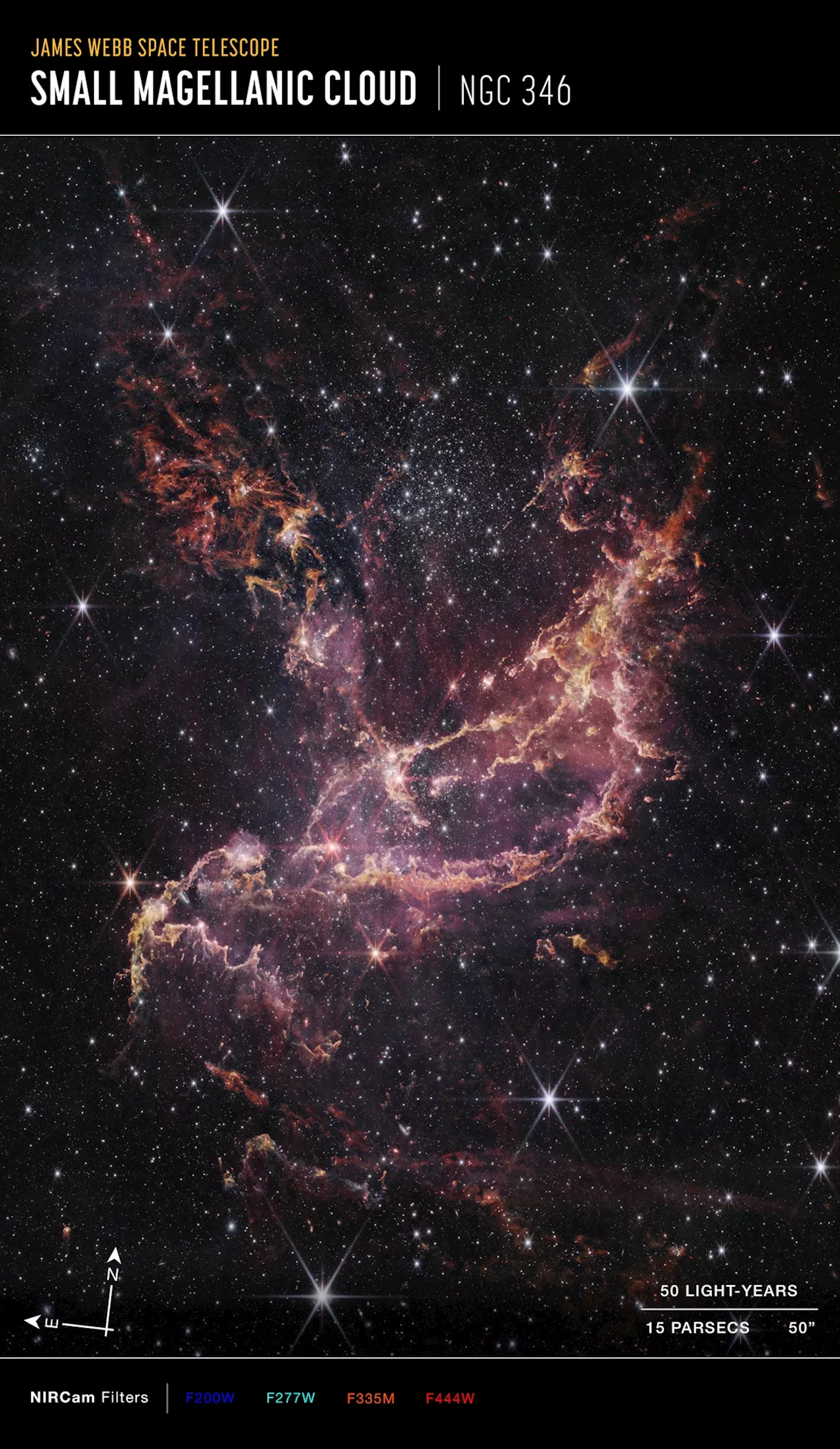
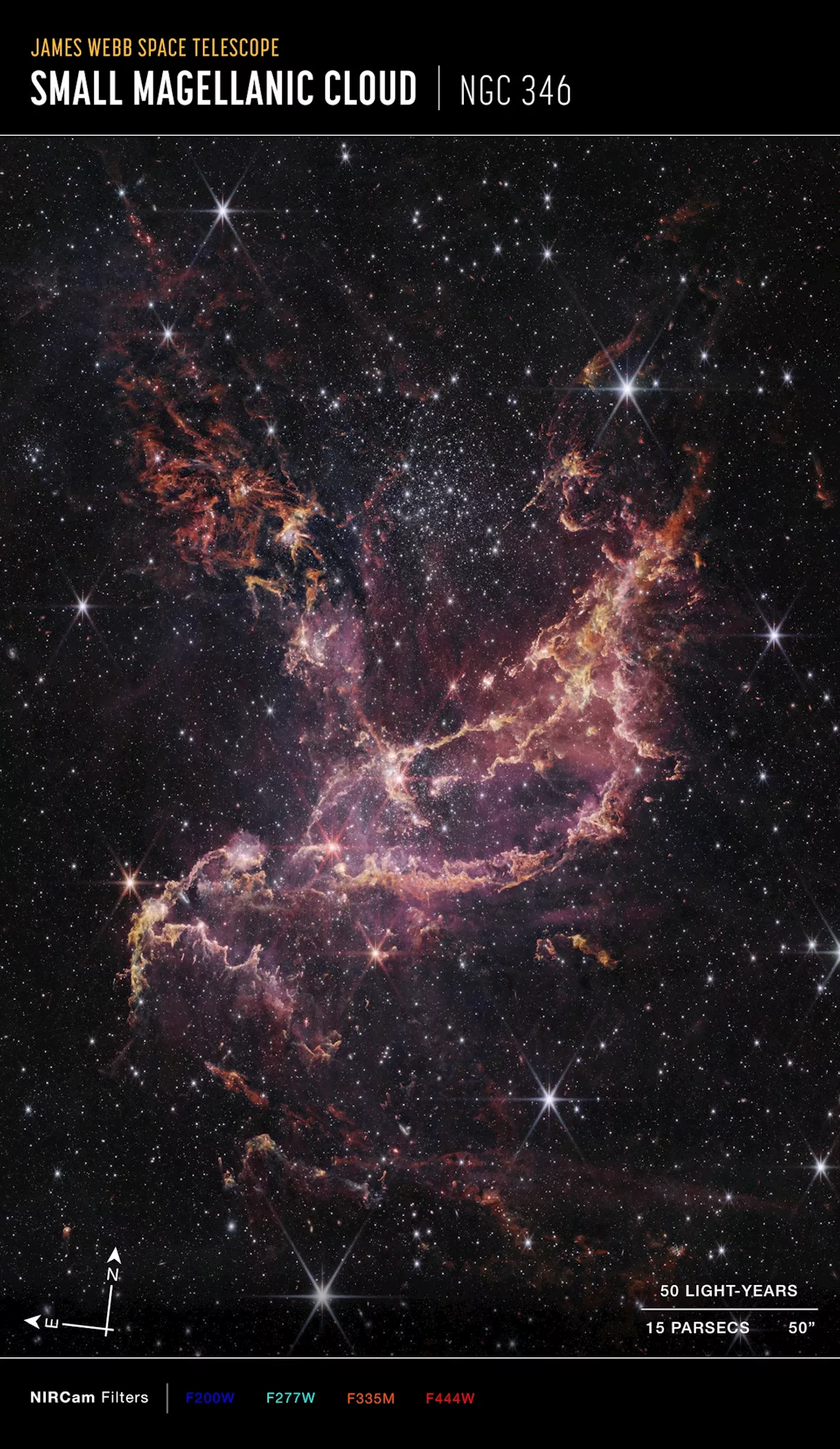
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured an image of NGC 346, a massive star cluster in the Small Magellanic Cloud, revealing insights into the early Universe and challenging existing models of planet formation. The discovery of stars with planet-forming disks in a galaxy with low heavy element content suggests that planets may have formed earlier than previously thought.
Image of the star cluster NGC 346 , captured by Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam). Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Olivia C. Jones (UK ATC), Guido De Marchi (ESTEC), Margaret Meixner (USRA)( JWST ) was specifically intended to address some of the greatest unresolved questions in cosmology. These include all of the major questions scientists have been pondering since the, how the first stars and galaxies came together, how planetary systems formed, and when the first black holes appeared.
