Researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, have interrogated several interconnected questions related to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) heteroplasmy and the influence of nuclear genetics.
In their paper,"Nuclear genetic control of mtDNA copy number and heteroplasmy in humans," published in, the team provides a comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms behind mtDNA interactions and their potential implications for human health and evolution.
The study finds that individuals carrying harmful mtDNA mutations at low heteroplasmy levels displayed intermediate disease traits. This suggests that the level of heteroplasmy can affect the manifestation level of a disease. Nuclear genetic variants were found to influence the levels of mtDNA indels, possibly affecting the replicative efficiency of mtDNA molecules with different alleles. The levels of mtDNA in cells have previously been associated with diseases.Unexpectedly, the study found that approximately 25% of the variation in mtCN between individuals can be attributed to differences in blood-cell composition.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 The interplay between the microbiota, the epigenome, and nutrition among obese adults during behavioral weight reductionStudy evaluated associations between gut microbiome (MB), deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation (DNAme), and nutrition.
The interplay between the microbiota, the epigenome, and nutrition among obese adults during behavioral weight reductionStudy evaluated associations between gut microbiome (MB), deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation (DNAme), and nutrition.
Read more »
 Oxford Researchers Reveal How To Maximize Solid-State Battery PotentialOxford University researchers have unveiled mechanisms causing lithium metal solid-state batteries to fail, potentially revolutionizing EV and aviation battery performance.
Oxford Researchers Reveal How To Maximize Solid-State Battery PotentialOxford University researchers have unveiled mechanisms causing lithium metal solid-state batteries to fail, potentially revolutionizing EV and aviation battery performance.
Read more »
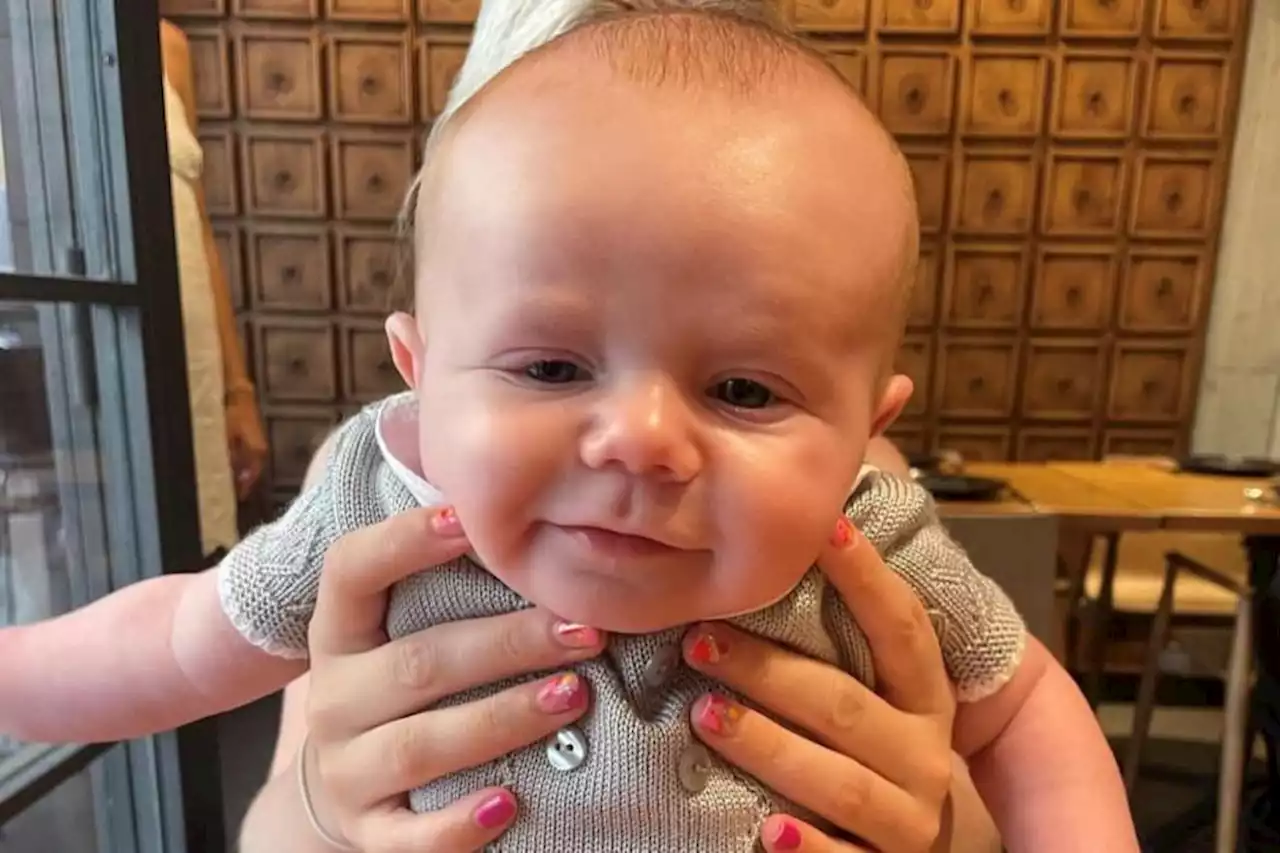 Stem cell DNA match sought for three-month-old boy with aggressive rare cancerJust 3,100 people are thought to be diagnosed with acute myeloid leukaemia in the UK each year.
