A new study has found that imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam is a viable treatment option for critically ill patients with hospital-acquired or ventilator-associated pneumonia. The drug demonstrated non-inferiority to piperacillin-tazobactam in terms of 28-day all-cause mortality, clinical response rates, and microbiological response rates.
In a multinational phase 3 trial, imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam demonstrated noninferiority to piperacillin-tazobactam in treating critically ill patients with hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia (HABP) or ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (VABP), with a comparable safety profile.
This multinational phase 3 trial, conducted between September 2018 and July 2022, compared imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam with piperacillin-tazobactam for HABP and VABP to support its use across multiple countries. Overall, 270 patients with HABP or VABP (mean age, 57.6 years; 73.3% men) were randomly assigned to receive either intravenous imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam (500 mg/250 mg) or piperacillin-tazobactam (4000 mg/500 mg) every 6 hours over 30 minutes for 7-14 days. Both treatment groups included critically ill patients, with 54.5% and 55.1% of patients in the imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam and piperacillin-tazobactam groups, respectively, having an Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score ≥ 15. The primary outcome was the 28-day all-cause mortality; secondary outcomes included the rates of clinical and microbiological responses, as well as the incidence of adverse events.Imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam was noninferior to piperacillin-tazobactam in terms of 28-day all-cause mortality (adjusted difference, 5.2%; 95% CI, −1.5-12.4;At the end of treatment, the rates of a favorable clinical response were comparable between the imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam (71.6%) and piperacillin-tazobactam (68.4%) groups. After treatment, microbiological response rates were 48.8% in the imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam group, whereas the rates were 47.9% in the piperacillin-tazobactam group. The incidence of drug-related adverse events was similar across the treatment groups, with diarrhea, increased levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, and abnormal hepatic function being the most common event
Imipenem-Cilastatin-Relebactam Piperacillin-Tazobactam Hospital-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia Ventilator-Associated Bacterial Pneumonia Clinical Trials
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New USC study shows an increase in public housing lowers rates of homelessness The USC Homelessness Policy Research Institute found that cities with more public housing options have lower rates of homelessness.
New USC study shows an increase in public housing lowers rates of homelessness The USC Homelessness Policy Research Institute found that cities with more public housing options have lower rates of homelessness.
Read more »
 The Comfort of Familiar Tropes in Unique ShowsThe article explores the prevalence of familiar tropes in new and unique television shows, arguing that this repetition offers a comforting sense of familiarity for viewers. It examines several shows, including a Japanese thriller, a Korean zombie drama, and a Brazilian science-fiction series, highlighting their similarities to popular shows like Squid Game and The Hunger Games. The author concludes that while these shows may not be entirely original, their execution and unique twists make them enjoyable experiences.
The Comfort of Familiar Tropes in Unique ShowsThe article explores the prevalence of familiar tropes in new and unique television shows, arguing that this repetition offers a comforting sense of familiarity for viewers. It examines several shows, including a Japanese thriller, a Korean zombie drama, and a Brazilian science-fiction series, highlighting their similarities to popular shows like Squid Game and The Hunger Games. The author concludes that while these shows may not be entirely original, their execution and unique twists make them enjoyable experiences.
Read more »
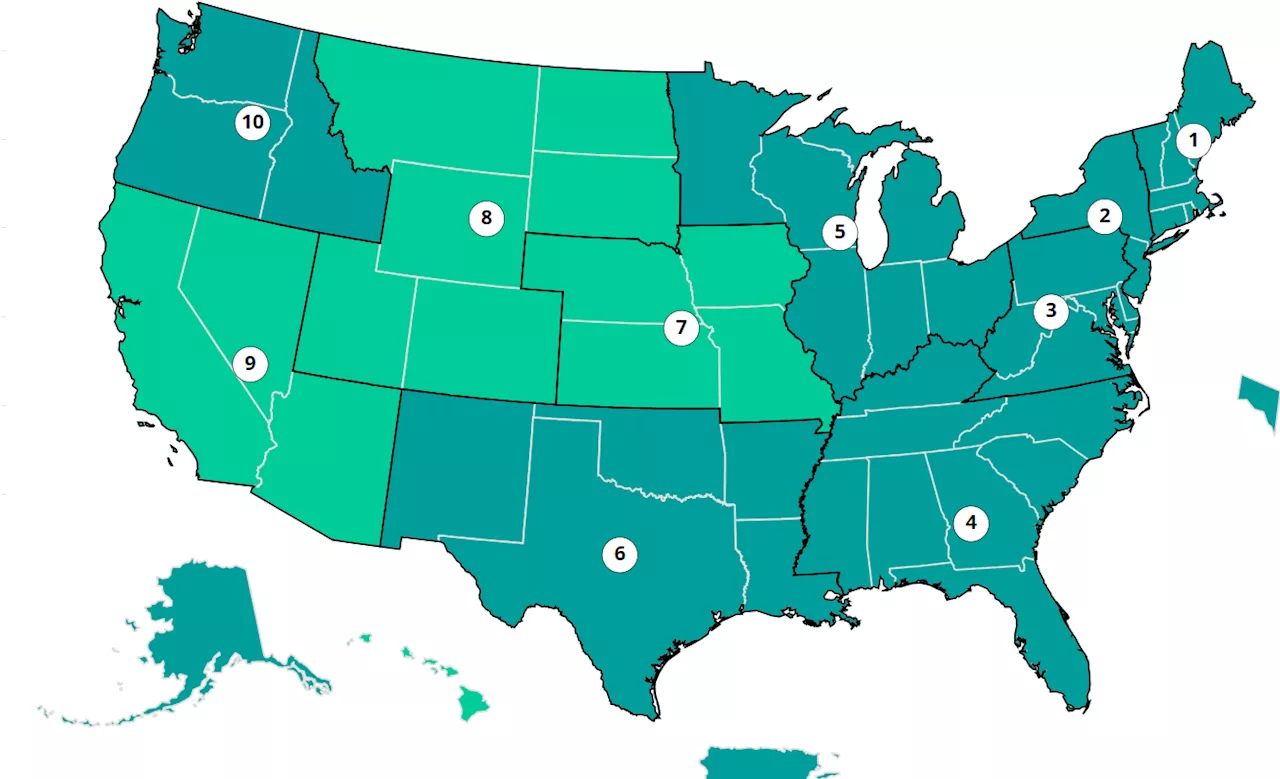 COVID Map Shows US Rates Across ThanksgivingFor the week ending November 30, four percent of cases nationwide came back positive.
