Neighborhood watch. 🔭 NASAWebb captured its first images & spectra of our planetary neighbor, Mars. Webb’s infrared-sensitivity and location gives unique insight to NASAMars short-term phenomena like dust storms, weather, & seasonal changes. More:
This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process.
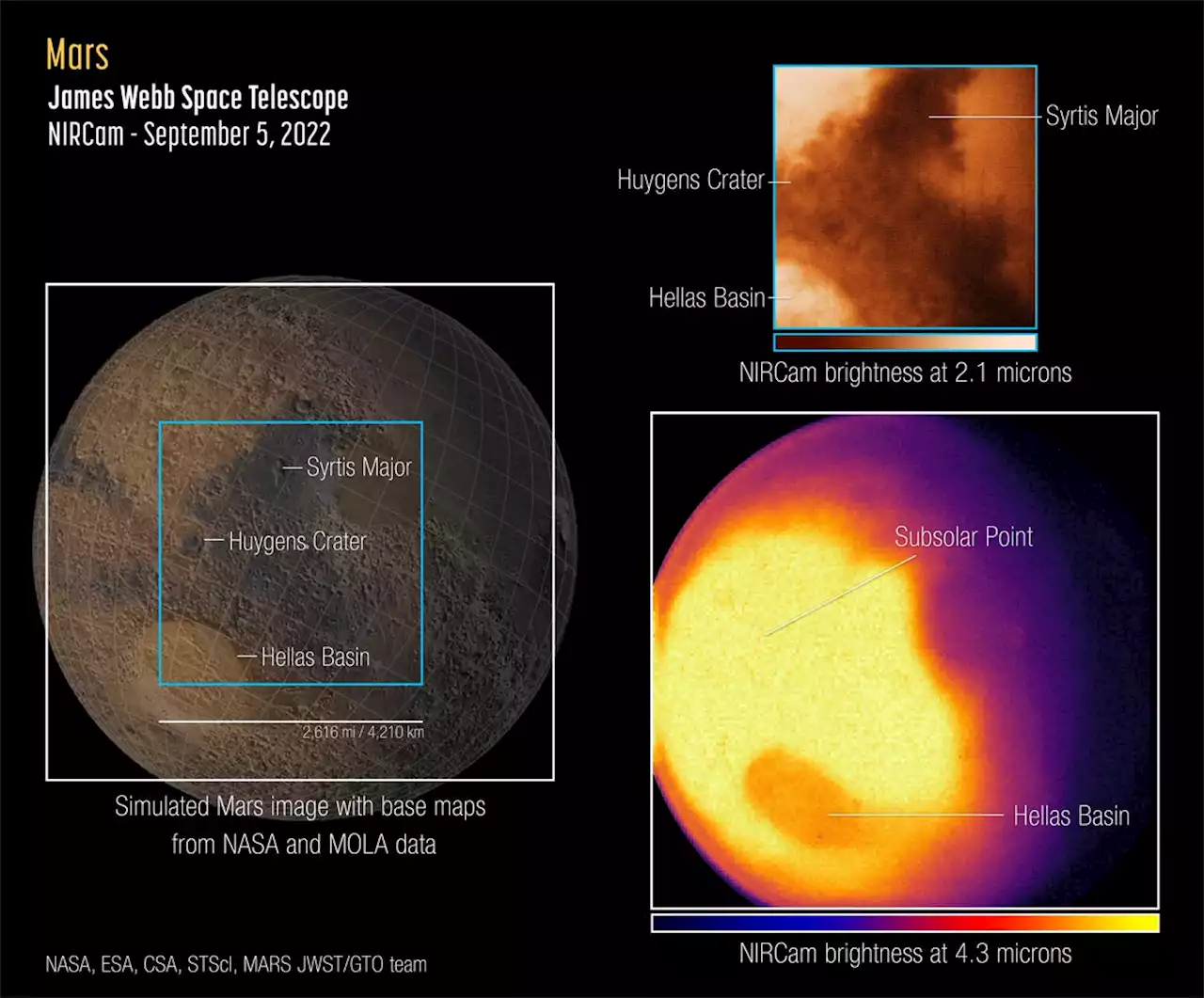
Webb’s first images of Mars, captured by its NIRCam instrument Sept. 5, 2022 [Guaranteed Time Observation Program 1415]. Left: Reference map of the observed hemisphere of Mars from NASA and the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter . Top right: NIRCam image showing 2.1-micron reflected sunlight, revealing surface features such as craters and dust layers. Bottom right: Simultaneous NIRCam image showing ~4.
However, temperature is not the only factor affecting the amount of 4.3-micron light reaching Webb with this filter. As light emitted by the planet passes through Mars’ atmosphere, some gets absorbed by carbon dioxide molecules. The Hellas Basin – which is the largest well-preserved impact structure on Mars, spanning more than 1,200 miles – appears darker than the surroundings because of this effect.