Stem cell DNA match sought for three-month-old boy with aggressive rare cancerJust 3,100 people are thought to be diagnosed with acute myeloid leukaemia in the UK each year.
Read more »
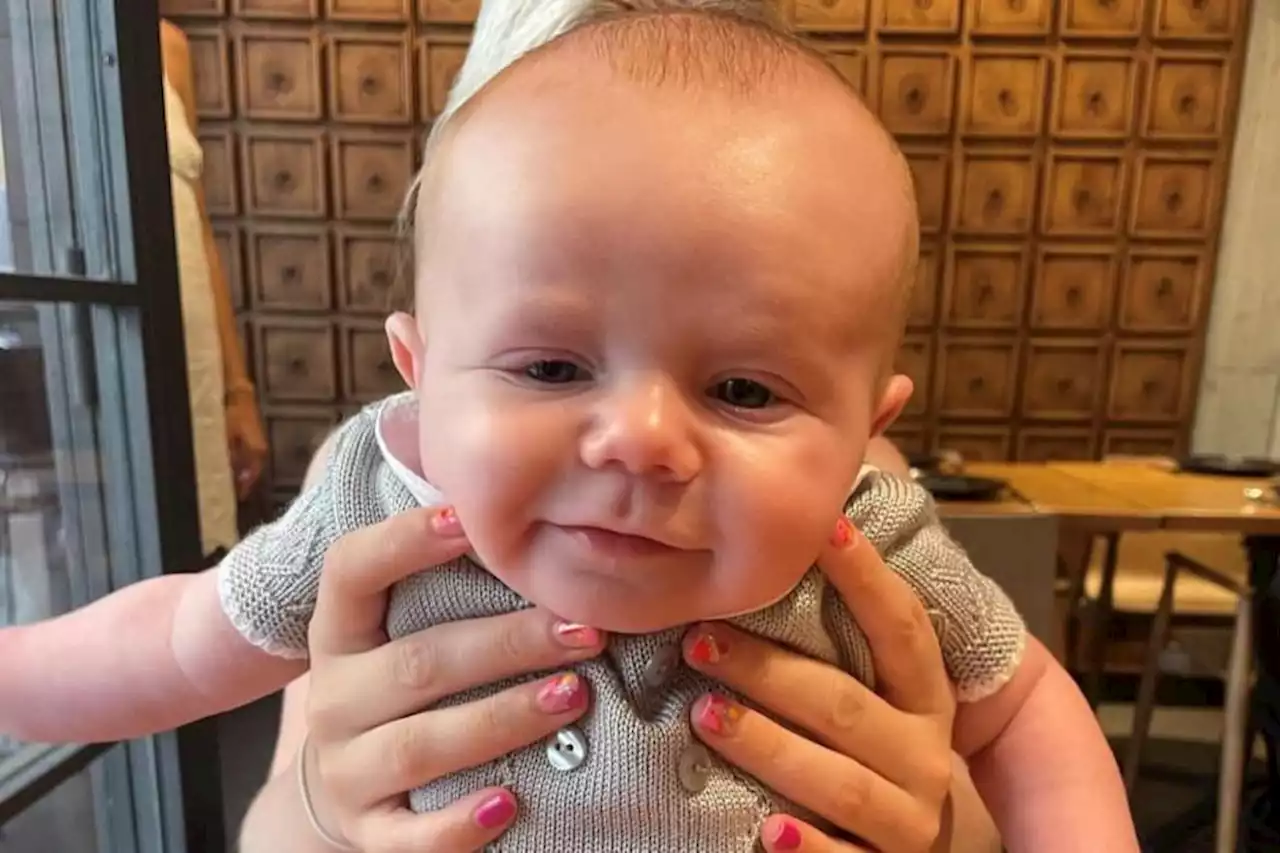 Stem cell DNA match sought for three-month-old boy with aggressive rare cancerJust 3,100 people are thought to be diagnosed with acute myeloid leukaemia in the UK each year.
Stem cell DNA match sought for three-month-old boy with aggressive rare cancerJust 3,100 people are thought to be diagnosed with acute myeloid leukaemia in the UK each year.
Read more »
 New DNA-based anticoagulant could treat heparin-induced thrombocytopeniaVarious medical circumstances, including heart attacks and extreme cases of COVID-19, necessitate the use of anticoagulants, medicines that prevent blood clots
New DNA-based anticoagulant could treat heparin-induced thrombocytopeniaVarious medical circumstances, including heart attacks and extreme cases of COVID-19, necessitate the use of anticoagulants, medicines that prevent blood clots
Read more »
 NUS researchers harness nature's design to develop novel pressure sensorResearchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have developed a novel aero-elastic pressure sensor, called 'eAir'.
NUS researchers harness nature's design to develop novel pressure sensorResearchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have developed a novel aero-elastic pressure sensor, called 'eAir'.
Read more »
