Science, Space and Technology News 2024
MIT researchers have discovered significant epigenetic modifications in ALS patients that could lead to targeted therapies. These modifications, identified in motor neurons from 380 ALS patients, indicate that ALS might consist of various subtypes, each with distinct genetic influences on disease progression.researchers identified genomic regions with chemical modifications linked to disease progression.
Working with the Answer ALS consortium, a team of MIT researchers has analyzed epigenetic modifications — tags that determine which genes are turned on in a cell — in motor neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from 380 ALS patients. Over time, ALS progresses, and individuals affected by the disease gradually lose the ability to initiate and control voluntary movements such as walking, talking, and chewing, including the ability to breathe. The symptoms of ALS worsen progressively.ALS is a rare disease that is estimated to affect about 30,000 people in the United States.
In this study, Fraenkel and his colleagues wanted to see if patient-derived cells could offer any information about molecular differences that are relevant to ALS. They focused on epigenomic modifications, using a method called ATAC-seq to measure chromatin density across the genome of each cell. Chromatin is a complex ofand proteins that determines which genes are accessible to be transcribed by the cell, depending on how densely packed the chromatin is.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers breed tomato plants that contain the complete genetic material of both parent plantsIn a new study published in Nature Genetics, led by Charles Underwood from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research in Cologne, Germany, scientists established a system to generate clonal sex cells in tomato plants and used them to design the genomes of offspring.