In particular,something very interesting in 2003 when observing a star almost as old as the Universe itself. Orbiting this ancient star was a massive planet whose very existence contradicted accepted models of planet formation since stars in the early Universe did not have time to produce enough heavy elements for planets to form. Thanks to recent observations by the JWST, an(LMC), which lacks large amounts of heavy elements, they found stars with planet-forming disks that are longer-lived than those seen around young stars in our Milky Way galaxy.. The paper detailing their findings appeared on December 16th in the Astrophysical Journal Letters. The study was a collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA), NASA’s Ames Research Center, and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The James Webb Space Telescope image of NGC 346, a massive star cluster in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Credit: NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Olivia C. Jones (UK ATC)/Guido De Marchi (ESTEC)/Margaret Meixner (USRA)(Population III stars) formed 13.7 billion years ago, just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. These stars were very hot, bright, massive, short-lived, and composed of hydrogen and helium, with very little in the way of heavy elements. These elements were gradually forged in the interiors of Population III stars, which distributed them throughout the Universe once they exploded in a supernova and blew off their outer layers to form star-forming nebulae. These nebulae and their traces of heavier elements would form the next generation of stars (Population II)
JWST NGC 346 Planet Formation Early Universe Star Cluster
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 JWST Reveals Surprising Planet Formation in Ancient Star ClusterThe James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured images of the star cluster NGC 346 in the Small Magellanic Cloud, revealing unexpected findings about planet formation in the early Universe. Scientists discovered stars with planet-forming disks that are longer-lived than those seen around young stars in our Milky Way galaxy, even though these stars are located in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), which lacks large amounts of heavy elements.
JWST Reveals Surprising Planet Formation in Ancient Star ClusterThe James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured images of the star cluster NGC 346 in the Small Magellanic Cloud, revealing unexpected findings about planet formation in the early Universe. Scientists discovered stars with planet-forming disks that are longer-lived than those seen around young stars in our Milky Way galaxy, even though these stars are located in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), which lacks large amounts of heavy elements.
Read more »
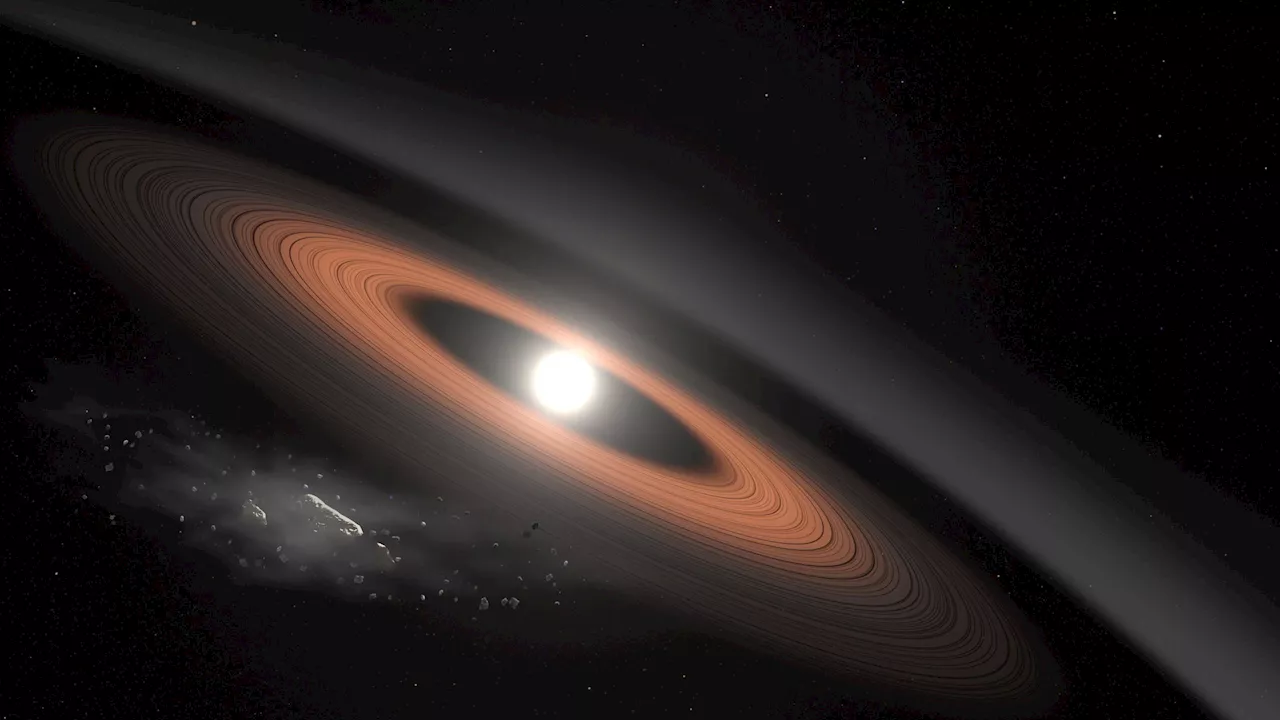 White Dwarfs Could Have Habitable Planets, Detectable by JWSTSpace and astronomy news
White Dwarfs Could Have Habitable Planets, Detectable by JWSTSpace and astronomy news
Read more »
 JWST Reveals Actively Forming Early Galaxy, Lightweight as a Baby Milky WayThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
JWST Reveals Actively Forming Early Galaxy, Lightweight as a Baby Milky WayThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »
 Unexpectedly Old Spiral Galaxy Found by JWSTA2744-GDSp-z4, a grand-design spiral galaxy with a redshift of 4.03, has been discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). This unusual finding challenges current understanding of galaxy formation as it suggests rapid formation within the early universe.
