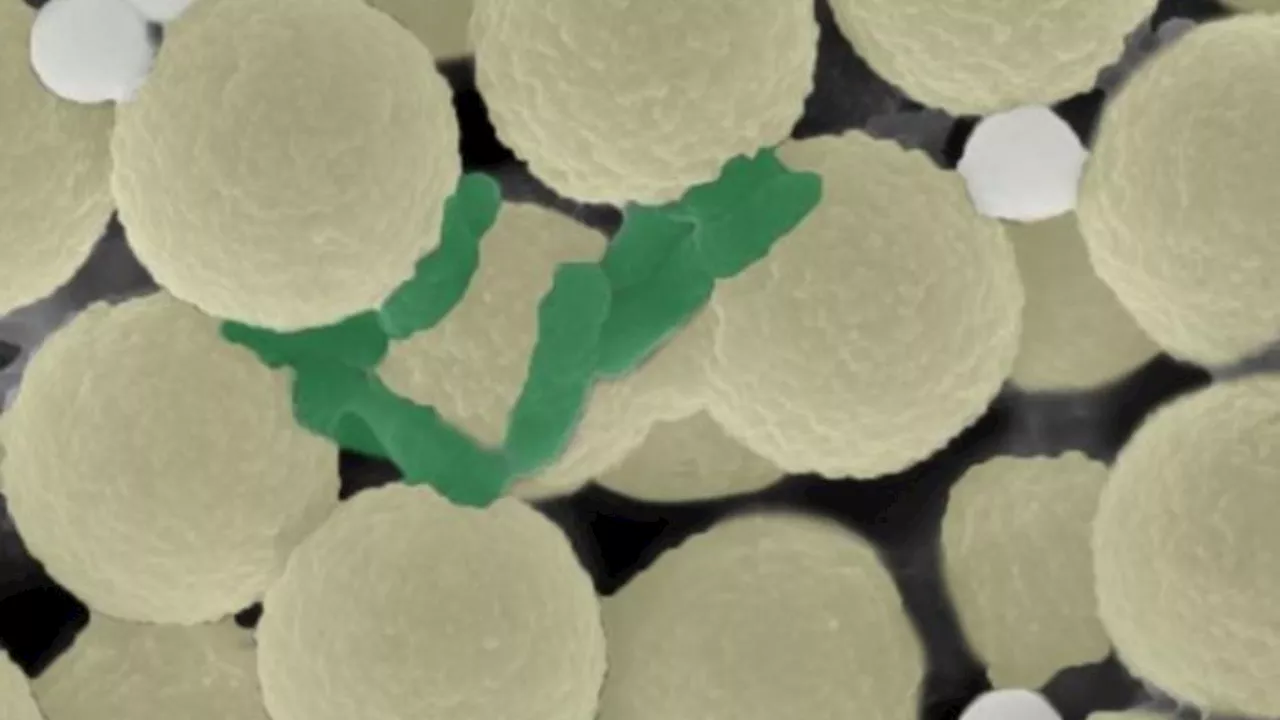
Researchers develop swarms of microrobots to combat microplastics and bacteria in water, aiming its restore natural balance.
The team linked positively charged polymer strands to magnetic microparticles, enabling movement solely in response to magnetic fields, to create the bots.To create the microrobots, the team connected strands of a positively charged polymer to magnetic microparticles, which respond solely to magnetic fields for movement.The small size of microplastics, measuring 5 millimeters or less, presents an additional facet to the plastic pollution dilemma.
According to researchers, it gets considerably more difficult to remove microplastics from rivers and oceans when they decompose from outdated food packaging, abandoned kid’s toys, and other poorly managed plastic debris. These microscopic pieces of plastic also draw germs, even pathogenic ones.Microbes and plastics are drawn to the polymer strands that emanate from the beads’ surface. Additionally, the completed items, or individual robots, had a diameter of 2.8 micrometers.
