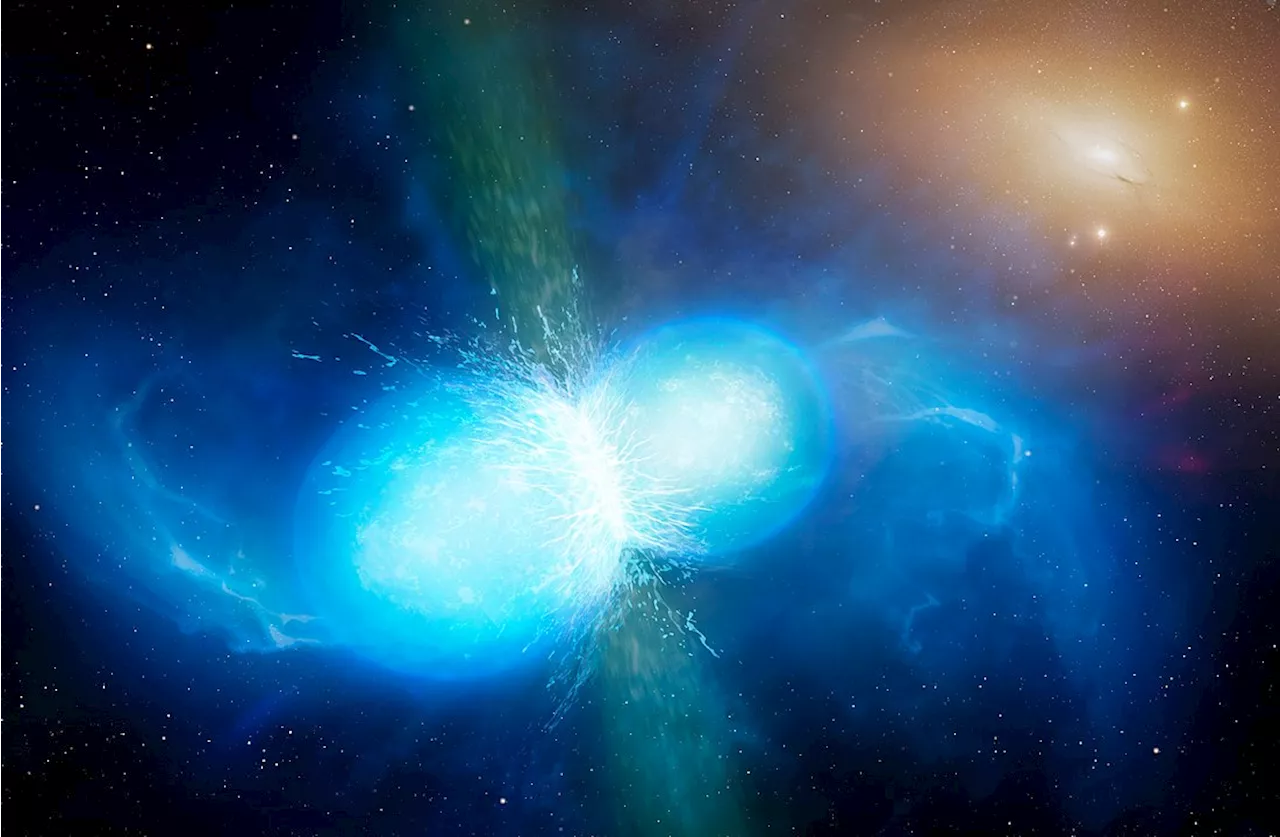
Scientists have observed a rare event where two neutron stars merge and explode as a kilonova, producing gravitational waves and a short gamma-ray burst. Detailed observations confirmed that this object, located in the galaxy NGC 4993, is indeed a kilonova and the main source of heavy chemical elements in the Universe. Gamma-ray telescopes observing neutron star collisions could potentially help identify the composition of dark matter.
This artist’s impression shows two tiny but very dense neutron stars at the point at which they merge and explode as a kilonova. Such a very rare event is expected to produce both gravitational waves and a short gamma-ray burst , both of which were observed on 17 August 2017 by LIGO–Virgo and Fermi/INTEGRAL respectively.
