Turbulent ocean currents, called eddies, are no longer being overlooked, thanks to the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite.
Eddies have been overlooked for too long. These turbulent swirls of water, ranging in size from a few kilometers to hundreds of kilometers across, peel off large ocean currents and mix heat and carbon dioxide into deeper ocean layers, like cream stirred into coffee. They are the most energetic feature of the ocean, critical to getting climate models right—but also largely invisible to satellites, except when they happen to sweep up a massive bloom of green phytoplankton.
For oceanographers it will be like slipping on a pair of eyeglasses, says Rosemary Morrow, a physical oceanographer at the Laboratory of Space, Geophysical, and Oceanographic Studies in Toulouse, France. The satellite7 kilometers across and cover nearly the entire globe every 21 days. On land, SWOT will be able to map the changing height of more than 6 million lakes, from the Great Lakes down to ponds, while also capturing flows in rivers wider than 100 meters.
SWOT gains a sharper view with the help of two 5-meter booms, each bearing an antenna to catch reflections of the radar signal SWOT pulses to Earth’s surface. The widely separated antennas give SWOT the resolution to measure the height of a patch of water just kilometers wide, rather than hundreds of kilometers, bringing small eddies into view.
Although SWOT is supposed to operate for just 3 years, its science team plans to look for correlations between the water flows it detects and features the ongoing Landsat missions see in visible light, such as changing lake and river widths. Those visible changes could serve as proxies for water levels, allowing researchers to continue to keep tabs on the planet’s flows, Pavelsky says. “Even once SWOT is gone, you can still continue that analysis.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Colossal Discovery on Mars Could Drive Surging Magma Under The SurfaceScientists may have just identified the culprit behind signs of recently active volcanism on Mars.
Colossal Discovery on Mars Could Drive Surging Magma Under The SurfaceScientists may have just identified the culprit behind signs of recently active volcanism on Mars.