Subsequently, the microrobots were incorporated into the tank and subjected to a rotating magnetic field for half an hour, with 10-second intervals of on-and-off exposure.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
![Microrobots Swarm the Seas, Capturing Microplastics and Bacteria [Video]](https://i.headtopics.com/images/2024/5/8/scitechdaily1/microrobots-swarm-the-seas-capturing-microplastics-microrobots-swarm-the-seas-capturing-microplastics-9D891C86C3D7F876017CE928941D8E82.webp?w=640) Microrobots Swarm the Seas, Capturing Microplastics and Bacteria [Video]Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Microrobots Swarm the Seas, Capturing Microplastics and Bacteria [Video]Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
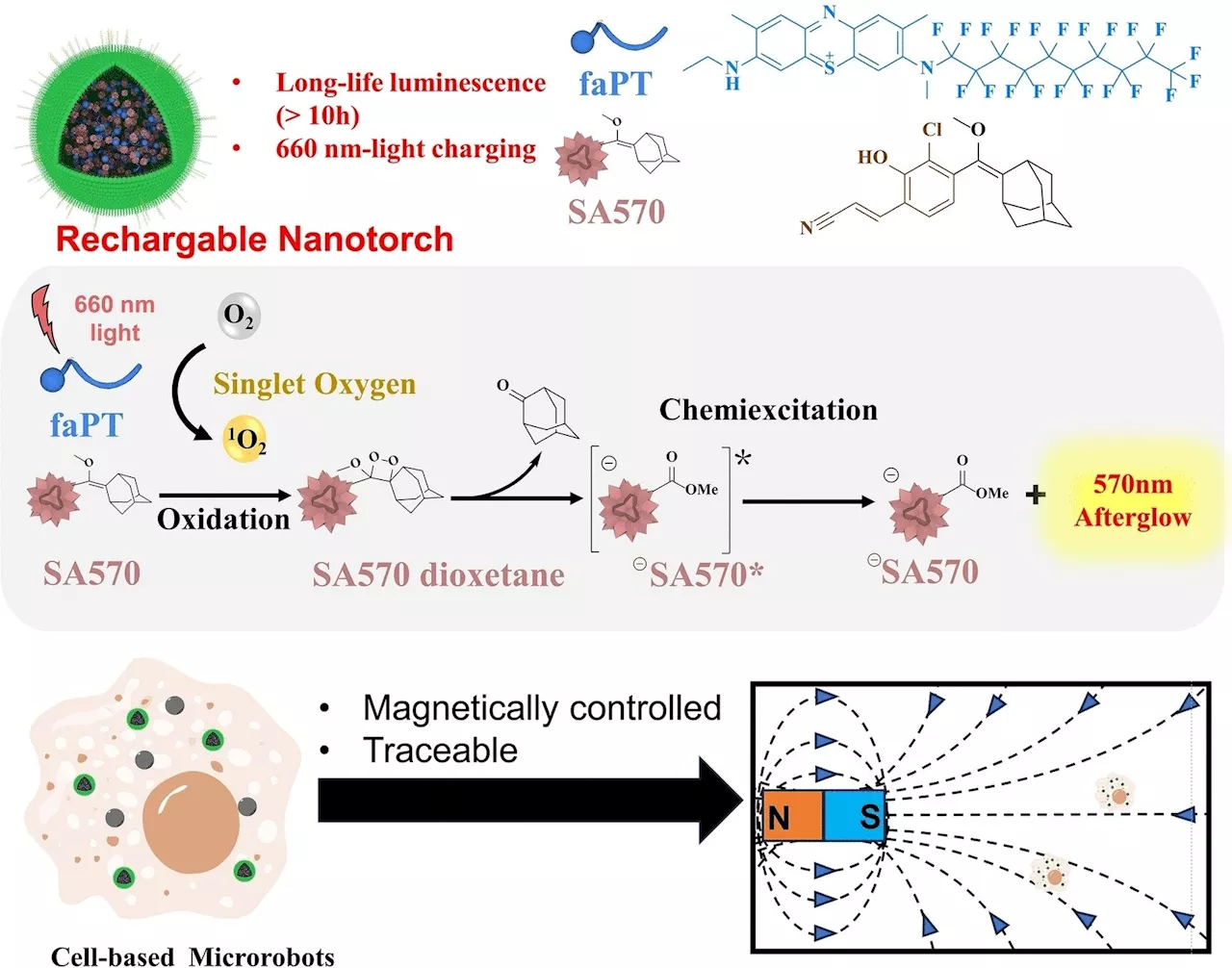 A rechargeable nanotorch: Afterglow luminescence imaging tracks cell-based microrobots in real timeAn afterglow luminescent nanoprobe opens up new possibilities for imaging living cells. As a research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, their new 'nanotorch' can continue to luminesce for more than 10 days after a single excitation.