Subsequent detailed observations with many ESO telescopes confirmed that this object, seen in the galaxy NGC 4993 about 130 million light-years from the Earth, is indeed a kilonova. Such objects are the main source of very heavy chemical elements, such as gold and platinum, in the Universe. Gamma-ray telescopes observing neutron star collisions might be the key to identifying the composition of dark matter. One leading theory explaining dark matter it that is mostly made from hypothetical particles called axions. If an axion is created within the intensely energetic environment of two neutron stars merging, it should then decay into gamma-ray photons which we could see using space telescopes like Fermi-LA
Neutron Stars Kilonova Gravitational Waves Gamma-Ray Burst Dark Matter Composition Space Telescopes
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Scientists create 5 new isotopes to learn how neutron star collisions forge goldRobert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Scientists create 5 new isotopes to learn how neutron star collisions forge goldRobert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Read more »
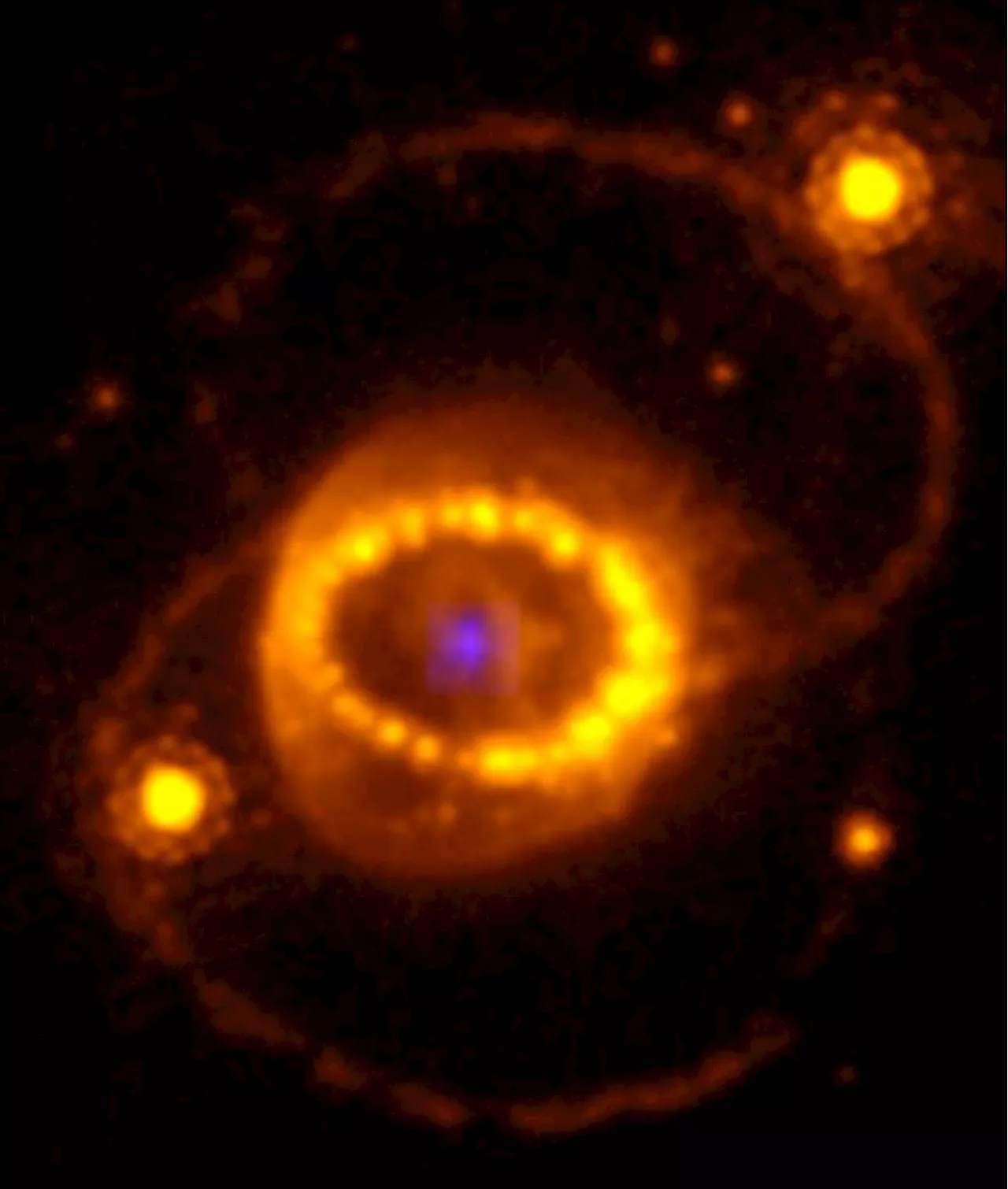 A Neutron Star Rests at Supernova 1987A’s CenterThe supernova has astonished experts since its discovery almost four decades ago
A Neutron Star Rests at Supernova 1987A’s CenterThe supernova has astonished experts since its discovery almost four decades ago
Read more »
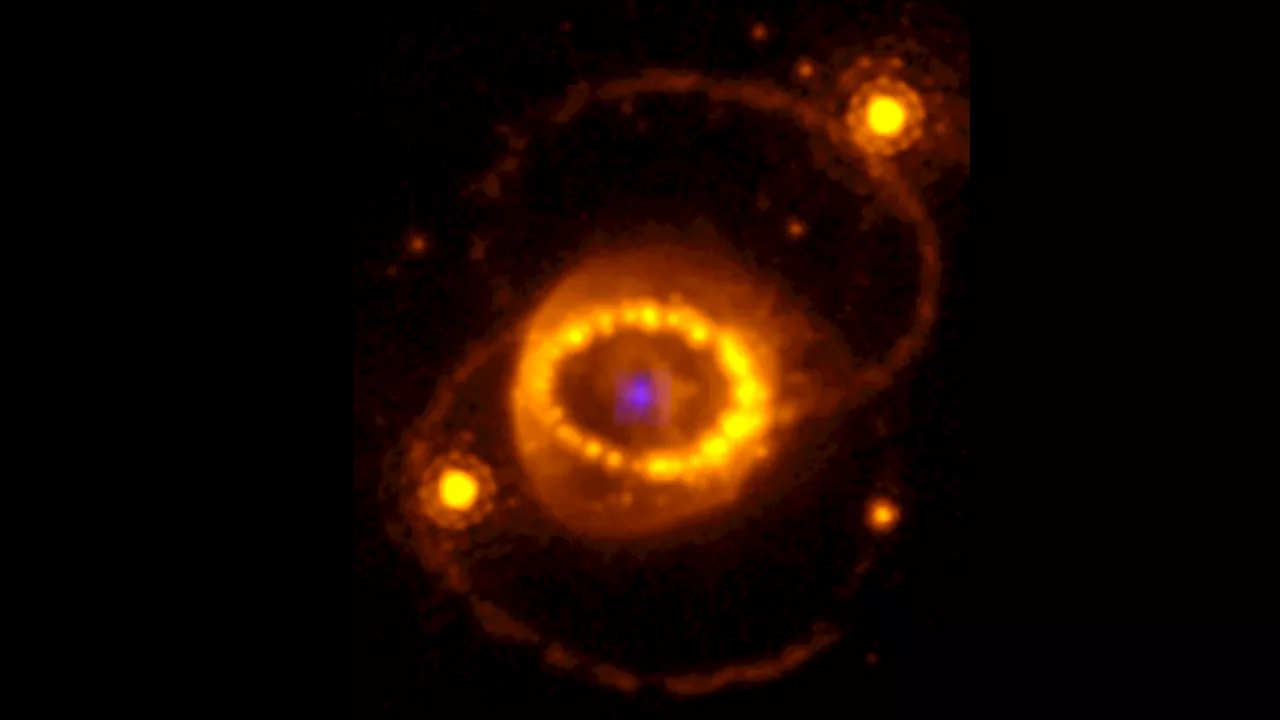 JWST spies hints of a neutron star left behind by supernova 1987ASigns of highly ionized atoms in dusty clouds at SN 1987A’s explosion site suggest a powerful source of X-rays — likely a neutron star — lurks within.
JWST spies hints of a neutron star left behind by supernova 1987ASigns of highly ionized atoms in dusty clouds at SN 1987A’s explosion site suggest a powerful source of X-rays — likely a neutron star — lurks within.