Unexpectedly Old Spiral Galaxy Found by JWSTA2744-GDSp-z4, a grand-design spiral galaxy with a redshift of 4.03, has been discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). This unusual finding challenges current understanding of galaxy formation as it suggests rapid formation within the early universe.
Read more »
 JWST Study Suggests 'Barren' TRAPPIST-1 World Might Have an Atmosphere After AllThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
JWST Study Suggests 'Barren' TRAPPIST-1 World Might Have an Atmosphere After AllThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »
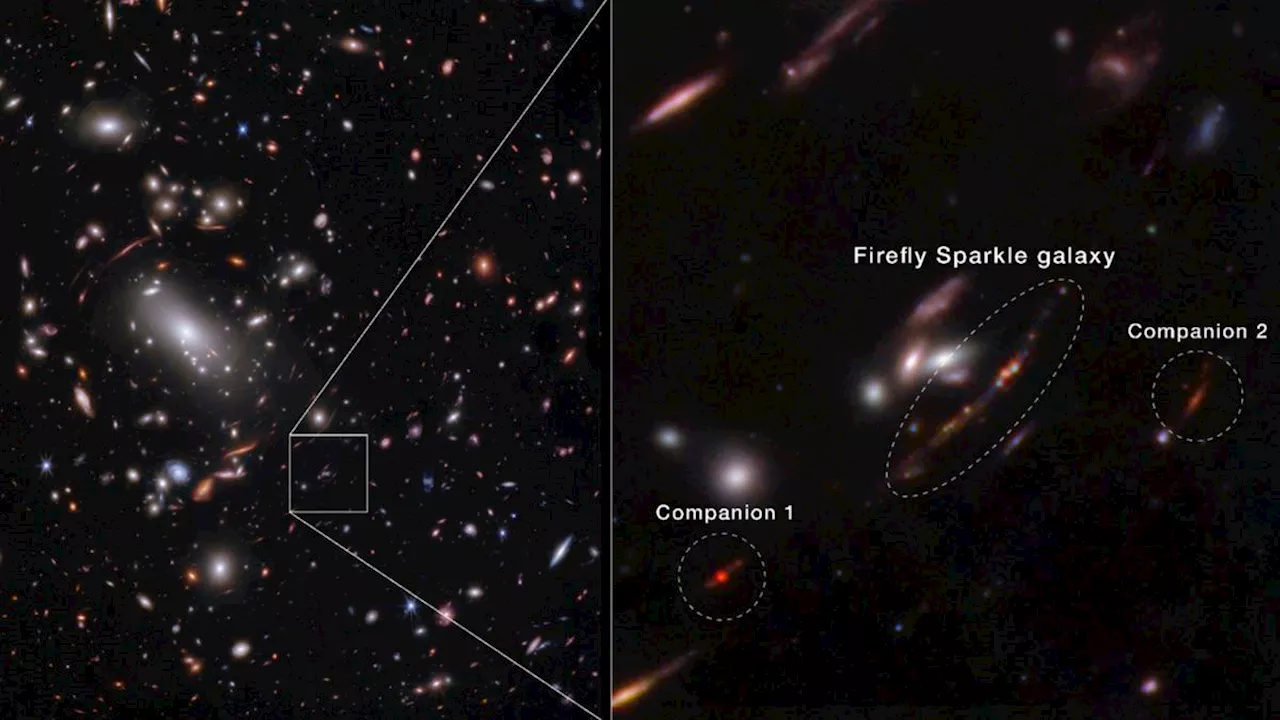 Astronomers Spot Baby Galaxy 'Firefly Sparkle' Using JWSTThe James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured the first image and mass measurement of a baby galaxy resembling the Milky Way, named 'Firefly Sparkle'.
Astronomers Spot Baby Galaxy 'Firefly Sparkle' Using JWSTThe James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured the first image and mass measurement of a baby galaxy resembling the Milky Way, named 'Firefly Sparkle'.
Read more »