A rechargeable nanotorch: Afterglow luminescence imaging tracks cell-based microrobots in real timeAn afterglow luminescent nanoprobe opens up new possibilities for imaging living cells. As a research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, their new 'nanotorch' can continue to luminesce for more than 10 days after a single excitation.
Read more »
 Researchers realize hydrogen formation by contact electrification of water microdroplets and its regulationDirect utilization of water as a source of hydrogen atoms and molecules is fundamental to the evolution of the ecosystem and industry. However, liquid water is an unfavorable electron donor for forming these hydrogen species due to its redox inertness.
Researchers realize hydrogen formation by contact electrification of water microdroplets and its regulationDirect utilization of water as a source of hydrogen atoms and molecules is fundamental to the evolution of the ecosystem and industry. However, liquid water is an unfavorable electron donor for forming these hydrogen species due to its redox inertness.
Read more »
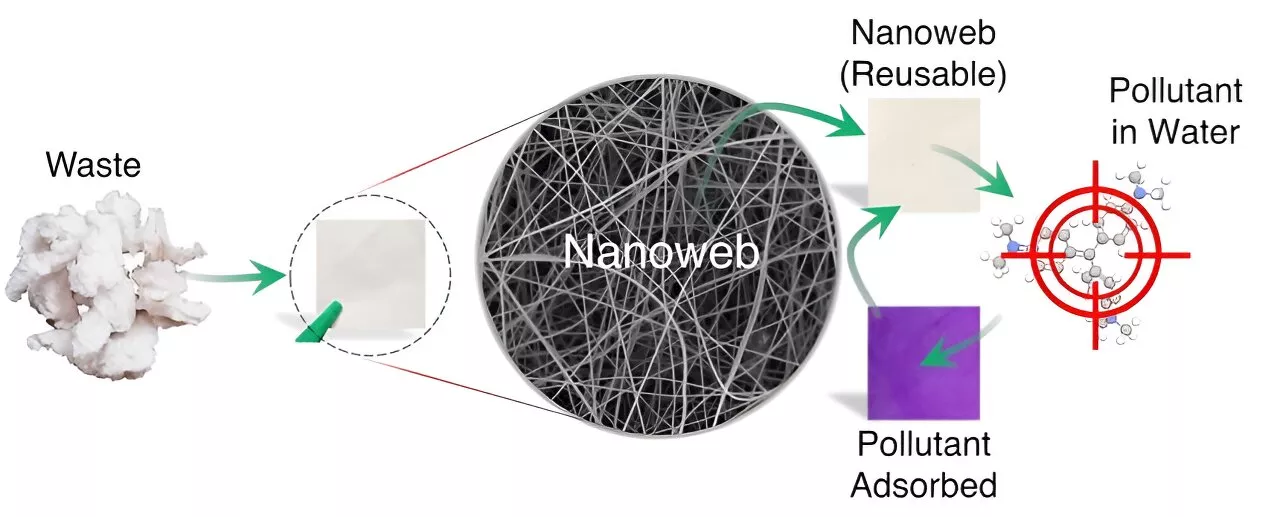 Nanofibers rid water of hazardous dyes: Researchers develop efficient filters based on cellulose wasteUsing waste to purify water may sound counterintuitive. But at TU Wien, this is exactly what has now been achieved. Researchers have developed a special nanostructure to filter a widespread class of harmful dyes from water.
Nanofibers rid water of hazardous dyes: Researchers develop efficient filters based on cellulose wasteUsing waste to purify water may sound counterintuitive. But at TU Wien, this is exactly what has now been achieved. Researchers have developed a special nanostructure to filter a widespread class of harmful dyes from water.