COVID Map Shows US Rates Across ThanksgivingFor the week ending November 30, four percent of cases nationwide came back positive.
Read more »
 Medicaid enrollment doesn’t reduce crime rates, new data showsPolitical News and Conservative Analysis About Congress, the President, and the Federal Government
Medicaid enrollment doesn’t reduce crime rates, new data showsPolitical News and Conservative Analysis About Congress, the President, and the Federal Government
Read more »
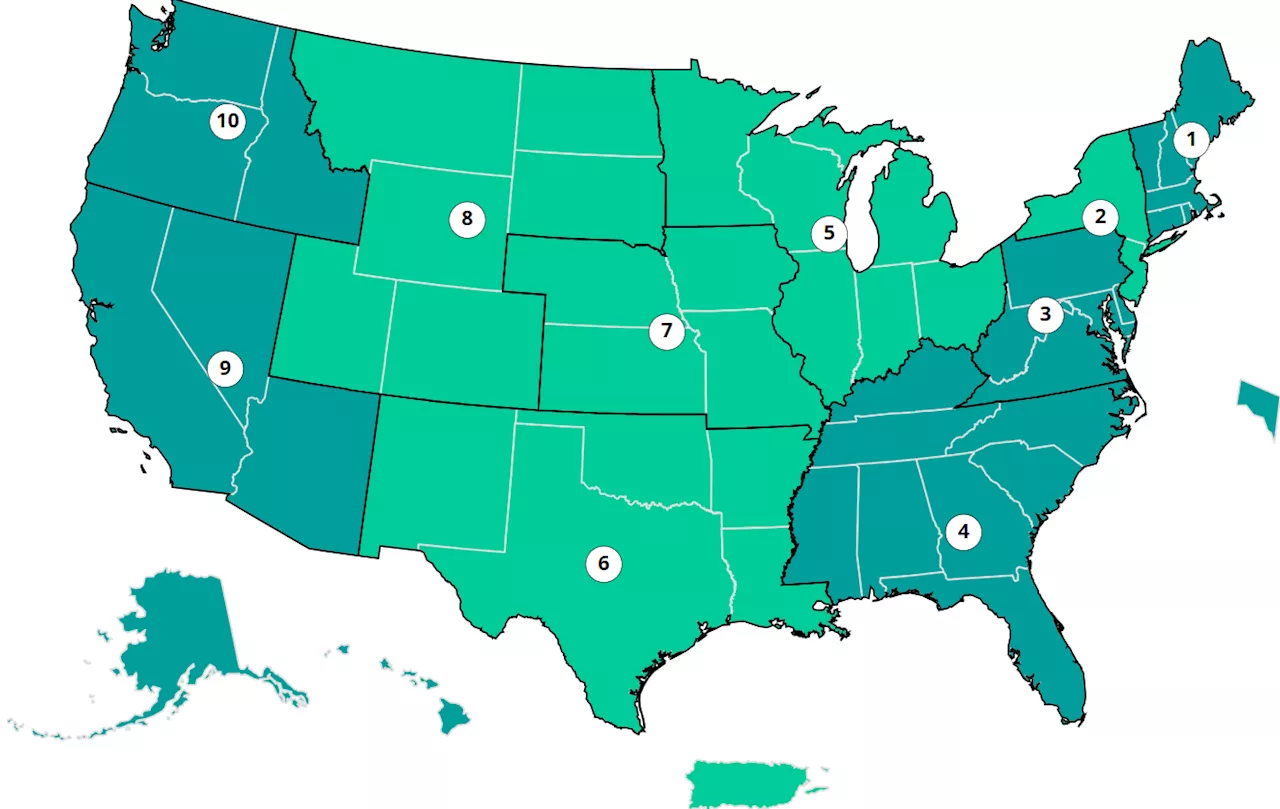 Covid Map Shows Latest Rates Across U.S. Before ChristmasThe CDC recommends that everyone aged 6 months and older should get a COVID-19 vaccine this season.
Covid Map Shows Latest Rates Across U.S. Before ChristmasThe CDC recommends that everyone aged 6 months and older should get a COVID-19 vaccine this season.
Read more »
 BOJ board divided on how soon to hike rates, December summary showsBOJ board divided on how soon to hike rates, December summary shows
BOJ board divided on how soon to hike rates, December summary showsBOJ board divided on how soon to hike rates, December summary shows
Read more »