Researchers have found evidence that low oxygen levels in tumors could actually enhance some of the body's immune responses against cancer, in contrast with the general paradigm that hypoxia exclusively helps cancer progression.
Low oxygen levels in tumors could enhance some of the body's immune responses against cancer." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 19 September 2024. <www.sciencedaily.comJosep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute. . Low oxygen levels in tumors could enhance some of the body's immune responses against cancer.Josep Carreras Leukaemia Research Institute."Low oxygen levels in tumors could enhance some of the body's immune responses against cancer." ScienceDaily. www.
Researchers have found that a strain of gut bacteria can boost immune responses and enhance cancer immunotherapy to fight sarcoma tumors in ... Researchers identified a key metabolite in cells that helps direct immune responses and explains at a single cell level why immune cells that most efficiently recognize pathogens, vaccines, or ...
Researchers have unveiled a detailed understanding of immune responses in cancer, marking a significant development in the field. Utilizing data from more than 1,000 tumors across 10 different ... A new study has revealed a single protein expressed at high levels by cancer cells across a broad range of malignancies that erects a multifaceted barrier to anti-cancer immune responses in mouse ...Will EEG Be Able to Read Your Dreams? The Future of the Brain Activity Measure as It Marks 100 Years
Lymphoma Cancer Breast Cancer Lung Cancer Colon Cancer Skin Cancer Brain Tumor
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
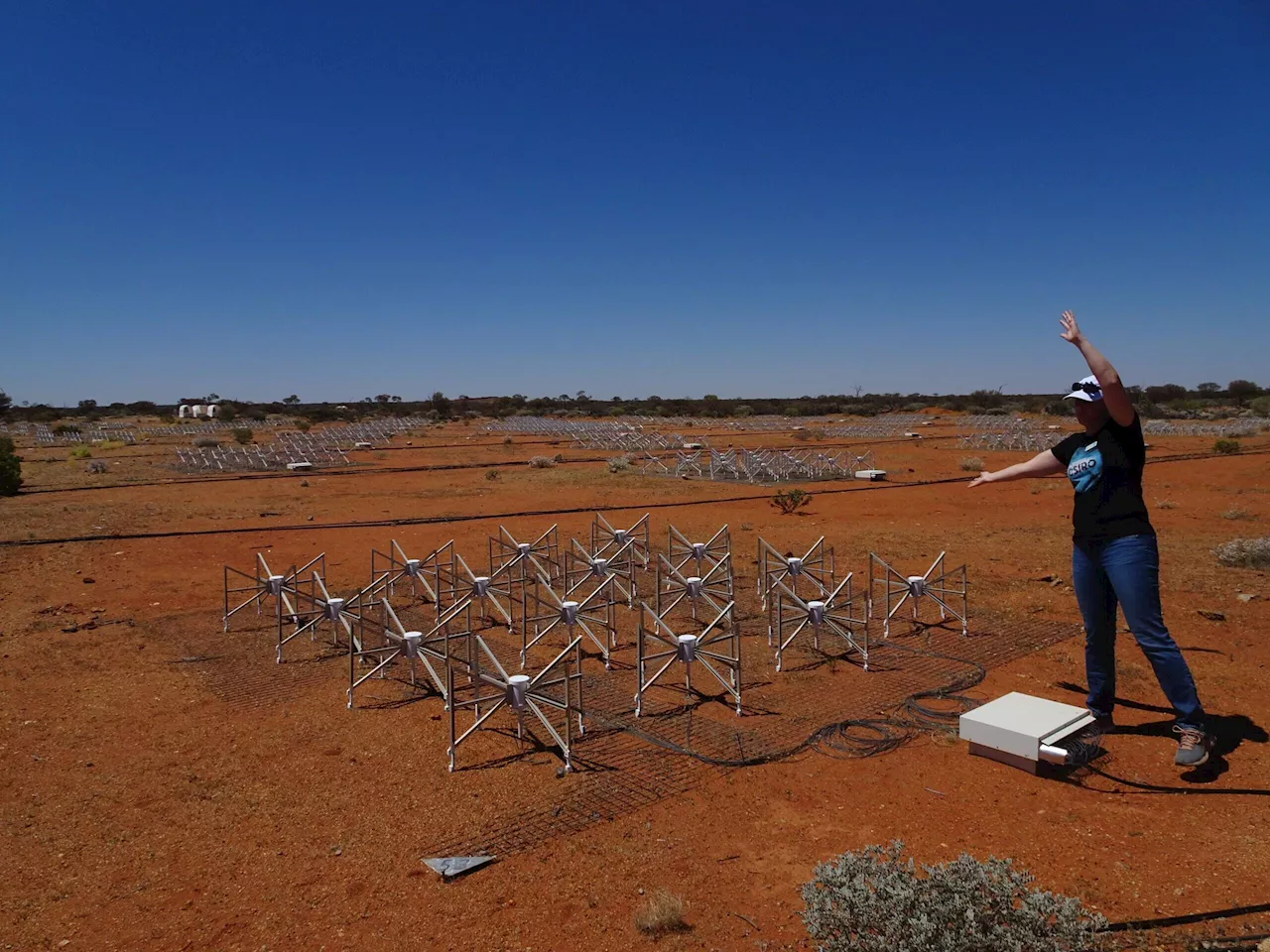 Researchers start first low frequency search for alien technology in distant galaxiesThe SETI Institute, the Berkeley SETI Research Center and the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research announced a study using the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) in Western Australia. Led by Dr. Chenoa Tremblay of the SETI Institute and Prof.