Read more »
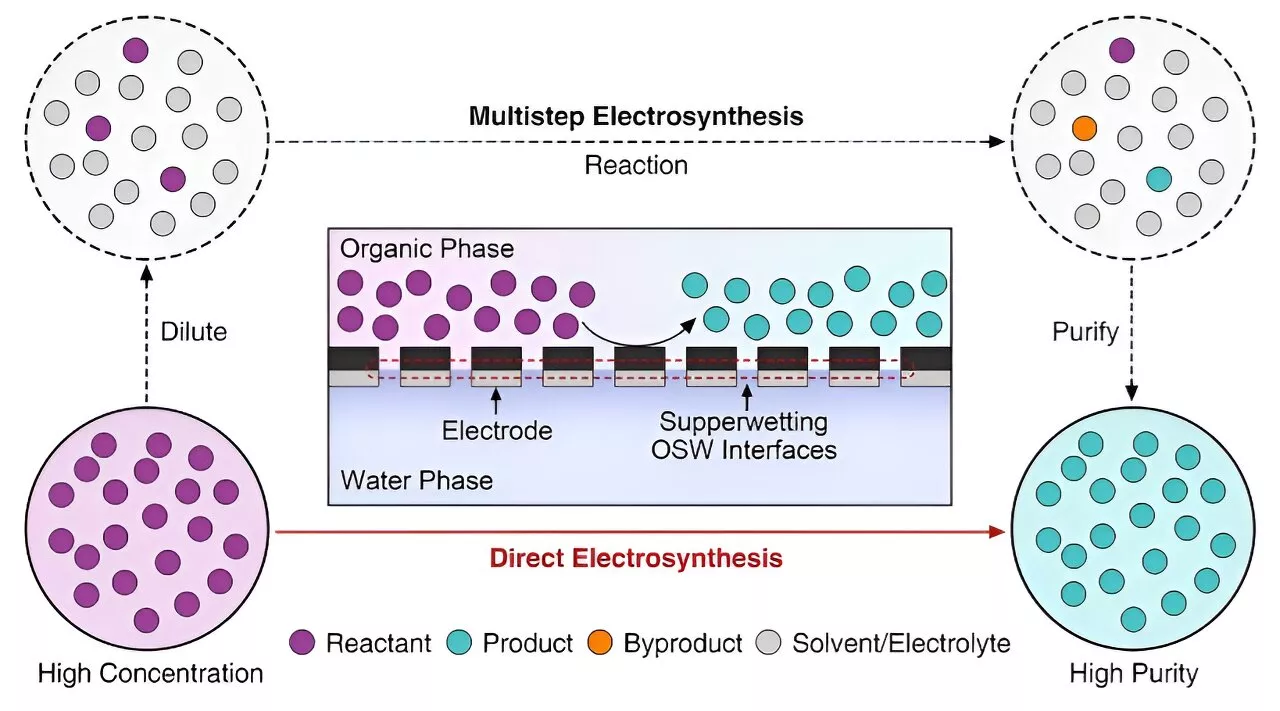 Researchers achieve electrosynthesis via superwetting organic-solid-water interfacesChinese scientists have recently achieved the direct synthesis of high-purity benzaldehyde chemicals from the selective electrooxidation of benzyl alcohol.
Researchers achieve electrosynthesis via superwetting organic-solid-water interfacesChinese scientists have recently achieved the direct synthesis of high-purity benzaldehyde chemicals from the selective electrooxidation of benzyl alcohol.
Read more »
 Researchers reveal water-assisted oxidative redispersion of metal nanoparticlesOxidative redispersion at elevated temperatures has long been utilized in heterogeneous catalysis for the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts and the synthesis of metal single atom and cluster catalysts. These redispersion processes require a considerable energy input.
Researchers reveal water-assisted oxidative redispersion of metal nanoparticlesOxidative redispersion at elevated temperatures has long been utilized in heterogeneous catalysis for the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts and the synthesis of metal single atom and cluster catalysts. These redispersion processes require a considerable energy input.
Read more »