An international research team has succeeded in developing a new type of material in the rather young research field of covalent organic frameworks. The new two-dimensional polymer is characterized by the fact that its properties can be controlled in a targeted and reversible manner.
This has brought the researchers a step closer to the goal of realizing switchable quantum states.
Previous research on COFs has generally focussed on the construction of rigid frameworks with static material properties. Dr Florian Auras and his team at the Chair of Molecular Functional Materials at TUD have now developed a design strategy for dynamic two-dimensional COFs that can open and close their pores in a controlled manner, similar to a sponge.
The surface of a material often has properties that are very different from the properties within the material. An international research team has now succeeded in investigating the surfaces of ...
Engineering And Construction Civil Engineering Chemistry Mobile Computing Information Technology
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Self-assembling and disassembling swarm molecular robots via DNA molecular controllerResearchers from Tohoku University and Kyoto University have successfully developed a DNA-based molecular controller that autonomously directs the assembly and disassembly of molecular robots. This pioneering technology marks a significant step towards advanced autonomous molecular systems with potential applications in medicine and nanotechnology.
Self-assembling and disassembling swarm molecular robots via DNA molecular controllerResearchers from Tohoku University and Kyoto University have successfully developed a DNA-based molecular controller that autonomously directs the assembly and disassembly of molecular robots. This pioneering technology marks a significant step towards advanced autonomous molecular systems with potential applications in medicine and nanotechnology.
Read more »
 Self-assembling and disassembling swarm molecular robots via DNA molecular controllerResearchers have succeeded in developing a DNA-based molecular controller. Crucially, this controller enables the autonomous assembly and disassembly of molecular robots, as opposed to manually directing it.
Self-assembling and disassembling swarm molecular robots via DNA molecular controllerResearchers have succeeded in developing a DNA-based molecular controller. Crucially, this controller enables the autonomous assembly and disassembly of molecular robots, as opposed to manually directing it.
Read more »
 Researchers explore the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials of essential oilsEssential oils, also known as ethereal oils, are volatile, aromatic compounds derived from plants. Found in only about 10% of the plant kingdom, these oils are present in secretory structures such as glands, ducts, cavities, and hairs.
Researchers explore the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials of essential oilsEssential oils, also known as ethereal oils, are volatile, aromatic compounds derived from plants. Found in only about 10% of the plant kingdom, these oils are present in secretory structures such as glands, ducts, cavities, and hairs.
Read more »
 Molecules in Motion: Advanced Spectroscopy Captures Molecular Dynamics in Real-TimeScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Molecules in Motion: Advanced Spectroscopy Captures Molecular Dynamics in Real-TimeScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
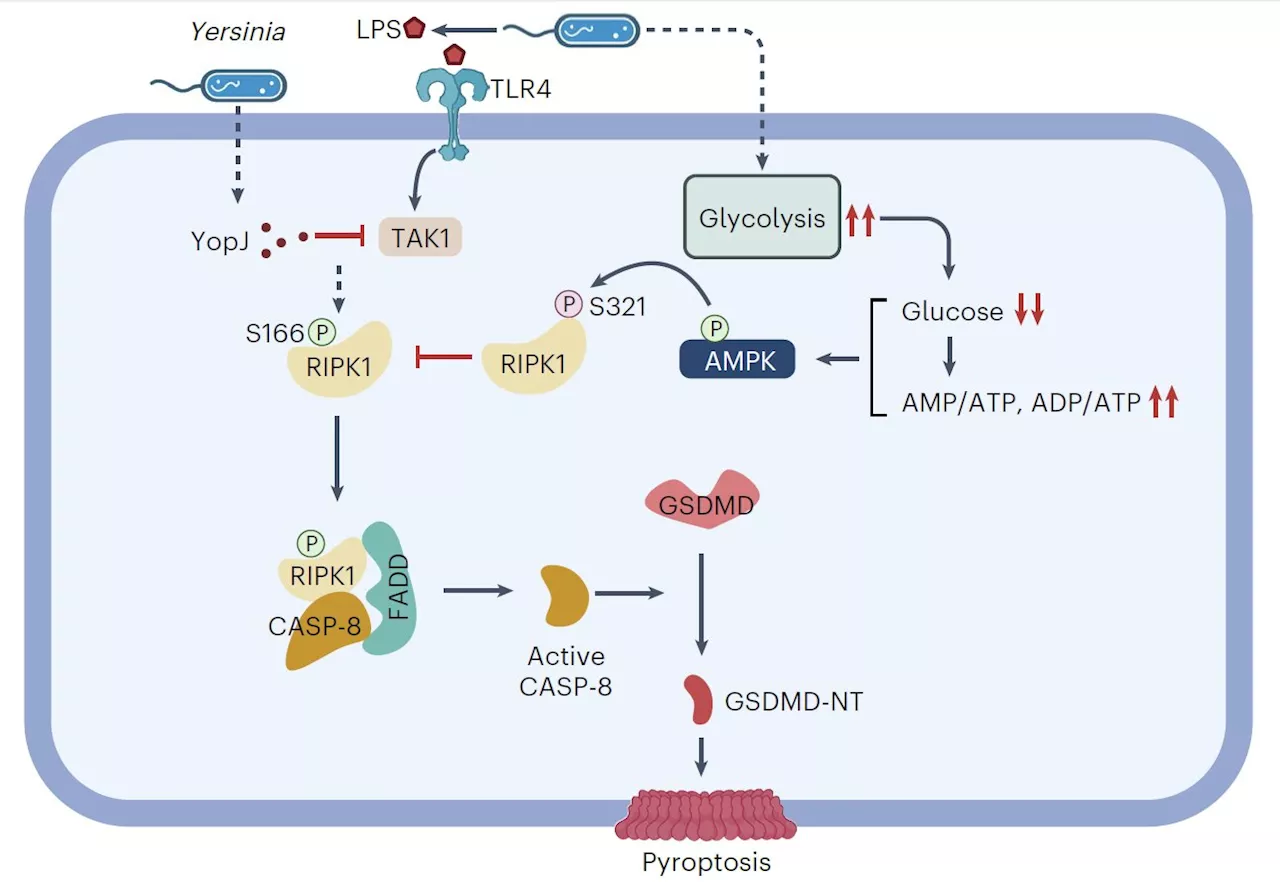 Scientists reveal molecular link between glucose sensing and pyroptosis cell deathAccording to a study published in Nature Microbiology on June 6, researchers led by Prof. Xu Daichao from the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have uncovered the molecular link between glucose sensing and non-classical pyroptosis.
Scientists reveal molecular link between glucose sensing and pyroptosis cell deathAccording to a study published in Nature Microbiology on June 6, researchers led by Prof. Xu Daichao from the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have uncovered the molecular link between glucose sensing and non-classical pyroptosis.
Read more »
 Unveiling the Molecular Mechanisms Behind PTSD and Depression: Latest FindingsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Unveiling the Molecular Mechanisms Behind PTSD and Depression: Latest FindingsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