Researchers start first low frequency search for alien technology in distant galaxiesThe SETI Institute, the Berkeley SETI Research Center and the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research announced a study using the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) in Western Australia. Led by Dr. Chenoa Tremblay of the SETI Institute and Prof.
Read more »
 Researchers identify genes for low glycemic index and high protein in riceA team of researchers at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) has identified genes and markers responsible for low glycemic index (GI) and high protein content in rice, using genetics and artificial intelligence classification methods.
Researchers identify genes for low glycemic index and high protein in riceA team of researchers at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) has identified genes and markers responsible for low glycemic index (GI) and high protein content in rice, using genetics and artificial intelligence classification methods.
Read more »
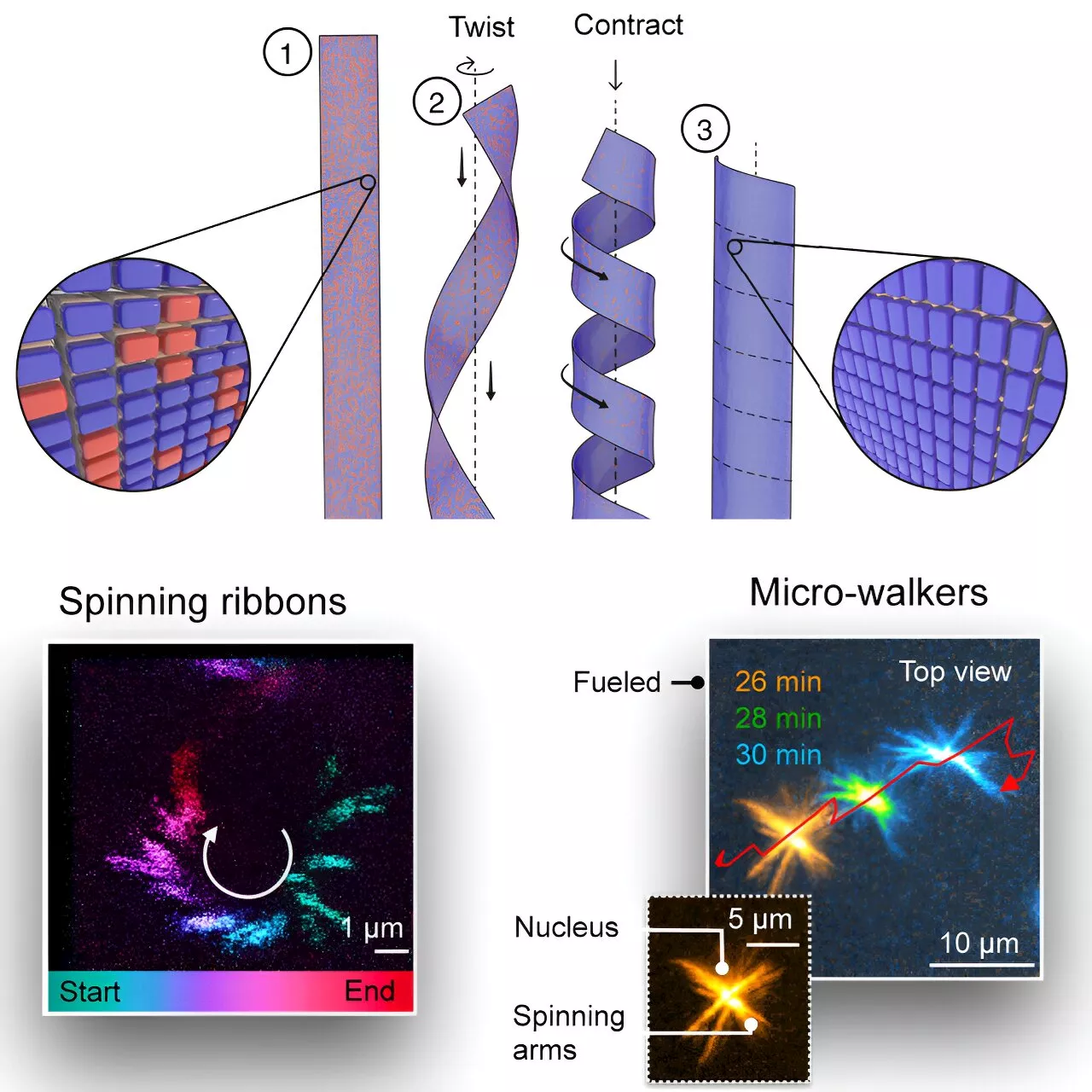 Synthetic mini-motor: Researchers convert chemical energy into rotational energy at the supramolecular levelResearchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have developed an artificial motor at the supramolecular level that can develop impressive power. This wind-up motor is a tiny ribbon made of special molecules. When energy is applied, this ribbon aligns itself, moves like a small fin and can thus push objects.
Synthetic mini-motor: Researchers convert chemical energy into rotational energy at the supramolecular levelResearchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have developed an artificial motor at the supramolecular level that can develop impressive power. This wind-up motor is a tiny ribbon made of special molecules. When energy is applied, this ribbon aligns itself, moves like a small fin and can thus push objects.
Read more »