Read more »
 Webb finds evidence for neutron star at heart of young supernova remnantNASA's James Webb Space Telescope has found the best evidence yet for emission from a neutron star at the site of a recently observed supernova. The supernova, known as SN 1987A, was a core-collapse supernova, meaning the compacted remains at its core formed either a neutron star or a black hole.
Webb finds evidence for neutron star at heart of young supernova remnantNASA's James Webb Space Telescope has found the best evidence yet for emission from a neutron star at the site of a recently observed supernova. The supernova, known as SN 1987A, was a core-collapse supernova, meaning the compacted remains at its core formed either a neutron star or a black hole.
Read more »
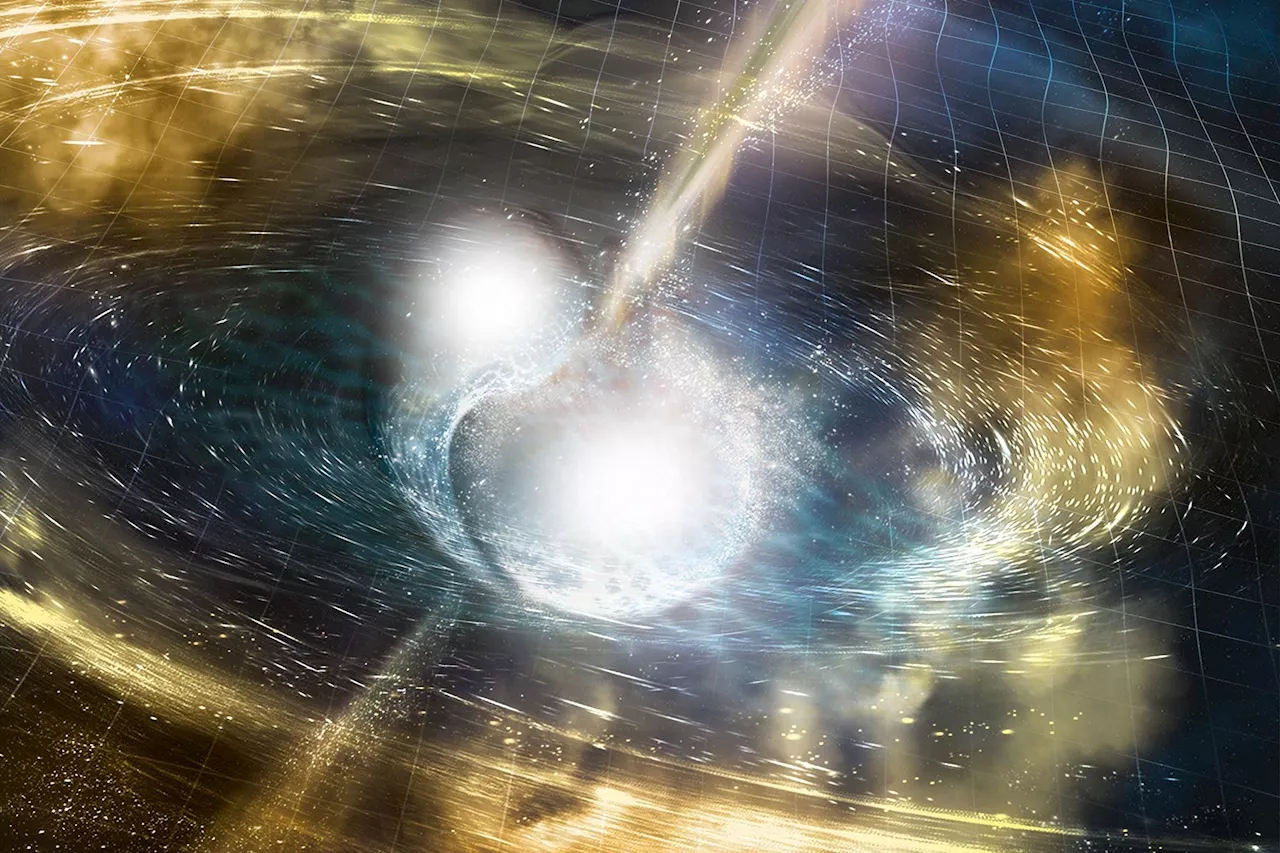 Physics Beyond Known Laws: Neutron Star Collisions Shed Light on Dark Matter MysteriesScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Physics Beyond Known Laws: Neutron Star Collisions Shed Light on Dark Matter MysteriesScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
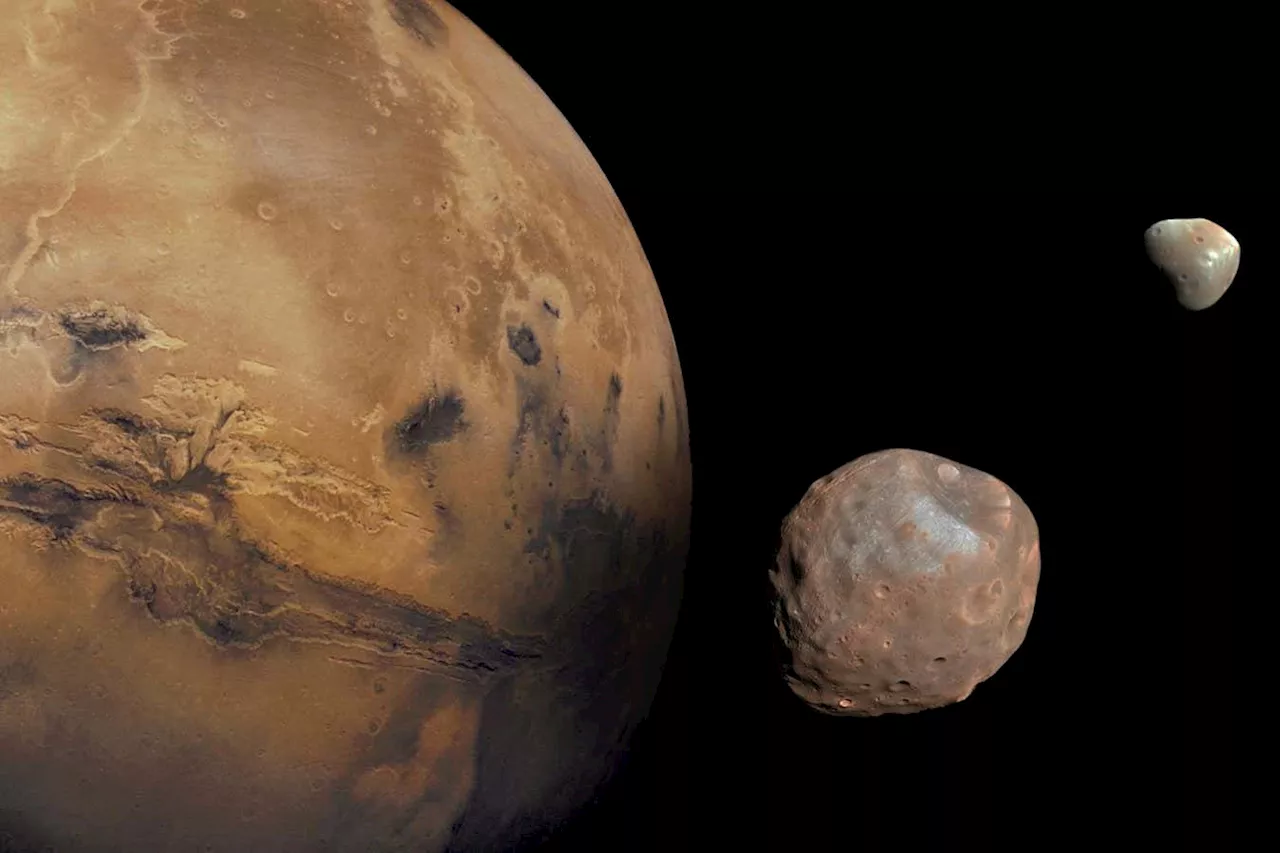 The moons of Mars may have been formed in an icy planetary collisionThe origins of Mars’s moons Phobos and Deimos have long been an enigma, but they may have been formed when a comet-like icy object slammed into the Red Planet
The moons of Mars may have been formed in an icy planetary collisionThe origins of Mars’s moons Phobos and Deimos have long been an enigma, but they may have been formed when a comet-like icy object slammed into the Red Planet
Read more »