Read more »
 Surprising Martian Discovery: Massive Mantle Plume Pushing the Surface of Mars UpwardGiant Mantle Plume Reveals Mars Is More Active Than Previously Thought Orbital observations unveil the presence of an enormous mantle plume pushing the surface of Mars upward and driving intense volcanic and seismic activity. On Earth, shifting tectonic plates reshuffle the planet’s surface and
Surprising Martian Discovery: Massive Mantle Plume Pushing the Surface of Mars UpwardGiant Mantle Plume Reveals Mars Is More Active Than Previously Thought Orbital observations unveil the presence of an enormous mantle plume pushing the surface of Mars upward and driving intense volcanic and seismic activity. On Earth, shifting tectonic plates reshuffle the planet’s surface and
Read more »
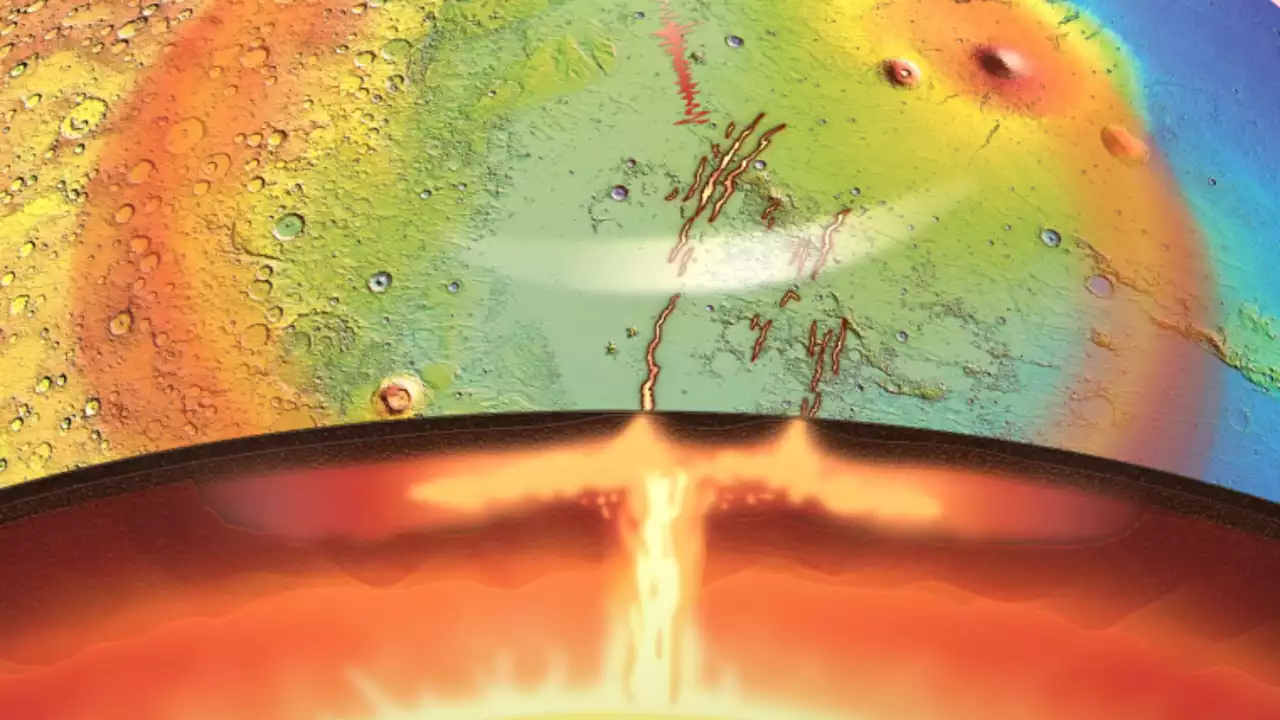 Giant mantle plume under Martian surface suggests the planet is not deadResearchers have found evidence that Mars may have a massive, active mantle plume below its surface, causing marsquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Giant mantle plume under Martian surface suggests the planet is not deadResearchers have found evidence that Mars may have a massive, active mantle plume below its surface, causing marsquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Read more »
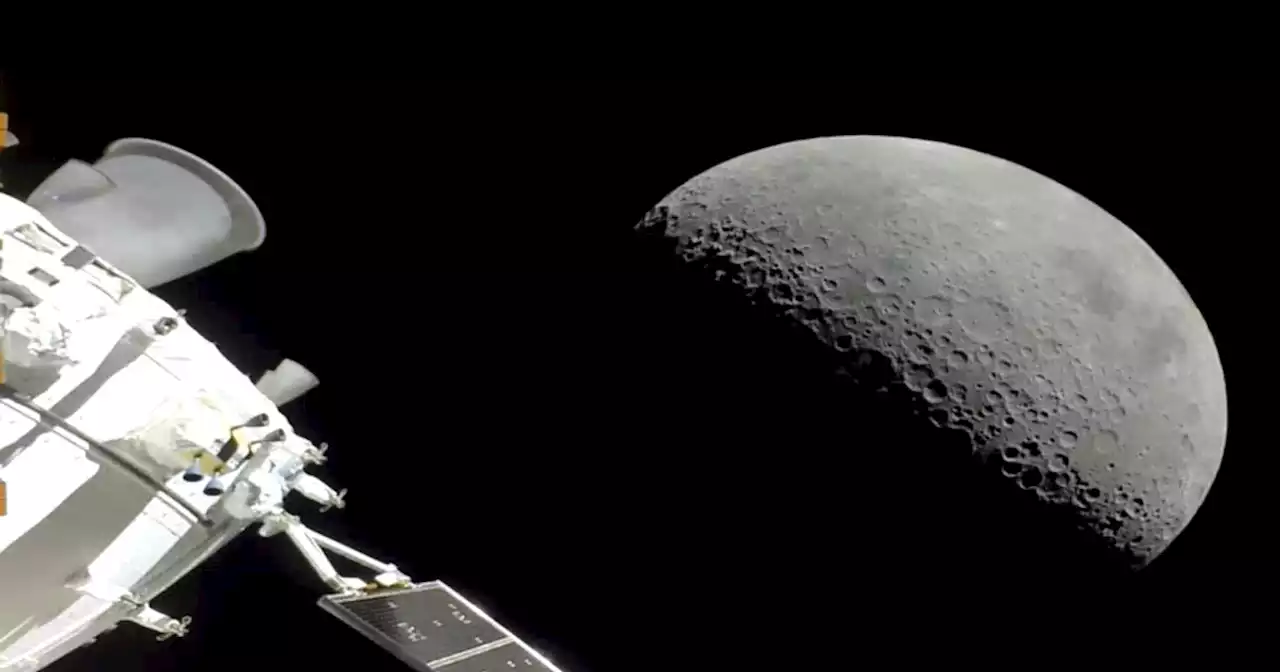 Watch: Artemis 1 Orion craft approaches cratered lunar surface in stunning flybyIt was suggested that the large crater seen in video from Artemis 1 is Kepler, which is a 19-mile divot near the landing zone for Apollo 12.
Watch: Artemis 1 Orion craft approaches cratered lunar surface in stunning flybyIt was suggested that the large crater seen in video from Artemis 1 is Kepler, which is a 19-mile divot near the landing zone for Apollo 12.
Read more »
 Apple TV+ Renews Hit Psychological Thriller Series for New SeasonGugu Mbatha-Raw's psychological thriller Surface has been renewed for a second season at AppleTVPlus
Apple TV+ Renews Hit Psychological Thriller Series for New SeasonGugu Mbatha-Raw's psychological thriller Surface has been renewed for a second season at AppleTVPlus
Read more »