 Researchers synthesize molecular aggregates for solar energy applicationsNo molecule stands alone—they need others, at least when it comes to being able to display useful photophysical, electronic, and chemical properties. When individual molecules combine into an aggregate, or a complex of two or more molecules, they become much more than the sum of their individual parts.
Researchers synthesize molecular aggregates for solar energy applicationsNo molecule stands alone—they need others, at least when it comes to being able to display useful photophysical, electronic, and chemical properties. When individual molecules combine into an aggregate, or a complex of two or more molecules, they become much more than the sum of their individual parts.
Read more »
 Researchers identify effective materials for protecting astronauts from harmful cosmic radiation on MarsResearchers have identified specific materials, including certain plastics, rubber, and synthetic fibers, as well as Martian soil (regolith), which would effectively protect astronauts by blocking harmful space radiation on Mars.
Researchers identify effective materials for protecting astronauts from harmful cosmic radiation on MarsResearchers have identified specific materials, including certain plastics, rubber, and synthetic fibers, as well as Martian soil (regolith), which would effectively protect astronauts by blocking harmful space radiation on Mars.
Read more »
 Researchers have discovered the brain circuit that controls our ability to recall information and memoriesResearchers have identified the specific cell group in the brain that plays a central role in our ability to discriminate familiar and novel things, which is called recognition memory. This discovery is significant as it may impact our understanding -- and treatment -- of several cognitive disorders.
Researchers have discovered the brain circuit that controls our ability to recall information and memoriesResearchers have identified the specific cell group in the brain that plays a central role in our ability to discriminate familiar and novel things, which is called recognition memory. This discovery is significant as it may impact our understanding -- and treatment -- of several cognitive disorders.
Read more »