Researchers breed tomato plants that contain the complete genetic material of both parent plantsIn a new study published in Nature Genetics, led by Charles Underwood from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research in Cologne, Germany, scientists established a system to generate clonal sex cells in tomato plants and used them to design the genomes of offspring.
Read more »
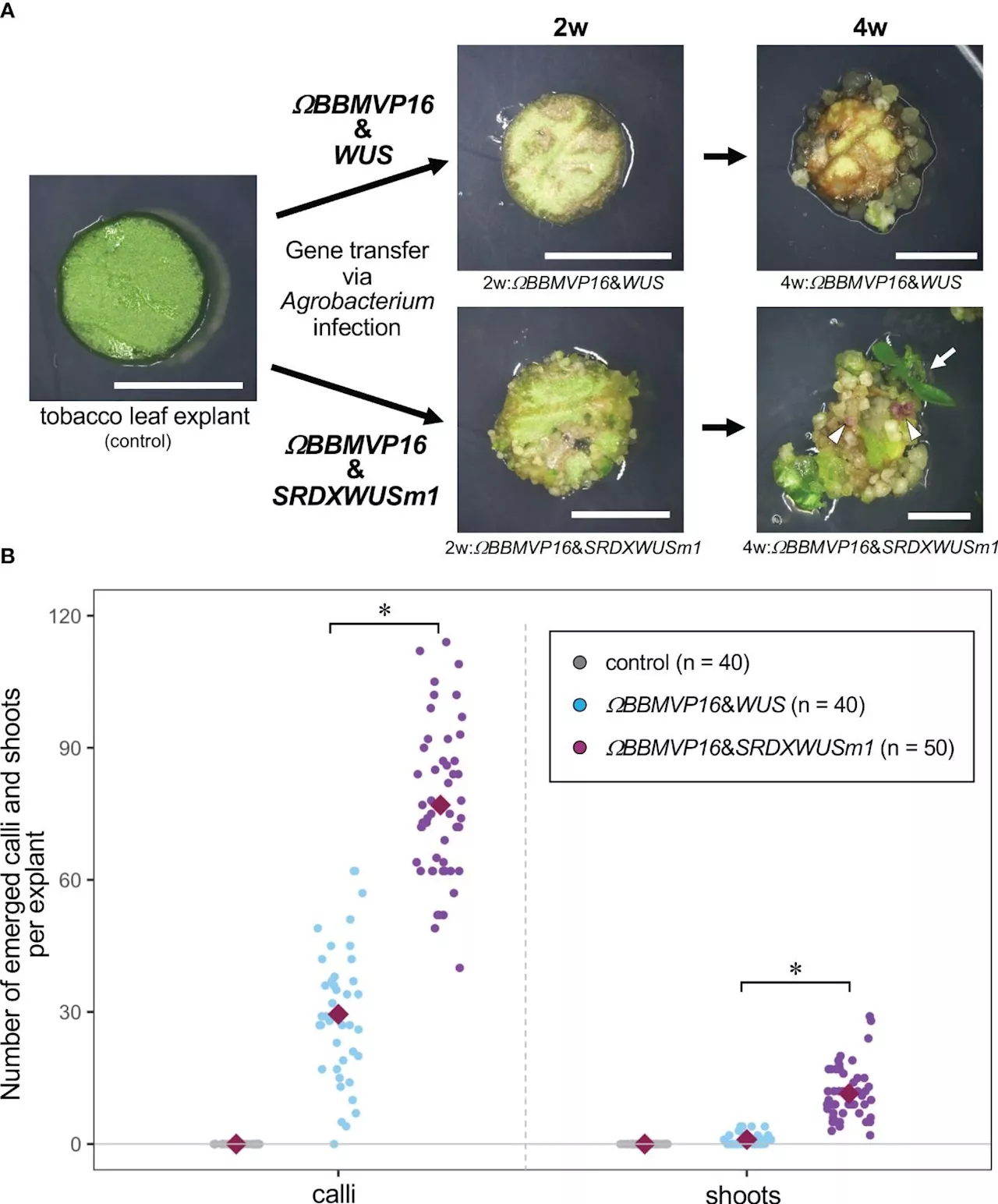 Researchers develop genetic plant regeneration approach without the application of phytohormonesFor ages now, plants have been the primary source of nutrition for animals and mankind. Additionally, plants are used for the extraction of various medicinal and therapeutic compounds. However, their indiscriminate use, along with the rising demand for food, underscores the need for novel plant breeding practices.
Researchers develop genetic plant regeneration approach without the application of phytohormonesFor ages now, plants have been the primary source of nutrition for animals and mankind. Additionally, plants are used for the extraction of various medicinal and therapeutic compounds. However, their indiscriminate use, along with the rising demand for food, underscores the need for novel plant breeding practices.
Read more »
 After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological diseaseSpinocerebellar ataxia 4 is a devastating progressive movement disease that can begin as early as the late teens. Now, a multinational research team has conclusively identified the genetic difference that causes the disease, bringing answers to families and opening the door to future treatments.
After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological diseaseSpinocerebellar ataxia 4 is a devastating progressive movement disease that can begin as early as the late teens. Now, a multinational research team has conclusively identified the genetic difference that causes the disease, bringing answers to families and opening the door to future treatments.
Read more »
