enhancers are what distinguishes a liver cell from cells in the lung or neurons in the brain.
The new research method allows a simpler connection to be made between genes and enhancers than was possible with earlier methods. "What is exciting is that some of these distant enhancers are novel regulatory elements that have not been discovered before," says Ay.
Research Blood Brain Cancer Cell Cytosine DNA Gene Gene Expression Genome Genomic Immunology Liver Machine Learning Neurons Ph
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Placental DNA methylation patterns altered by pregnancy air pollution exposure, research revealsThe relationship between prenatal air pollutant exposure concentrations and changes in placental deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation.
Placental DNA methylation patterns altered by pregnancy air pollution exposure, research revealsThe relationship between prenatal air pollutant exposure concentrations and changes in placental deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation.
Read more »
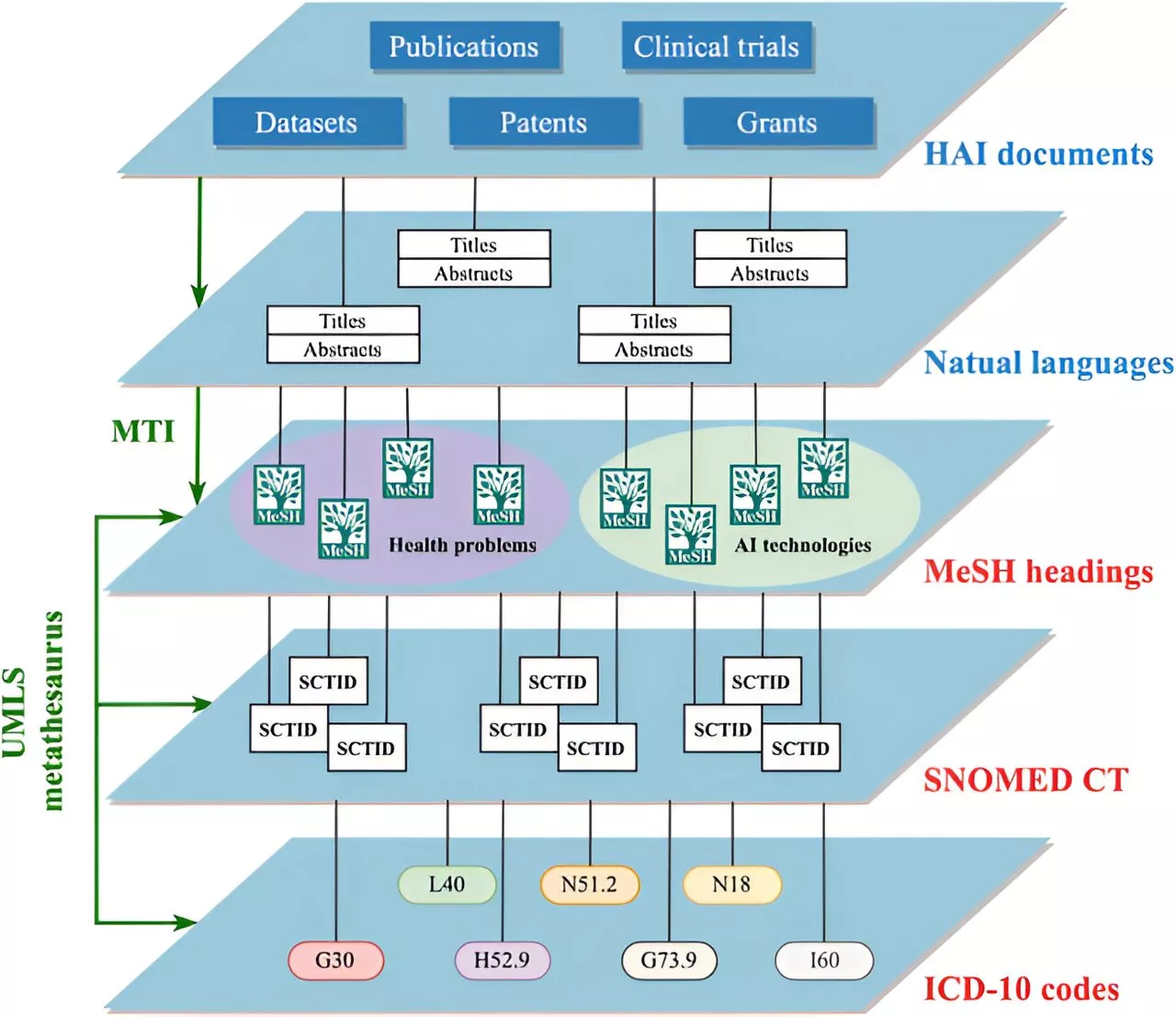 Research provides curated bibliographic dataset of advances in health AI researchA study published in Health Data Science introduces a curated bibliographic dataset that aims to revolutionize the landscape of Health Artificial Intelligence (AI) research.
Research provides curated bibliographic dataset of advances in health AI researchA study published in Health Data Science introduces a curated bibliographic dataset that aims to revolutionize the landscape of Health Artificial Intelligence (AI) research.
Read more »
 Scientists call for equitable research partnerships to advance microbiome researchLeading African scientists have issued a compelling call for more equitable research partnerships in a new paper published in Nature Medicine. The paper underscores the critical need for fair and collaborative research efforts to explore the unique and diverse microbiomes found in African populations and environments.
Scientists call for equitable research partnerships to advance microbiome researchLeading African scientists have issued a compelling call for more equitable research partnerships in a new paper published in Nature Medicine. The paper underscores the critical need for fair and collaborative research efforts to explore the unique and diverse microbiomes found in African populations and environments.
Read more »
 Breast Cancer Now funds new research to investigate how breast cancer cells survive and growResearchers in Sheffield are investigating how breast cancer cells survive and grow, thanks to new funding from Breast Cancer Now.
Breast Cancer Now funds new research to investigate how breast cancer cells survive and growResearchers in Sheffield are investigating how breast cancer cells survive and grow, thanks to new funding from Breast Cancer Now.
Read more »
 New research examines past and guides future efforts to reduce cancer disparitiesInvestigators at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have examined the historical evolution of Community Outreach and Engagement initiatives at both the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and National Cancer Institute-Designated Cancer Centers (NCI-DCCs).
New research examines past and guides future efforts to reduce cancer disparitiesInvestigators at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have examined the historical evolution of Community Outreach and Engagement initiatives at both the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and National Cancer Institute-Designated Cancer Centers (NCI-DCCs).
Read more »
 New research finds no causal link between vitamin E levels and osteoarthritisA recent study used Mendelian randomization to explore the link between osteoarthritis (OA) and alpha-tocopherol, a form of vitamin E, and found no evidence of a causal relationship between the two.
New research finds no causal link between vitamin E levels and osteoarthritisA recent study used Mendelian randomization to explore the link between osteoarthritis (OA) and alpha-tocopherol, a form of vitamin E, and found no evidence of a causal relationship between the two.
Read more »