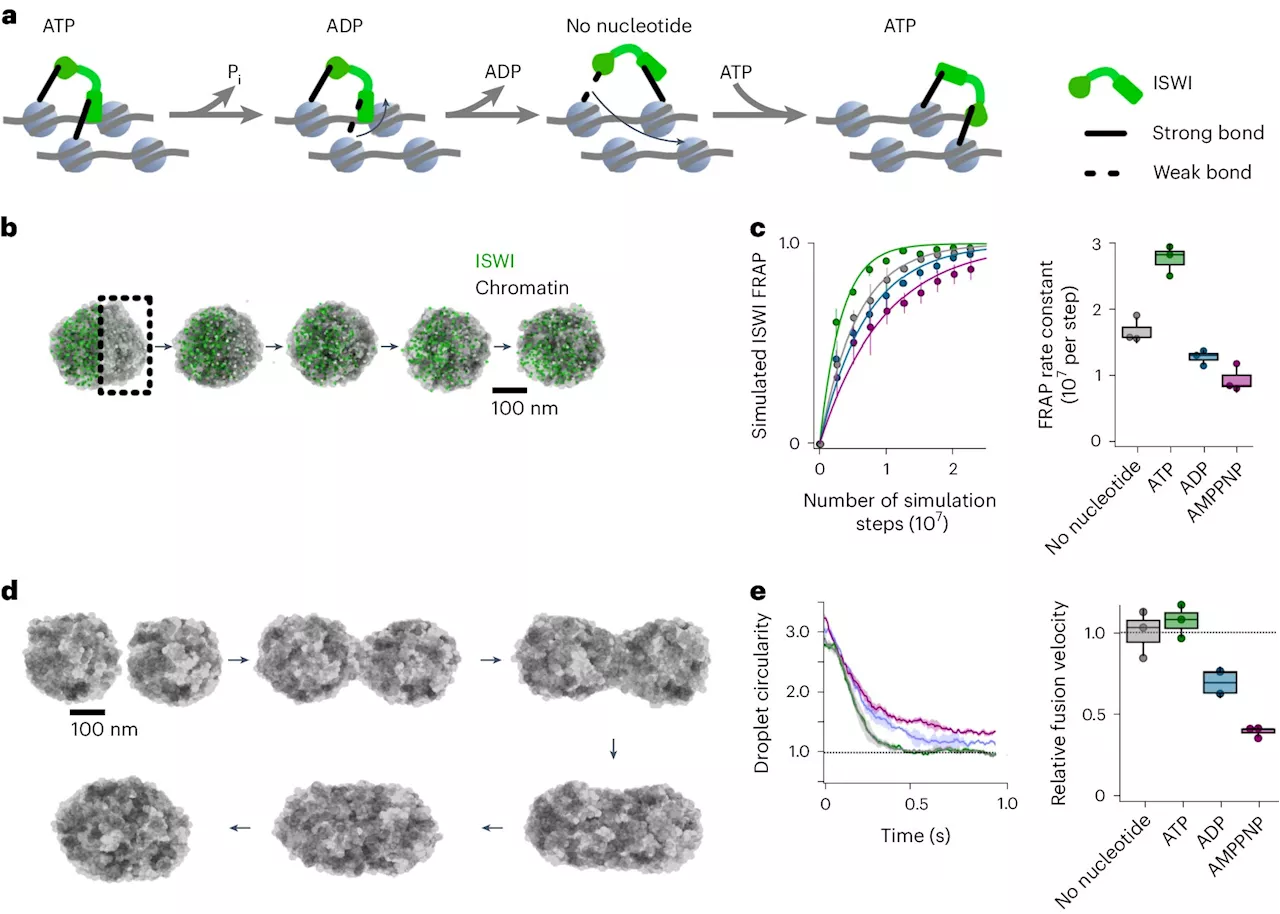 Researchers decipher how an enzyme modifies the genetic material in the cell nucleusInside the cell nucleus, the DNA molecule is found in a densely packed DNA-protein complex known as chromatin. Here the DNA is wrapped around a core of histone proteins and densely packed to form nucleosomes. The structure of the nucleosomes determines which genes are accessible and active and therefore plays an important role in gene regulation.
Researchers decipher how an enzyme modifies the genetic material in the cell nucleusInside the cell nucleus, the DNA molecule is found in a densely packed DNA-protein complex known as chromatin. Here the DNA is wrapped around a core of histone proteins and densely packed to form nucleosomes. The structure of the nucleosomes determines which genes are accessible and active and therefore plays an important role in gene regulation.
Read more »
 Researchers identify characteristics of meltwater runoff in three sub-basins of the Urumqi River BasinGlacier runoff plays an important role in both contributing to and regulating river runoff. The contributions and regulating effects of various hydrological components can only be revealed through comparative studies on catchments with different glacier coverage.
Researchers identify characteristics of meltwater runoff in three sub-basins of the Urumqi River BasinGlacier runoff plays an important role in both contributing to and regulating river runoff. The contributions and regulating effects of various hydrological components can only be revealed through comparative studies on catchments with different glacier coverage.
Read more »
 As national wastewater testing expands, Texas researchers identify bird flu in nine citiesAs researchers increasingly rely on wastewater testing to monitor the spread of bird flu, some are questioning the reliability of the tests being used.
As national wastewater testing expands, Texas researchers identify bird flu in nine citiesAs researchers increasingly rely on wastewater testing to monitor the spread of bird flu, some are questioning the reliability of the tests being used.
Read more »